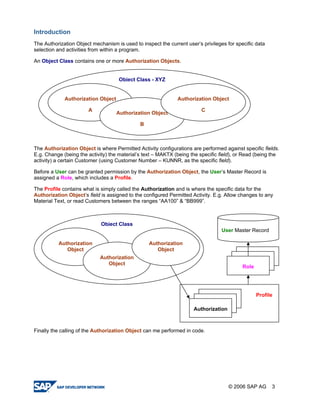
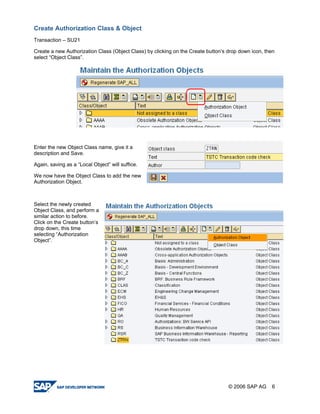
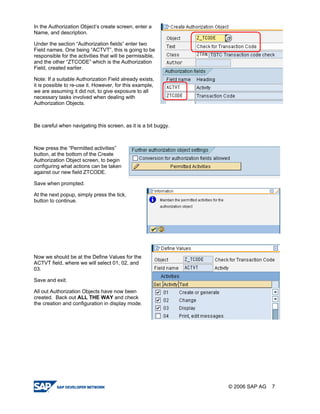
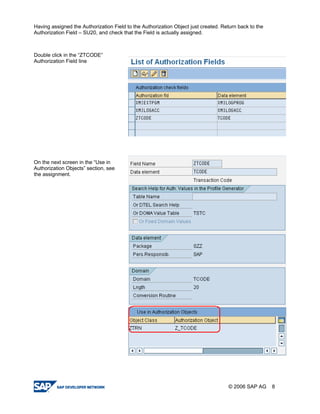
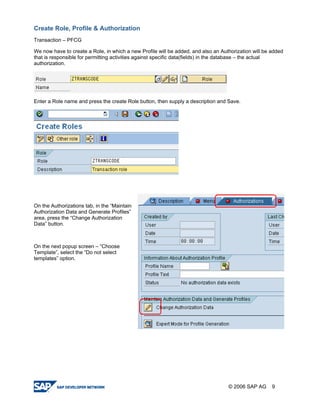
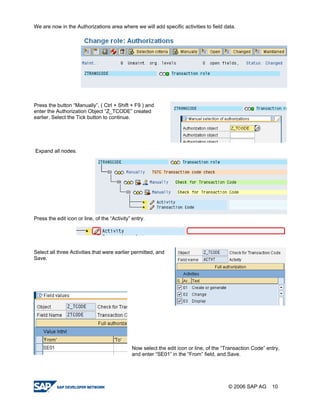
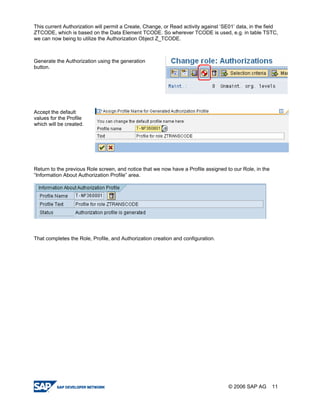
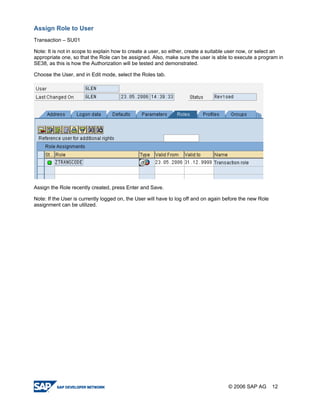
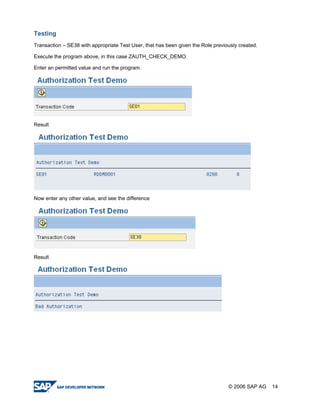
The document provides a guide to creating and using authorization objects in SAP systems in the simplest way. It explains how to create an authorization field, authorization class and object. It then demonstrates how to create a role, profile and authorization to control user permissions. The guide codes an authorization check in ABAP and provides steps to test the authorization configuration.