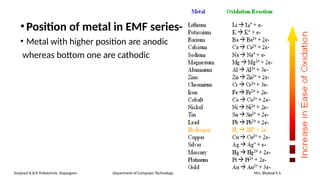
The document details the syllabus for a basic chemistry course focused on metal corrosion at Sanjivani K.B.P. Polytechnic, covering types, mechanisms, and factors affecting corrosion, along with methods for its control and prevention. It discusses dry and wet corrosion, emphasizing the electrochemical processes involved and various protective measures such as coatings and the use of inhibitors. Additionally, it provides insights into the learning outcomes related to understanding corrosion in terms of types, mechanisms, and preventive strategies.











![Protections of metals from corrosion
• Modification of environment
A] Removal of corrosion stimulant-
To avoid corrosion due to oxygen, dissolved oxygen from
water is removed either by deaeration or using reducing
substances like hydrazine N2H4 or sodium sulphite Na2SO3.
* Corrosion of acid is removed by neutralization using lime.
* Corrosion due to moisture or humid air is minimized by
using silica gel.
Sanjivani K.B.P. Polytechnic, Kopargaon Department of Computer Technology Mrs. Bhattad K.S.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corrosion-241111045920-b9addf2c/85/Corrosion-and-its-protection-pptx-17-320.jpg)
![•B] Use of inhibitors-
•These are substances added to environment to
reduce corrosion.
•Inhibitors are substance which creates physical
barrier between the metal and environment.
•Quinoline, organic amines, cyanides, chromates are
effective inhibitors
Sanjivani K.B.P. Polytechnic, Kopargaon Department of Computer Technology Mrs. Bhattad K.S.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corrosion-241111045920-b9addf2c/85/Corrosion-and-its-protection-pptx-18-320.jpg)

![Protective coating -Hot Dipping
• A] Galvanizing- The process of coating of more active Zn over less active iron
by hot dipping is known as galvanizing.
• This is anodic coating.
• Zn protect base metal though coating is broken.
• Widely used for roofing sheets, nails
fencing wires, buckets, vehicles, etc.
• Galvanizing is not for food storage.
• As it is poisonous coating.
• If powder coating of Zn is done then
it is called is Sherardizing. Ex Screw,
nut, bolt, gauze etc.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UE7zY9JoVIc
Sanjivani K.B.P. Polytechnic, Kopargaon Department of Computer Technology Mrs. Bhattad K.S.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corrosion-241111045920-b9addf2c/85/Corrosion-and-its-protection-pptx-20-320.jpg)


