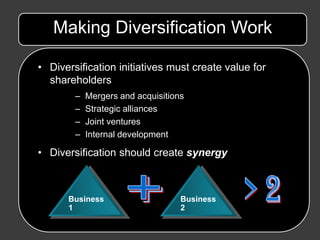
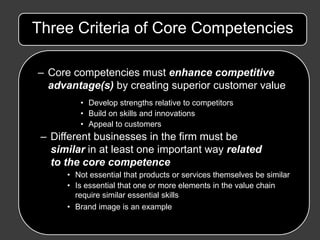
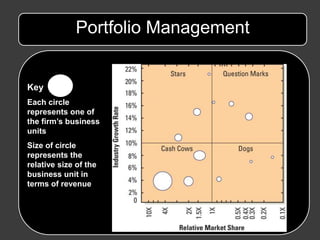
Managerial motives that are not aligned with shareholder value creation can undermine the potential benefits of diversification strategies. Proper governance and incentives are needed to ensure strategies like mergers, acquisitions, alliances and joint ventures are undertaken to generate true synergies rather than serving other managerial aims.