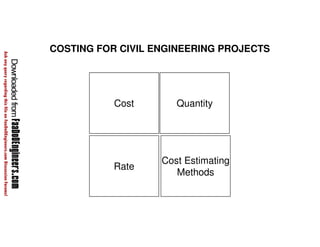
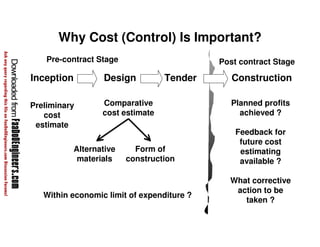
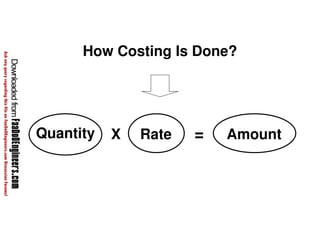
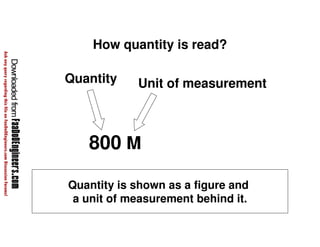
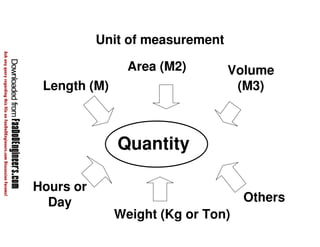
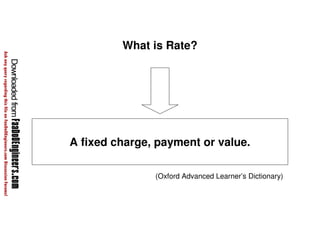
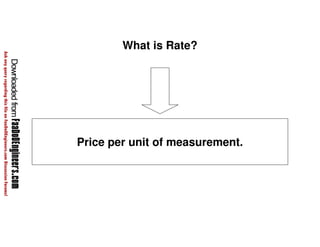
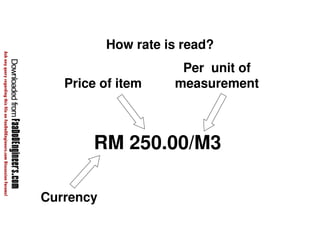
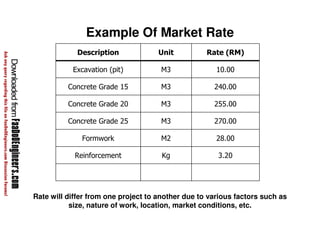
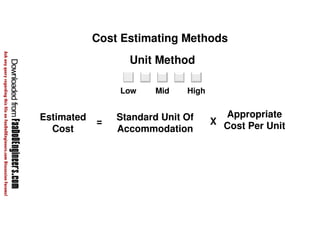
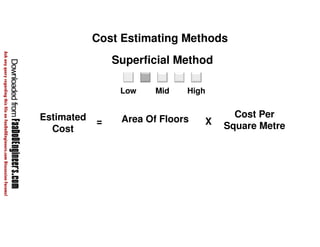
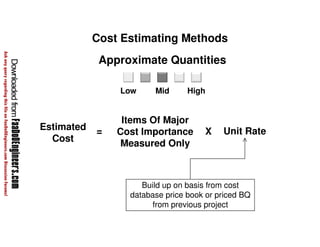
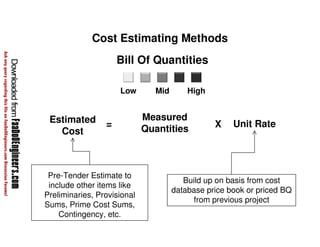
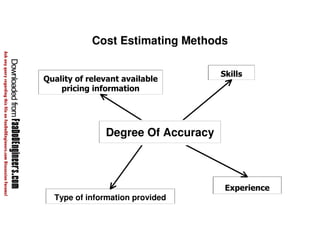
This document discusses cost estimation methods for civil engineering projects. It explains that cost is estimated by multiplying the quantity of materials or work by the rate per unit. It then describes different cost estimating methods used in civil engineering, including the unit method, superficial method, approximate quantities method, and bill of quantities method. These methods involve measuring quantities of major work items and multiplying them by unit rates to estimate total costs. The quality of available pricing information, type of information provided, estimator skills and experience affect the accuracy of cost estimates.