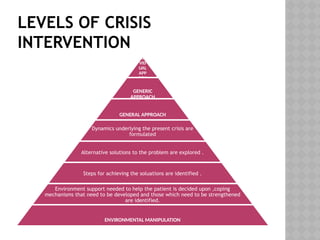
Crisis intervention is a technique aimed at helping individuals or families cope with intense feelings during a crisis, focusing on providing cognitive perception, managing overwhelming emotions, and returning them to a pre-crisis state. It incorporates the five stages of grief as identified by Elizabeth Kubler-Ross and employs nursing assessments to determine needs, coping resources, and support systems. Key roles of nurses include performing crisis assessments, exploring alternative solutions, and utilizing various intervention techniques to promote adaptive behavior and self-esteem.