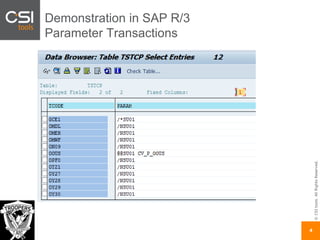
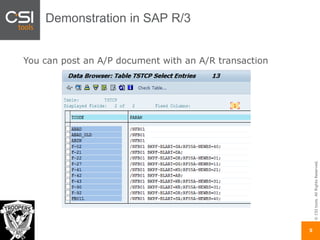
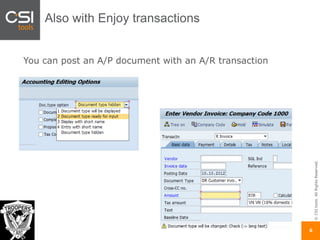
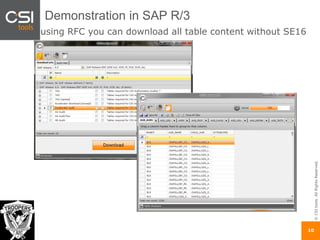
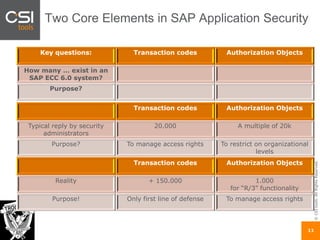
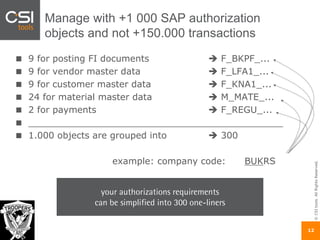
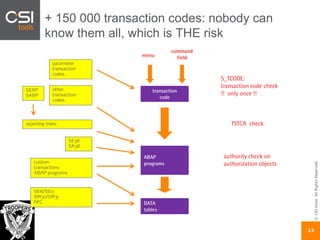
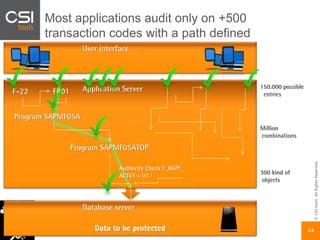
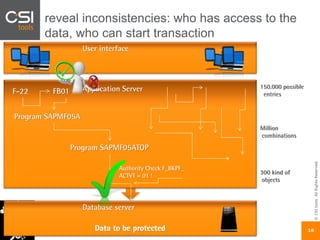
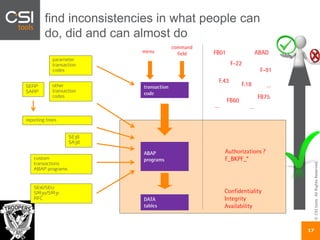
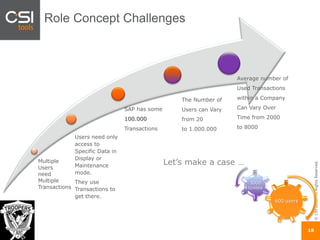
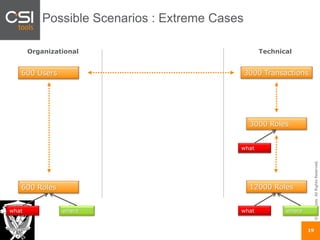
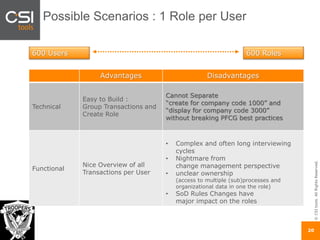
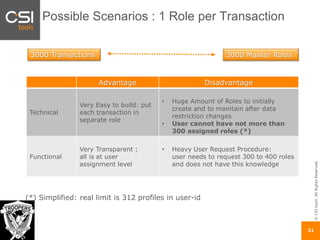
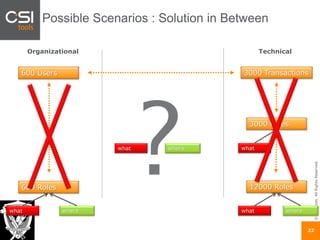
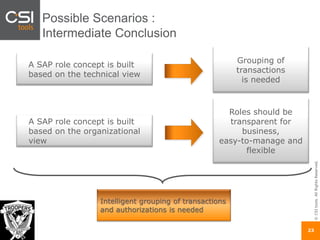
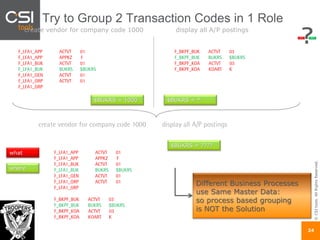
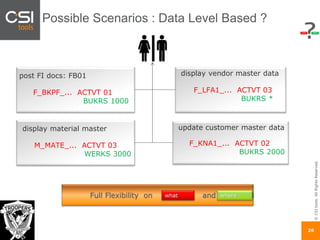
The document discusses SAP authorizations and access management. It notes that while SAP systems have over 150,000 transaction codes, access is actually managed through around 1,000 authorization objects. If a user has access to a core authorization object, they have potential access to many transactions and functions. The document advocates simplifying authorizations by grouping them based on the types of master data, like vendor, customer, or material, rather than individual transactions. This allows for more flexibility in defining access policies at the data level rather than the transaction level. It also warns that authority checks can be disabled, leaving the system vulnerable.