This document provides an overview of SAP, including:
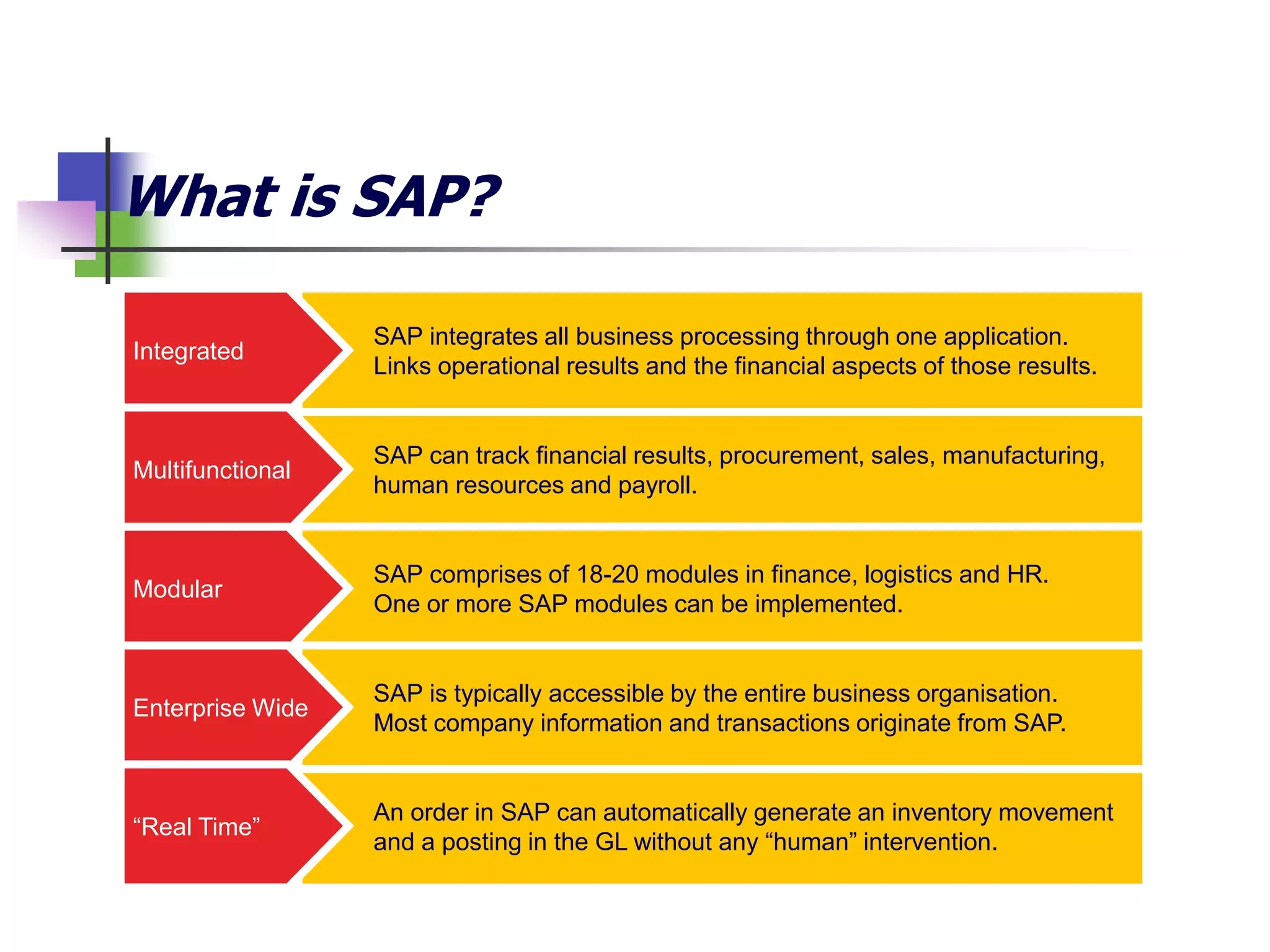
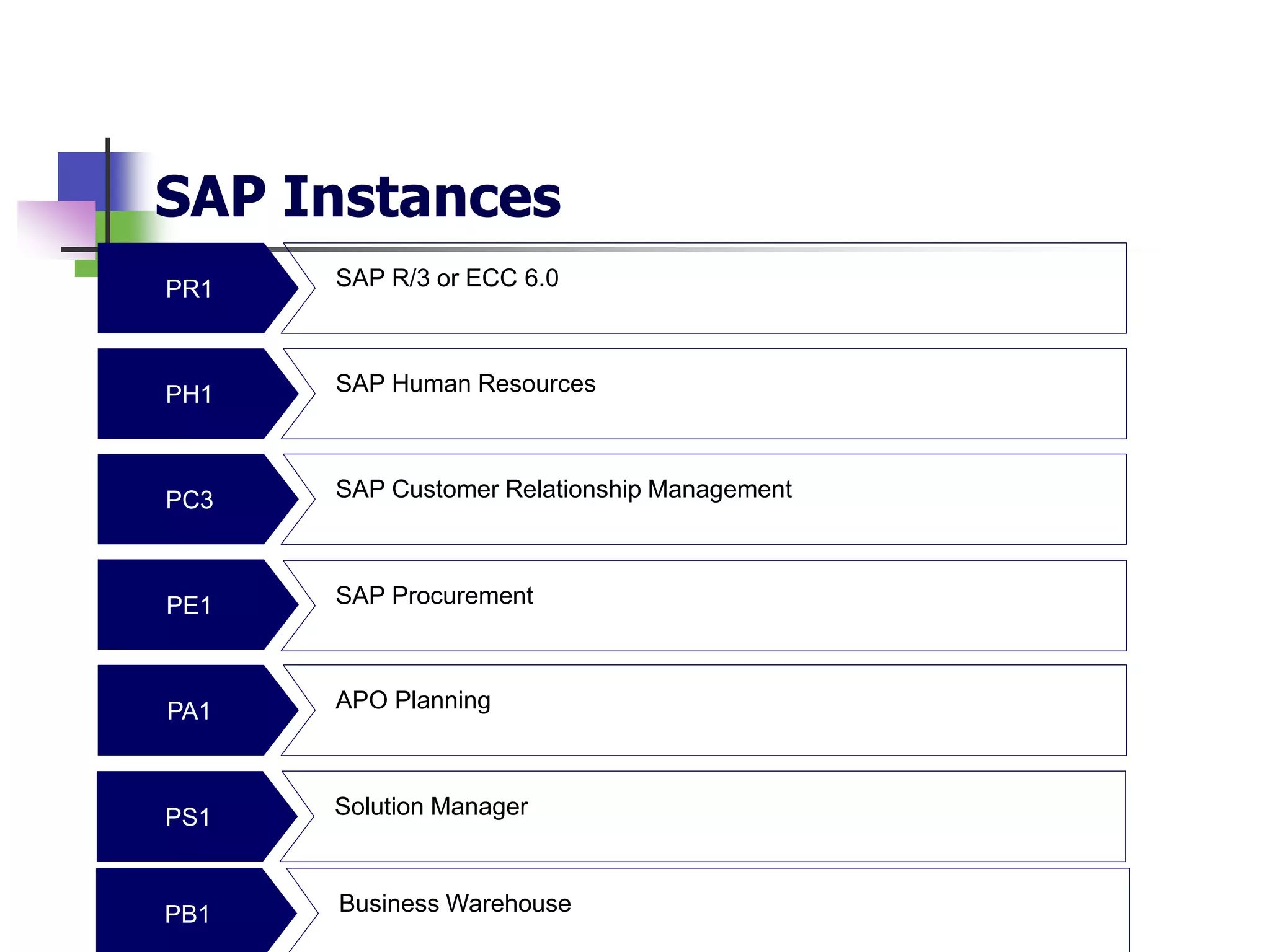
- SAP stands for Systems, Applications and Products in Data Processing and is an integrated software that tracks business processes through one application.
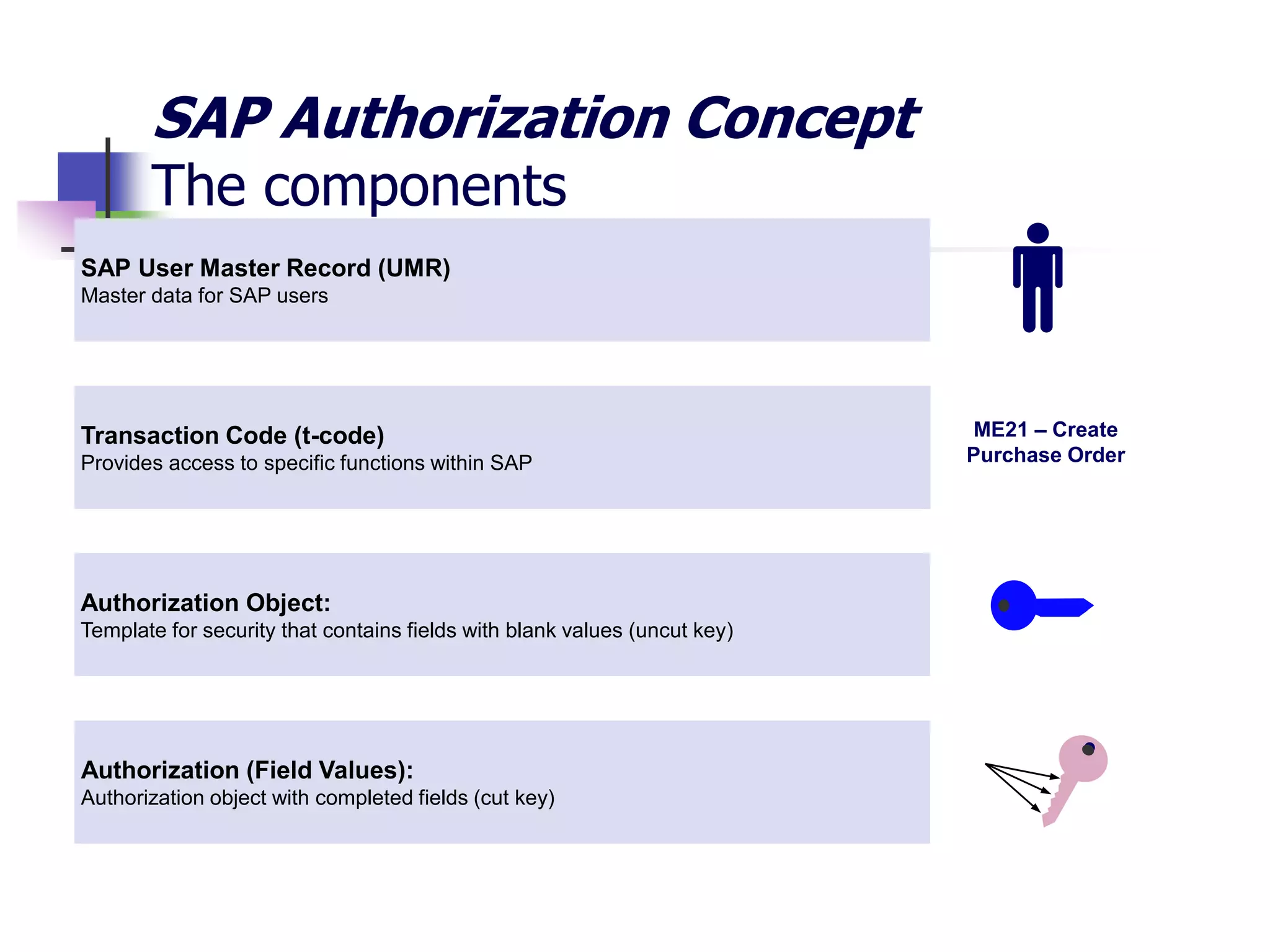
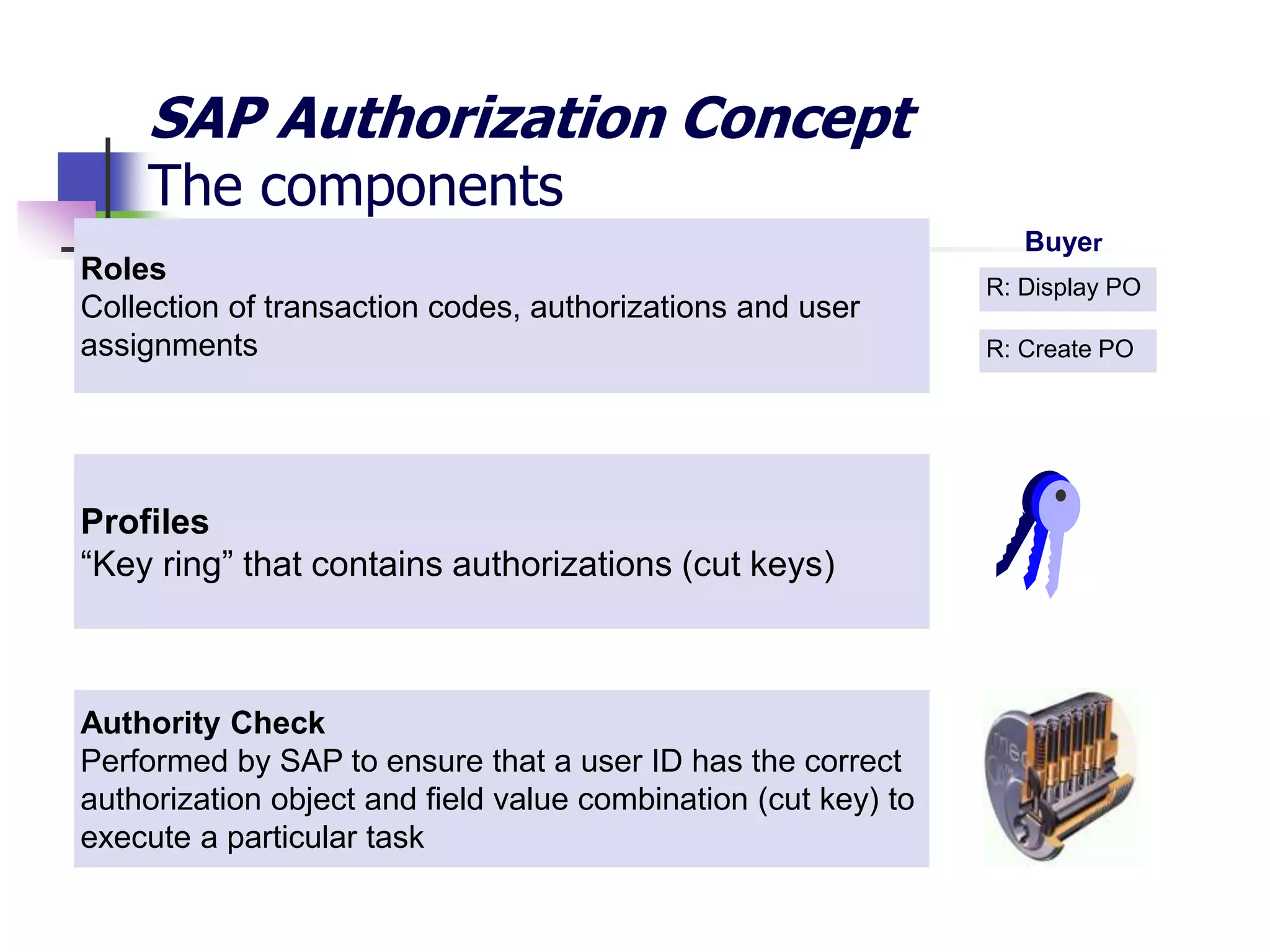
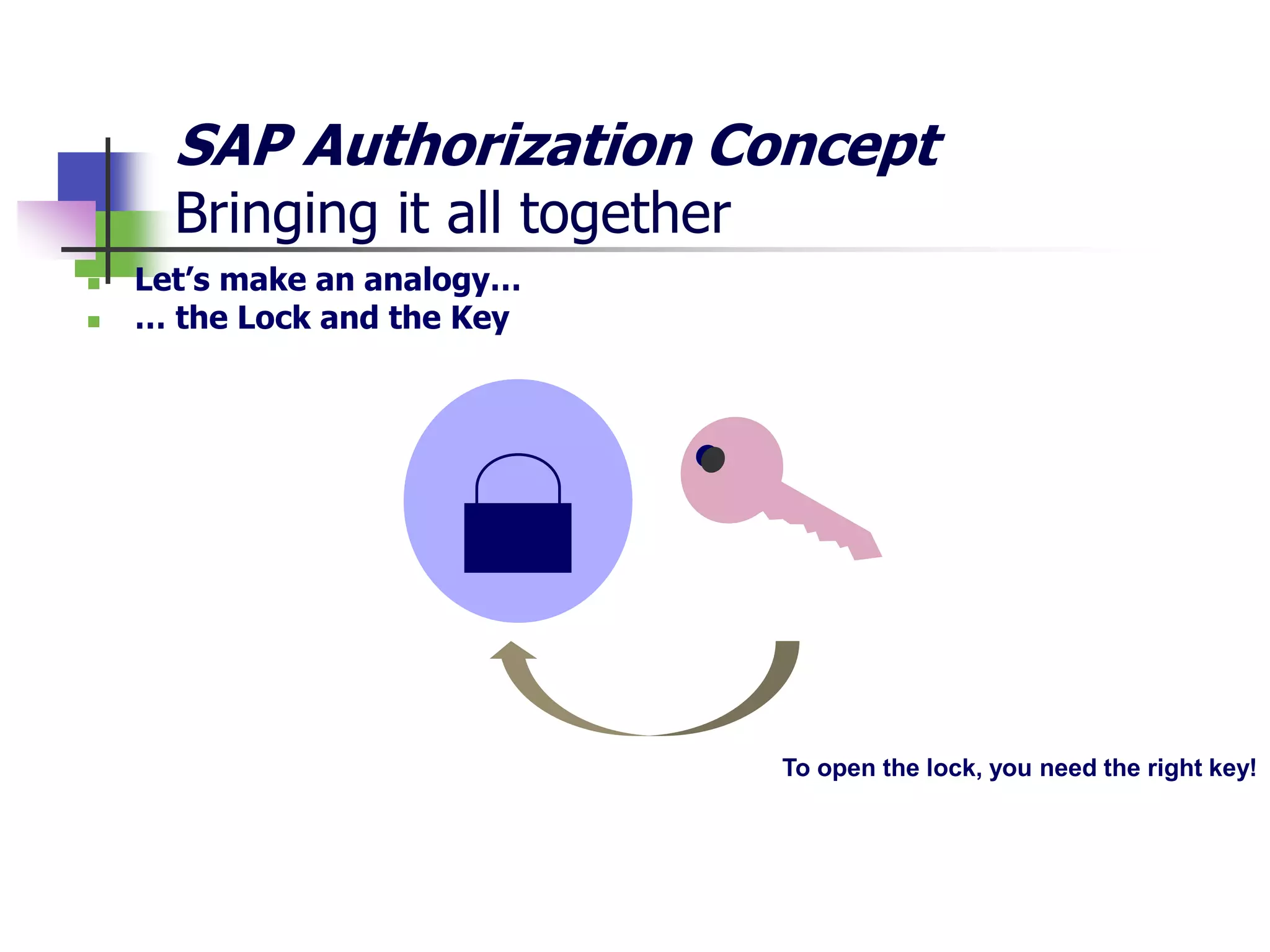
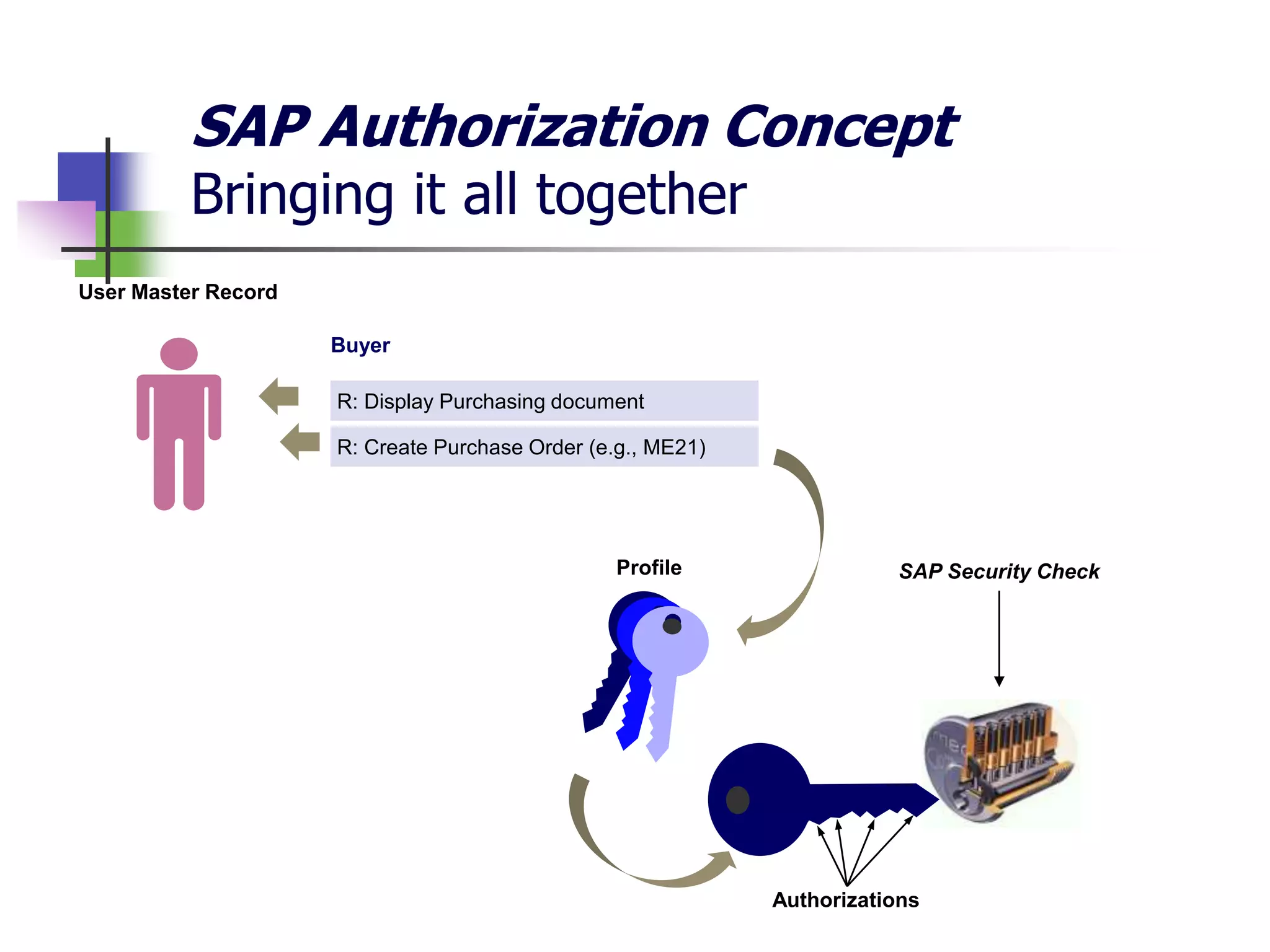
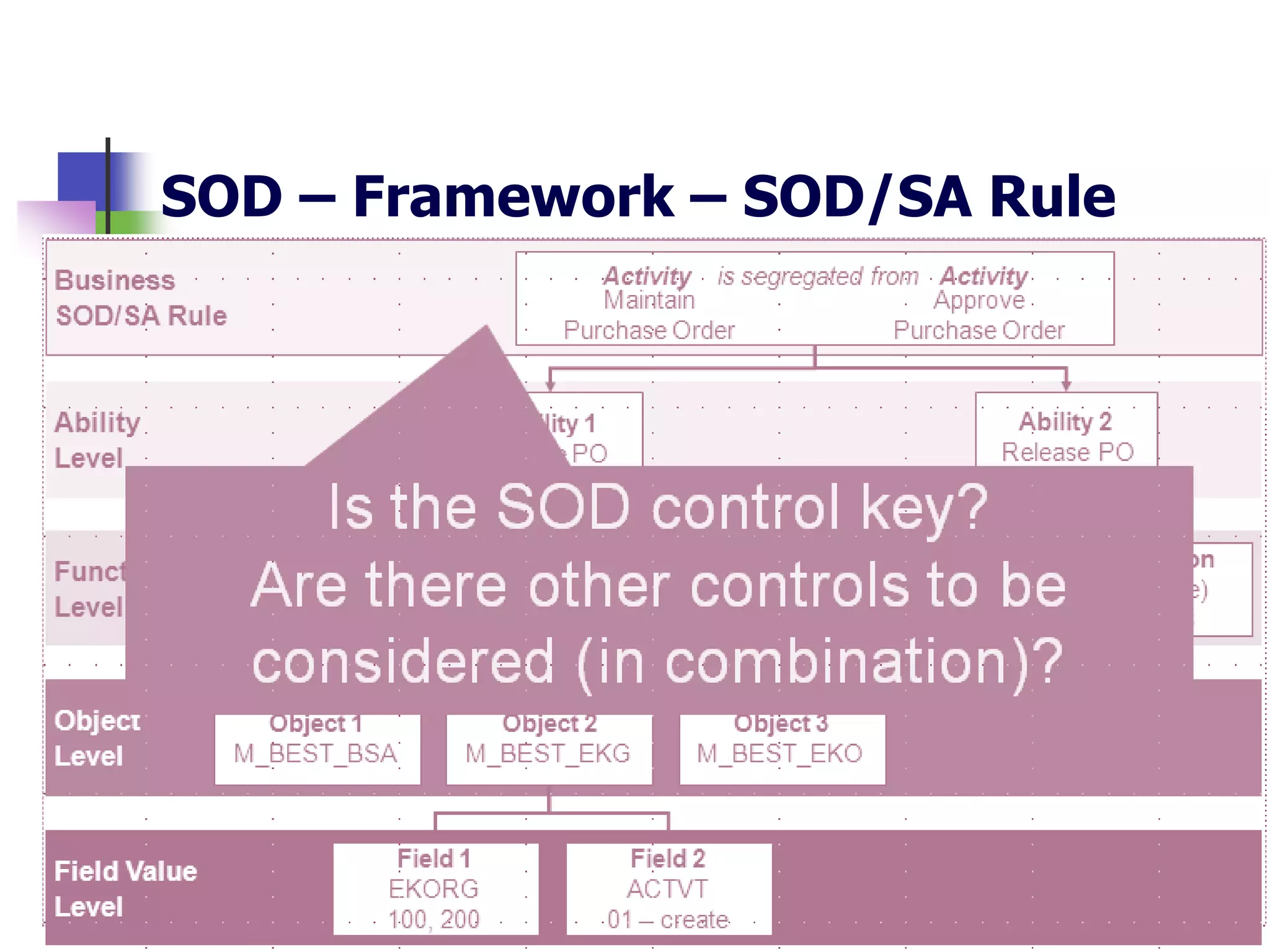
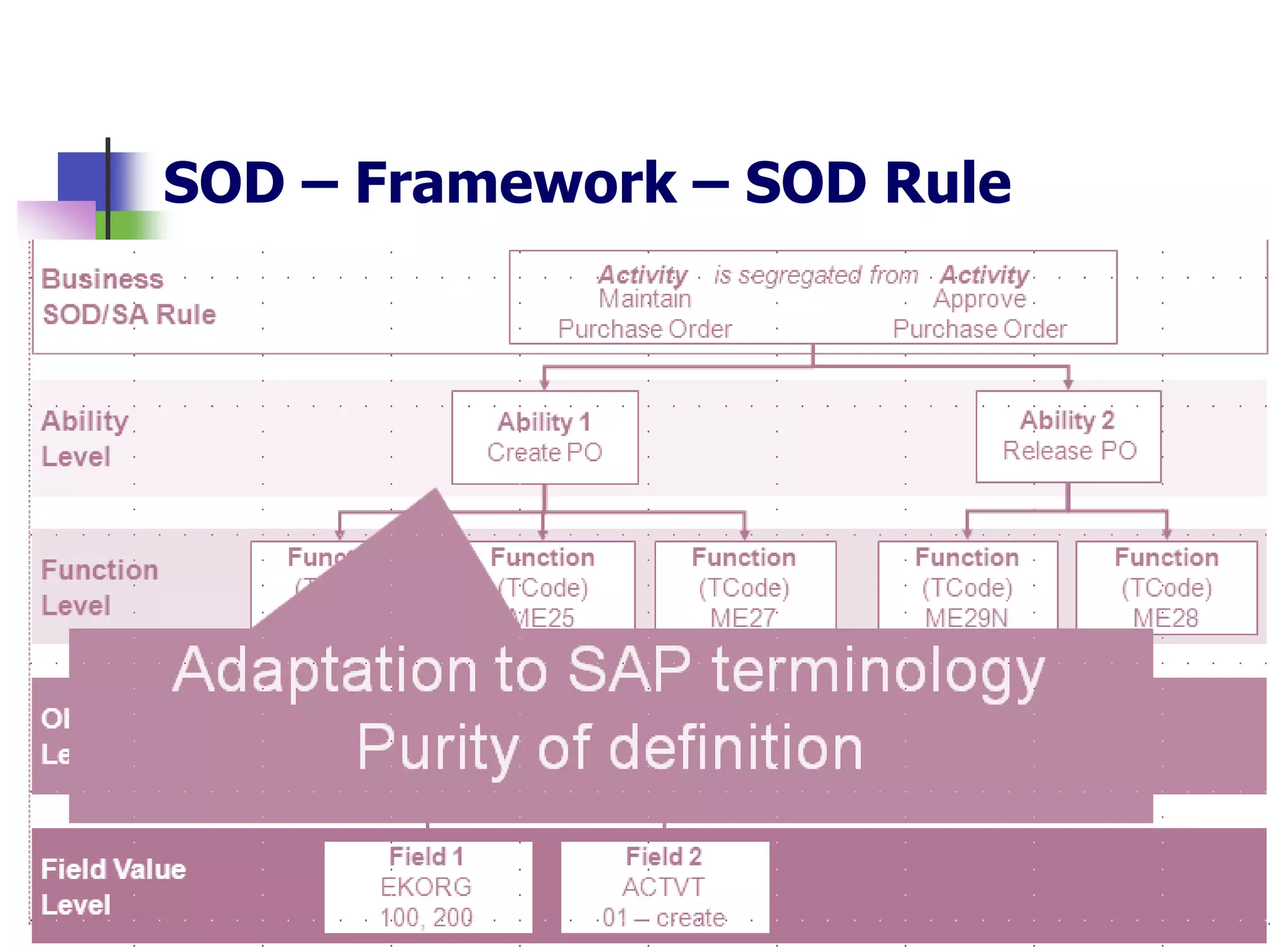
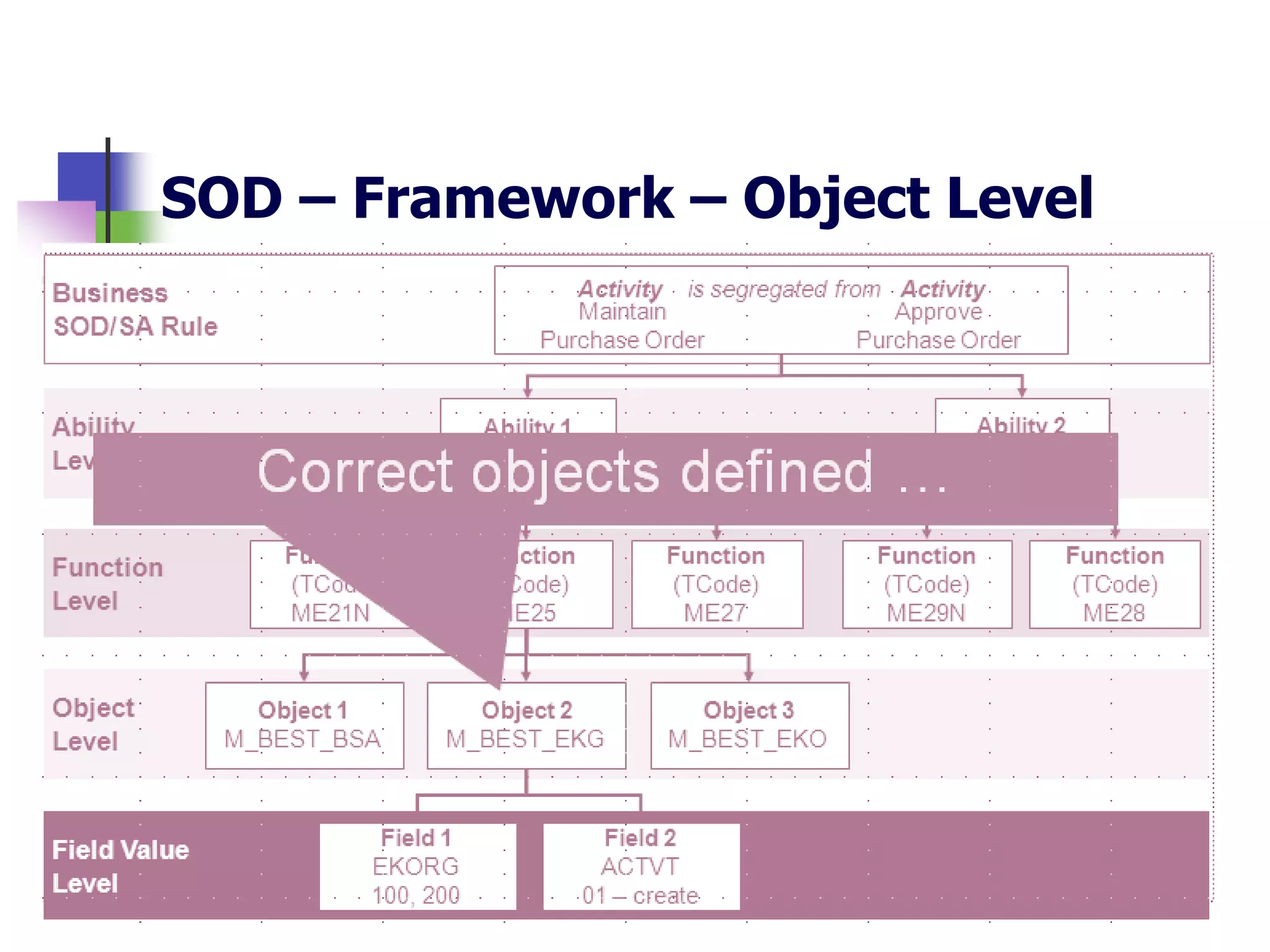
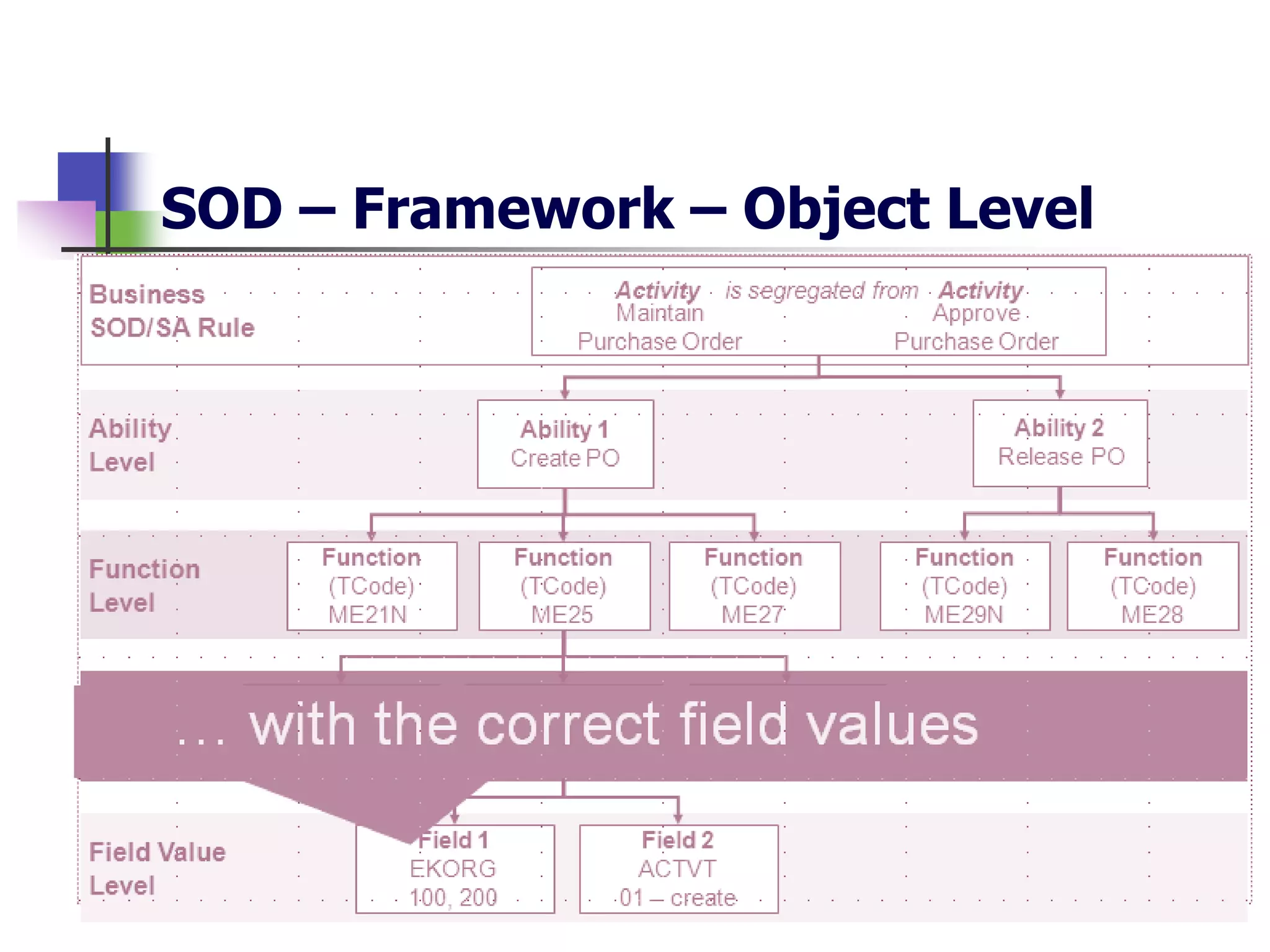
- SAP uses an authorization concept with three levels of security - transaction code, authorization object, and user authorization - to control user access.
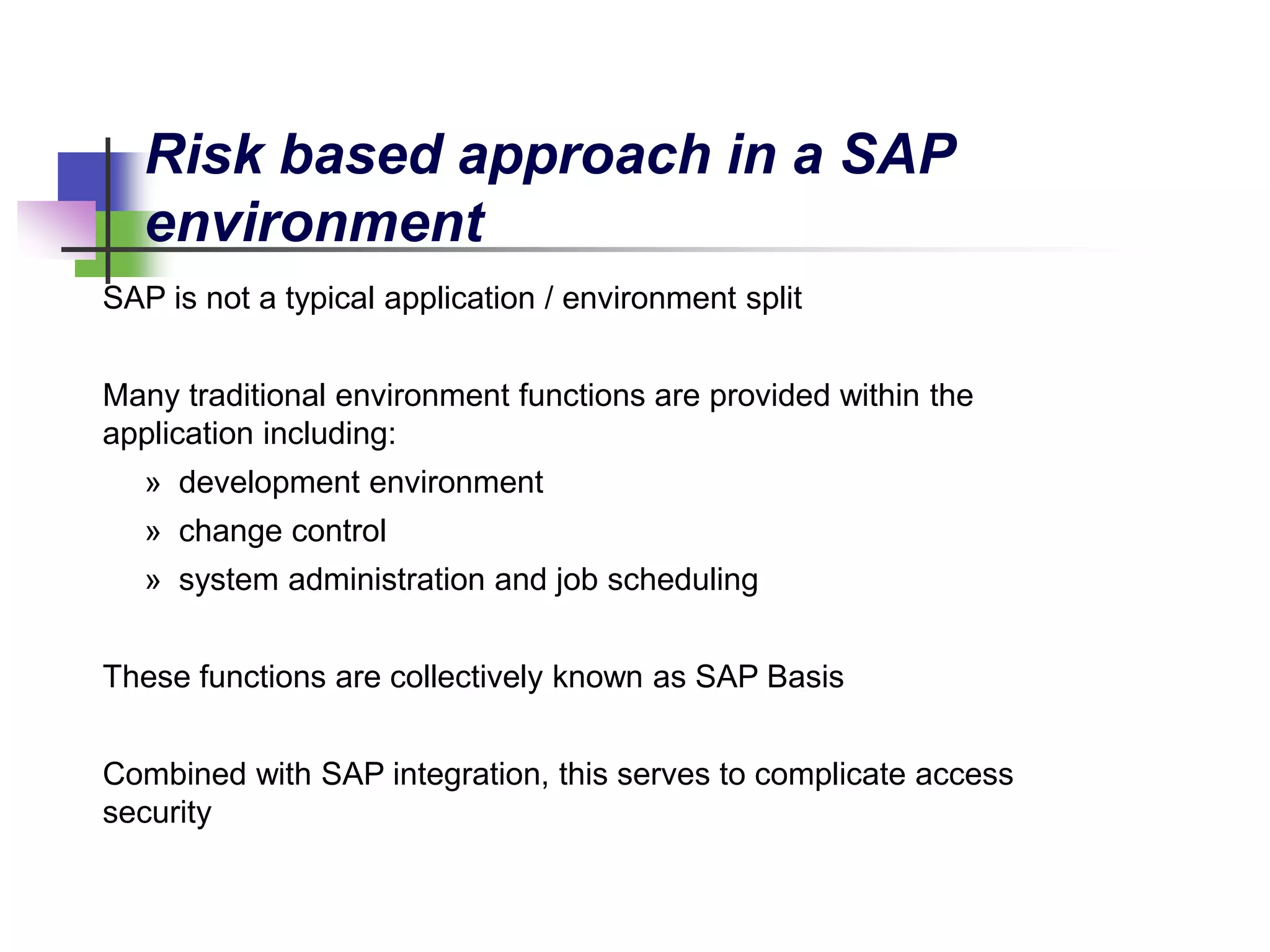
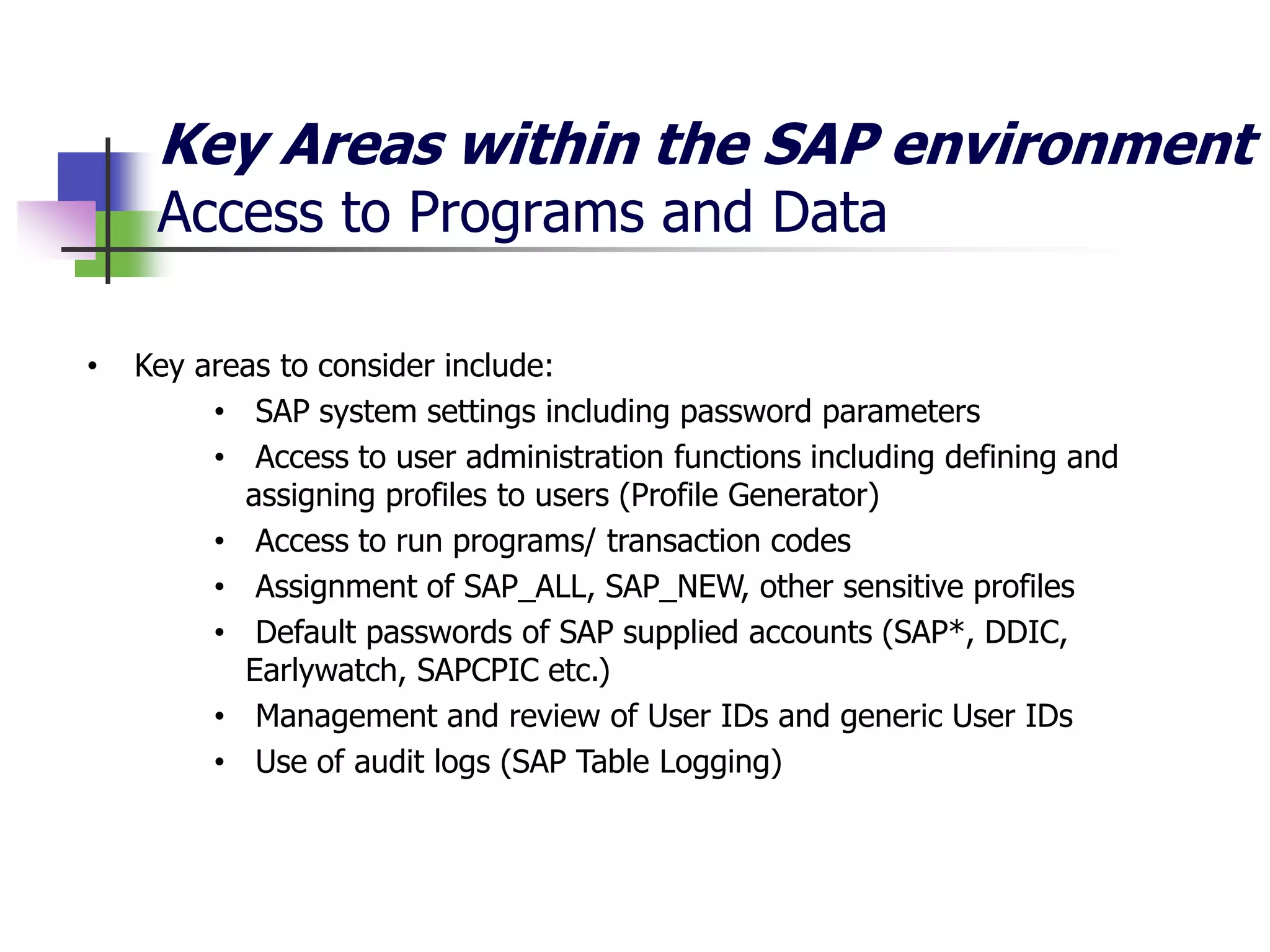
- When auditing IT general controls in SAP, it is important to consider controls around access management, change management, and computer operations due to the complexity of security in SAP.
- Key risks include segregation of duties due to financial transactions throughout the business, and complex access controls.