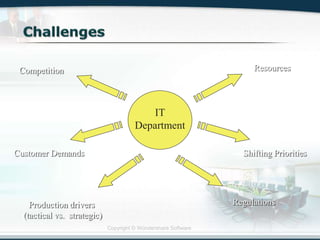
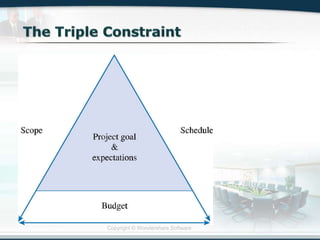
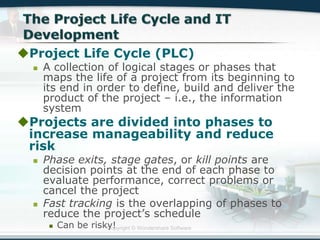
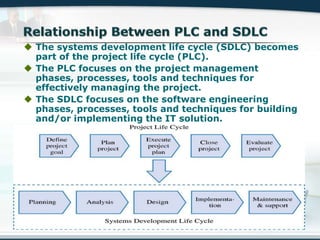
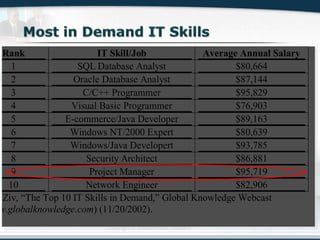
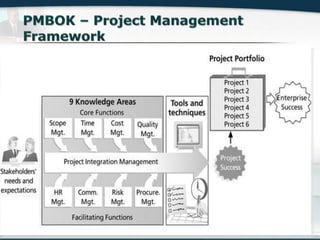
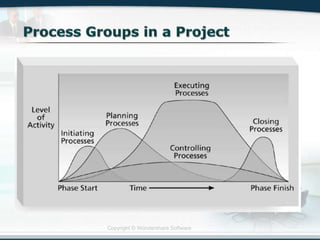
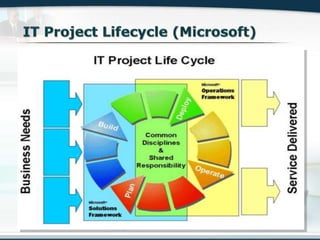
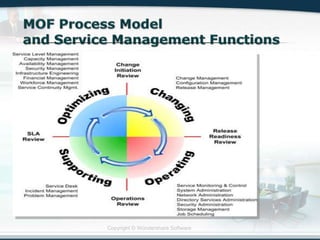
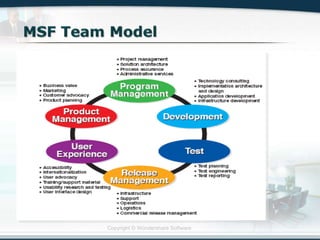
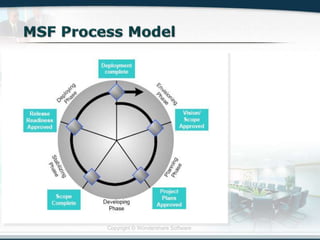
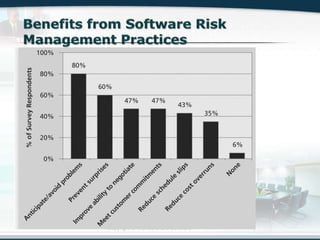
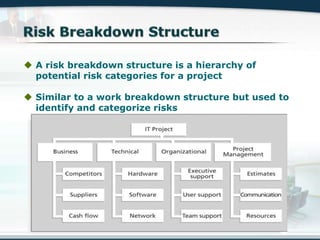
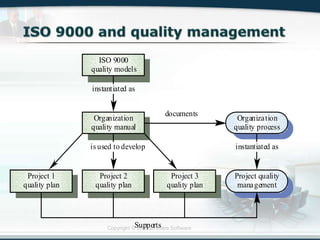
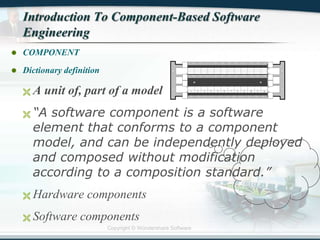
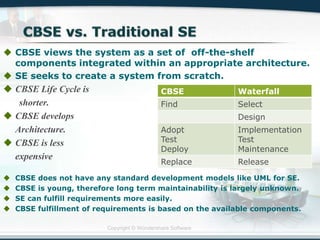
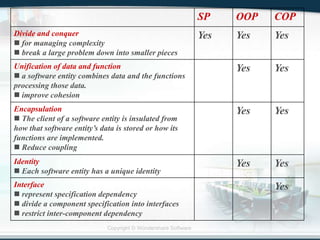
The document discusses the critical role of Information Technology (IT) in business, highlighting the need for effective project management in IT projects that often face high failure rates. It outlines the importance of methodologies, risk management, quality assurance, and component-based software engineering to enhance project outcomes. Additionally, it emphasizes executive support, user involvement, and skilled project managers as key factors for successful IT project execution.