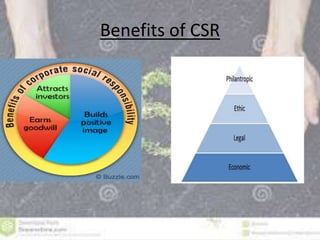
The document discusses corporate social responsibility (CSR) and its importance for businesses. It provides definitions of CSR and ethics, noting that CSR involves how businesses negotiate their role in society. Reasons for CSR include growing consumer and investor expectations, legislation around sustainability, and globalization promoting best practices. The document also discusses CSR frameworks like the Plan-Do-Check-Act method and outlines benefits to businesses like attracting employees, enhancing innovation, and building positive relations with governments and NGOs. Specific examples of CSR programs from companies like Tapal and The Body Shop are provided.