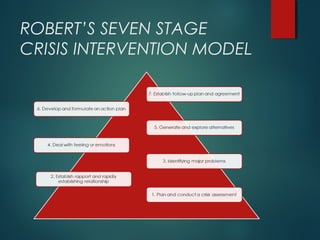
The document discusses crisis intervention and crisis theory. It defines a crisis as an unexpected event that throws a person off balance emotionally. Common crisis responses include apathy, depression, guilt and low self-esteem. The document then lists examples of crises and provides an overview of crisis theory, including its peak and turning point. It concludes by outlining Robert's seven stage model of crisis intervention, which includes conducting an assessment, establishing rapport, defining the problem, exploring feelings, past coping attempts, implementing an action plan, and following up.