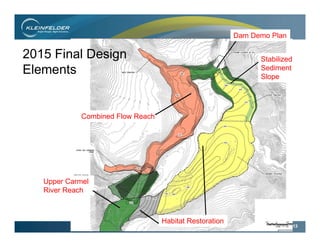
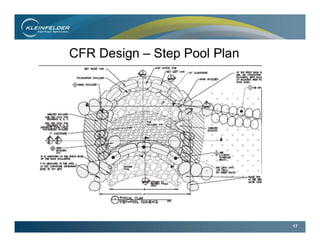
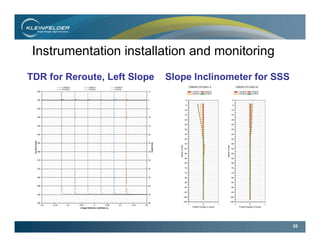
This document summarizes the final phase of the San Clemente Dam removal and stream restoration project in California. It describes the project location and history, provides an overview of key stakeholders and the project schedule, discusses the regional and site geology, and details the final design elements and construction phases. These included building a diversion dike, stabilizing sediment slopes, constructing a combined flow reach with step pools, removing the dam, and installing instrumentation to monitor slopes, embankments, and settlement. The project successfully removed an aging dam to restore fish habitat while mitigating geological hazards through engineering and post-construction monitoring.