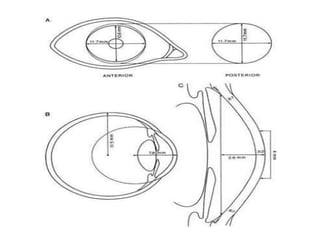
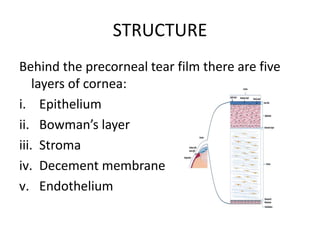
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that refracts light. It is avascular and has five layers - epithelium, Bowman's layer, stroma, Descemet's membrane, and endothelium. The stroma makes up most of the thickness and contains collagen bundles and proteoglycans. The cornea is nourished by the aqueous humor and innervated by nerves from the trigeminal nerve. It serves to transmit and refract light entering the eye, as well as protect the inner structures.