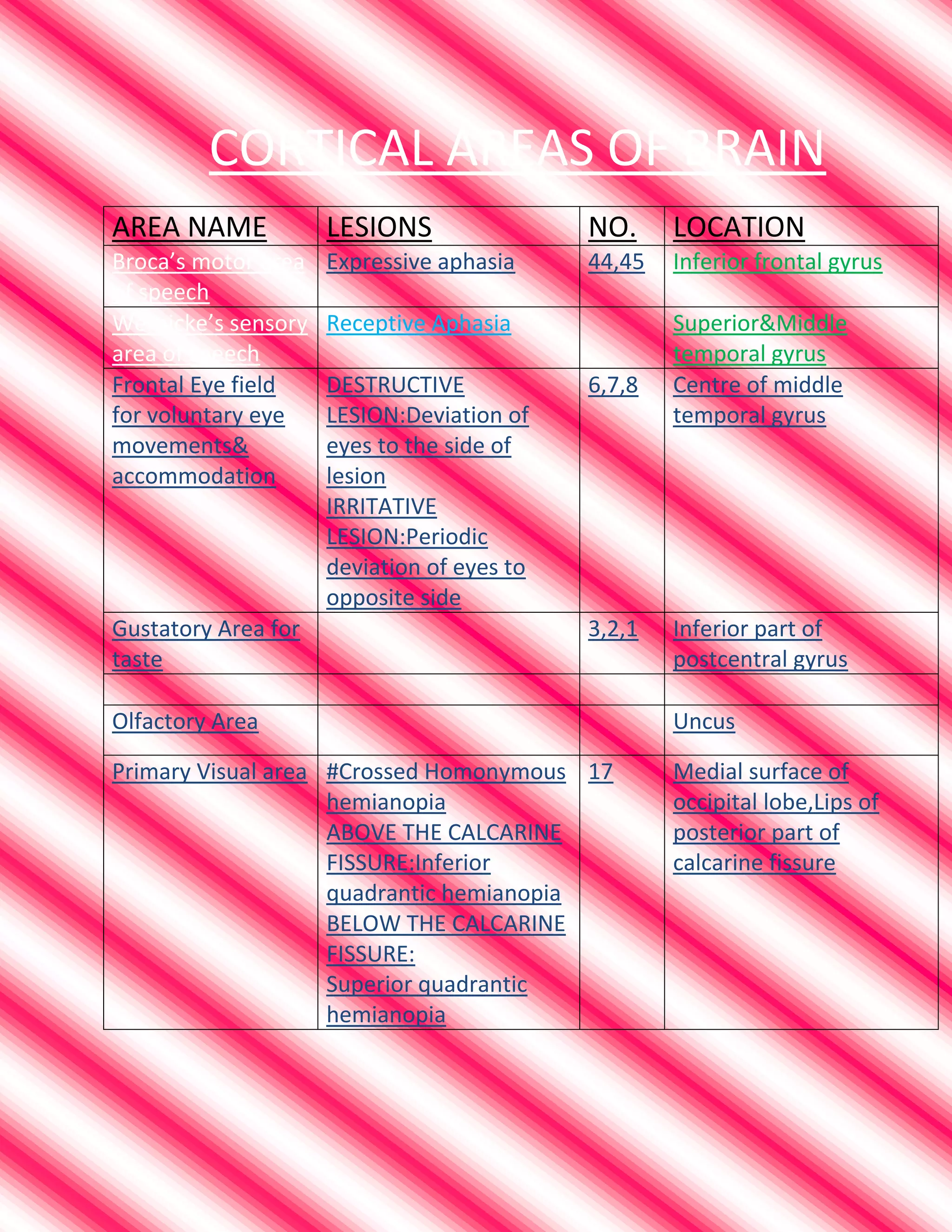
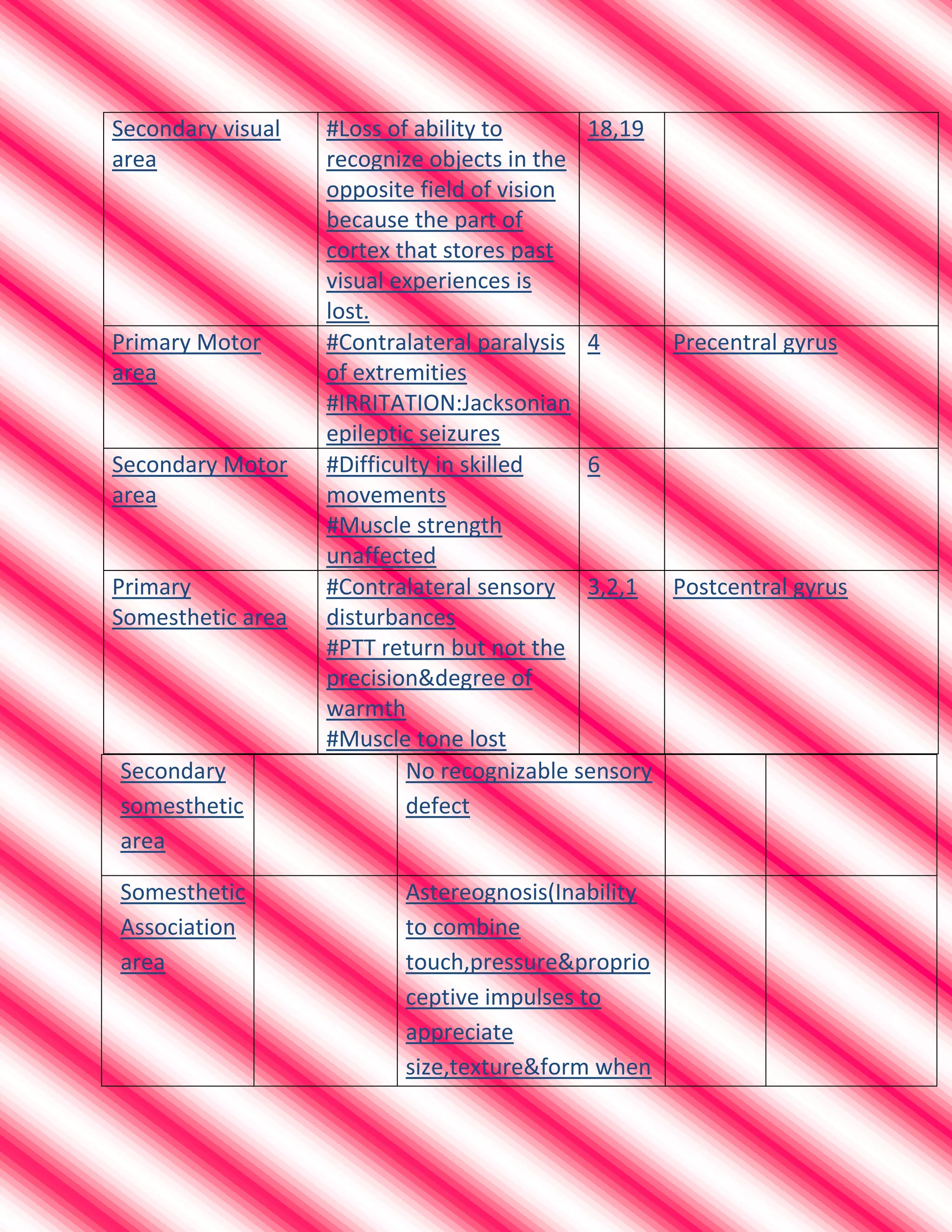
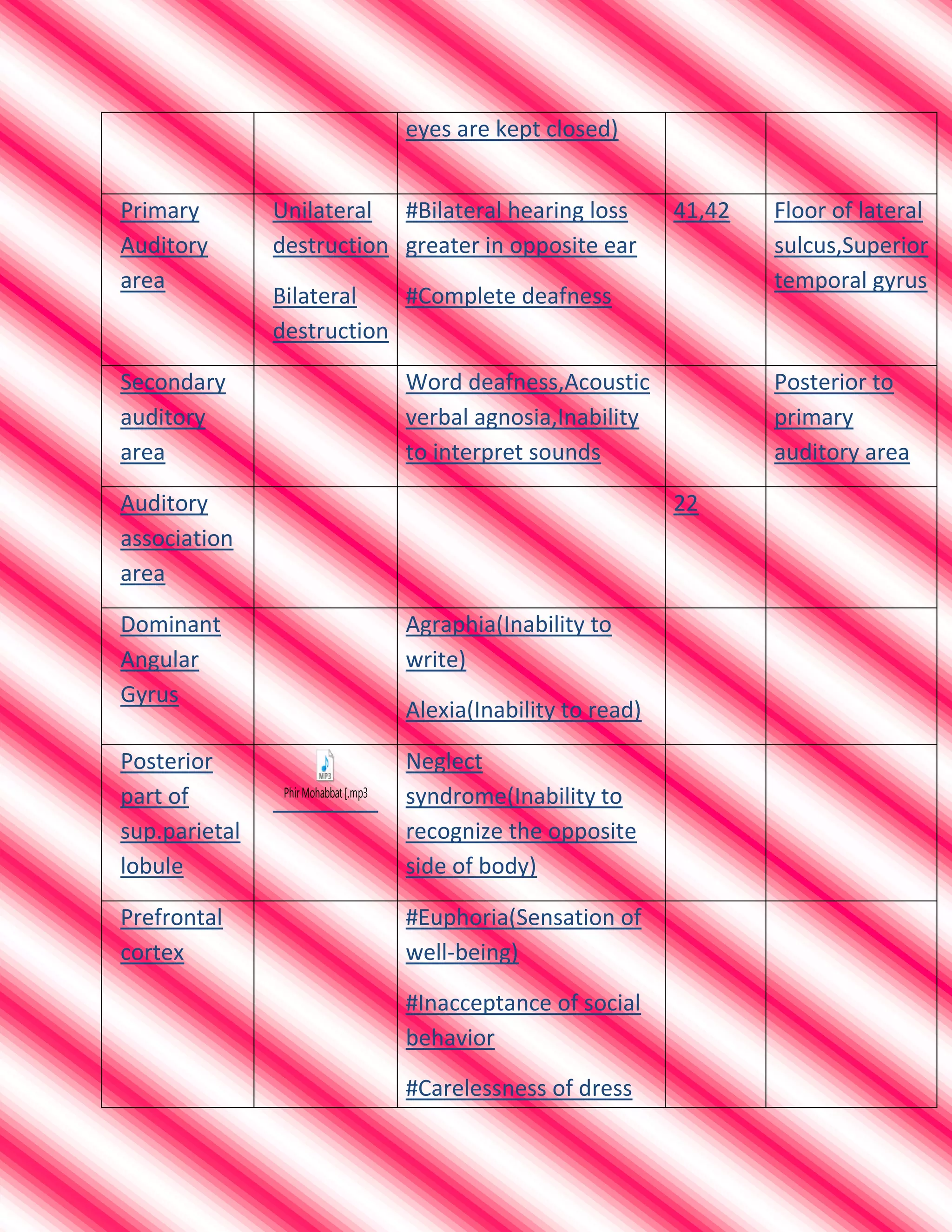
This document summarizes cortical areas of the brain and their functions. It lists various brain areas including Broca's area, Wernicke's area, the frontal eye field, the primary visual area, secondary visual area, primary motor area, secondary motor area, primary somatosensory area, secondary somatosensory area, primary auditory area, secondary auditory area, the angular gyrus, and the prefrontal cortex. For each area, it provides the name, location in the brain, and common lesions or effects of lesions in that area, such as different types of aphasia, visual field defects, motor or sensory deficits, or other cognitive impairments.