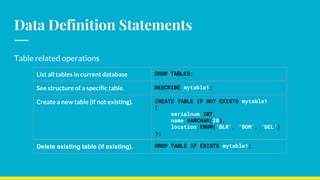
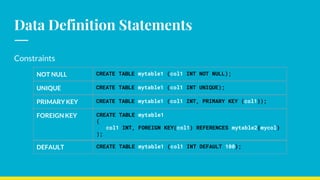
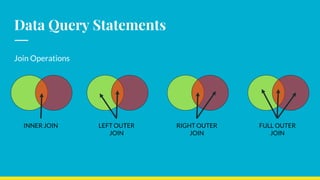
This document provides an overview of SQL concepts including installing MySQL, data types, data definition and manipulation statements, filtering, sorting, aggregation, and join operations. It covers downloading and installing MySQL, describes common data types like numeric, date/time, and string types. It also explains how to create databases and tables, add/update/delete data, and perform queries with WHERE, ORDER BY, LIMIT, and JOIN clauses.

![MySQL - Installation
DOWNLOAD
○ https://dev.mysql.com/downloads
■ MySQL Community Server
■ MySQL Shell
■ [OPTIONAL] MySQL Workbench
○ https://dev.mysql.com/doc/index-other.html
■ Example databases -> world database](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/crashcourseinsql-190619141156/85/Crash-course-in-sql-2-320.jpg)