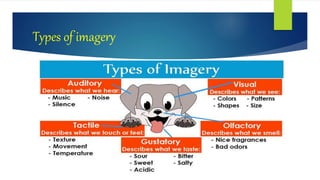
This document defines and provides examples of imagery in literature. Imagery uses descriptive language that appeals to the five senses to help readers visualize, hear, smell, taste, and feel an author's created world. It discusses the types of imagery, including visual, auditory, olfactory, gustatory, and tactile imagery. Examples are given of imagery's use in poetry, novels, songs, and films to engage readers and enhance storytelling. Related literary devices like metaphor, onomatopoeia, and personification are also forms of imagery.