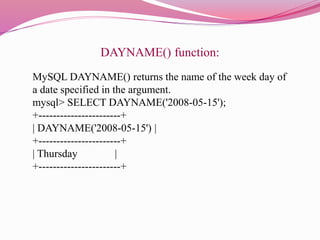
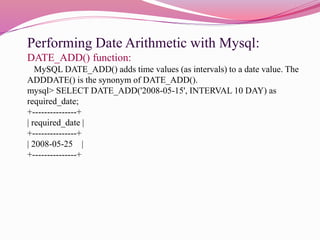
This document discusses various date and time functions in MySQL including DAYOFWEEK(), WEEKDAY(), DAYOFMONTH(), DAYNAME(), MONTH(), DAYOFYEAR(), WEEK(), HOUR(), MINUTE(), SECOND(), DATE_FORMAT(), DATE_ADD(), DATE_SUB(), CURDATE(), CURTIME(), NOW(), SYSDATE(), and TIMESTAMP(). It provides examples of how each function works and the type of values they return. The functions allow retrieving specific components of a date/time like day, month, year, hour, minute as well as formatting, adding, and subtracting dates/times in MySQL.