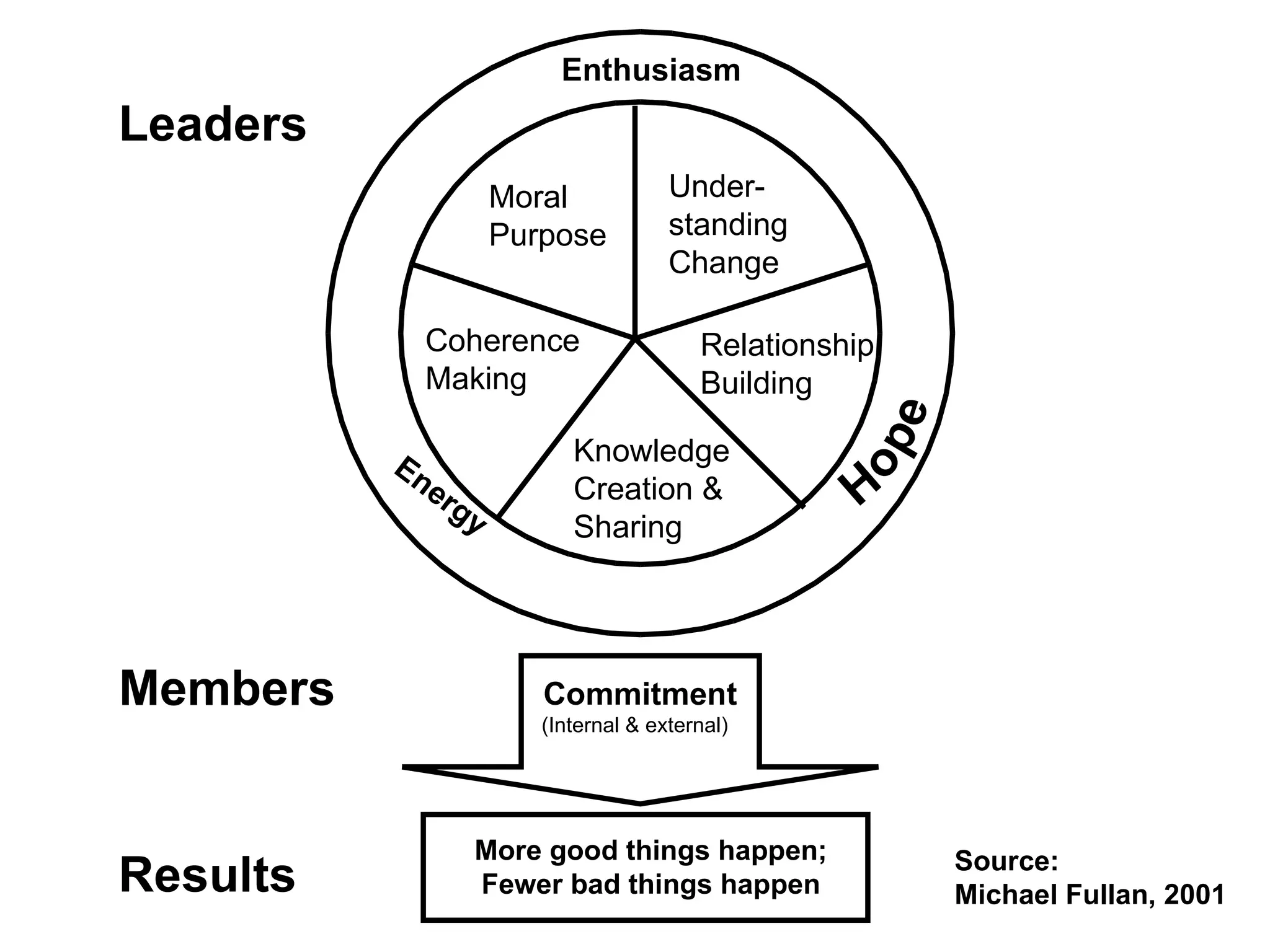
Fullan outlines a model for managing change that focuses on strong moral purpose, learning, sharing, and understanding over an extended period of time. He advocates creating a culture of change by developing an organization's capacity to incorporate new ideas and practices continuously, both internally and externally. Knowledge sharing is important for strengthening an organization's ability to access and leverage all types of knowledge, both explicit and tacit. Developing collaborative cultures that encourage knowledge generation and sharing can help organizations improve.












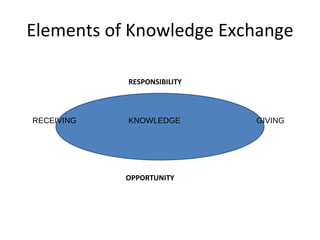
![Knowledge Creation and Sharing Dixon (2000) – “It is a kind of chicken-or-egg issue: which comes first, the learning culture or the exchange of knowledge? Given the many organization’s rather abysmal success rate at changing their culture, I would put my money on having exchange (of knowledge) impact the culture rather than waiting for the culture to change [pg.5-6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/teafall2009fullancreatingandsharingknowledge-091027140207-phpapp02/85/Creating-and-Sharing-Knowledge-15-320.jpg)