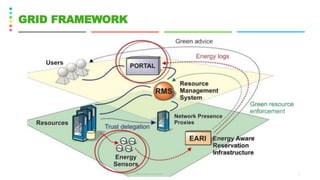
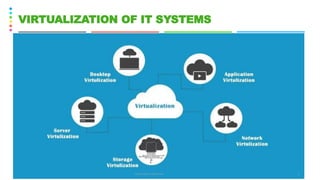
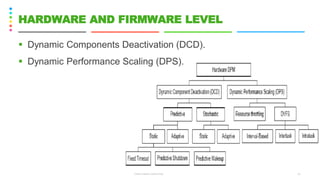
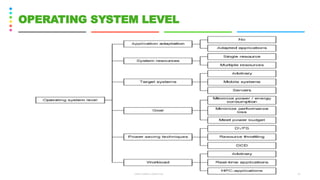
This document discusses the Green Grid framework and concepts related to green computing such as virtualization, telecommuting, and data centers. It covers virtualization of IT systems and how virtualization can promote green computing by improving server utilization rates and eliminating planned downtime. The document also discusses the role of electric utilities, power management at different levels including hardware, firmware, operating system, virtualization and data center levels, and defines key terms like hypervisor, virtual machine, and telecommuting.