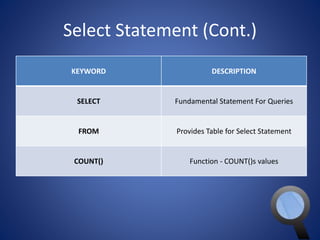
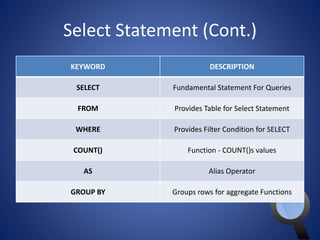
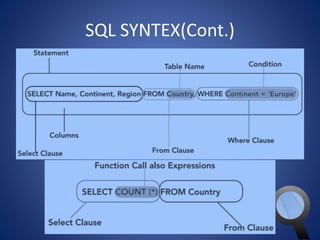
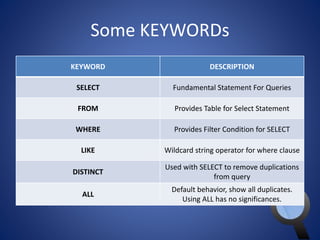
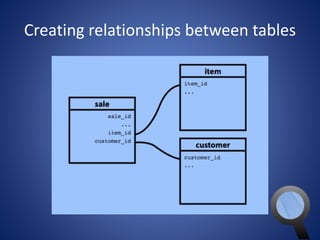
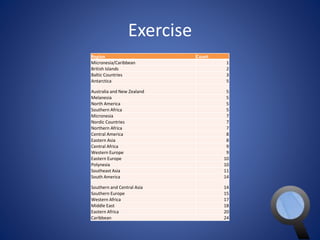
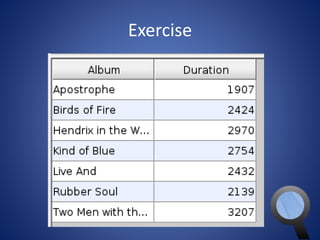
This document provides an overview of SQL and MySQL. It discusses topics such as creating and deleting databases and tables, importing data, using IDEs like Execute Query, configuring connections, performing queries with SELECT statements including filters, joins, and aggregates, updating and deleting data, indexing, and working with dates, strings, and numbers. Examples of SQL queries are provided throughout to demonstrate different SQL syntax and functions.








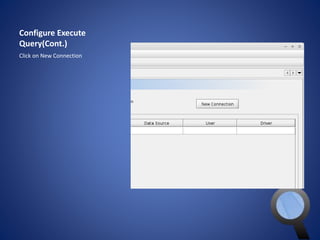
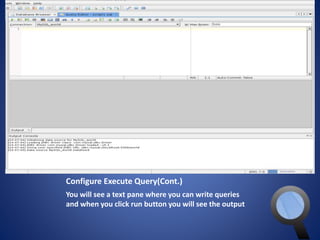
![Configure Execute
Query(Cont.)
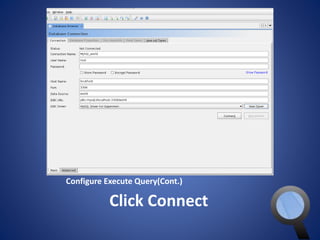
• In Connection Name any name
• User Name is must be choose as like
the user name exist in the MySQL DB
• Password field will contain the
password for the specific user of the
username provided
• Host Name will be localhost because
the server is running on your own
computer
• Port is 3306 for MySQL database
• Data Source is the name of the
database from which you want to
manipulate data
• JDBC URL should like that
jdbc:mysql://[host_name]:[port_num
ber]/[name_of_the database]
• In this case our database is world so
the url is
jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/world
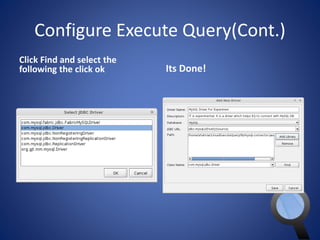
• But now we need to select a JDBC
Driver
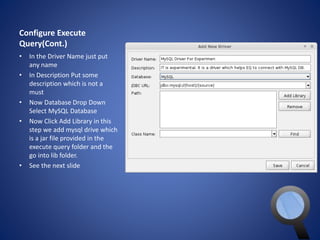
• To add new driver please click on
New Driver and follow next slides](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sql-140927080016-phpapp01/85/SQL-10-320.jpg)