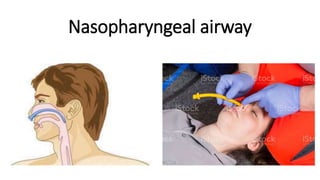
This document discusses cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). It defines CPR as a technique used to establish artificial ventilation and circulation for a patient whose heart has stopped. It notes that CPR may save a victim's life if started within 4 minutes of cardiac arrest and defibrillation is provided within 10 minutes, giving a 40% chance of survival. The document then outlines the basic steps of CPR including checking for response, opening the airway, checking for breathing, and beginning chest compressions at a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute with rescue breaths every 30 compressions. It also discusses advanced CPR techniques used in a hospital setting that include advanced airway management and use of defibrillation and