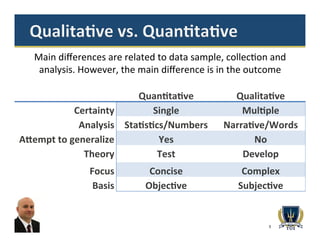
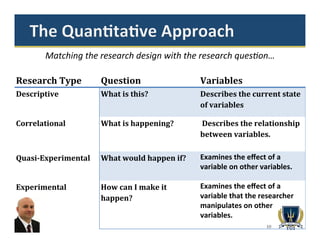
The document is an overview of quantitative research methodology presented by Dr. Carlos Cardillo, focusing on defining and differentiating quantitative and qualitative research methods. It emphasizes the importance of choosing the right research design based on research questions and variables, outlining various types of quantitative research designs such as descriptive, correlational, quasi-experimental, and experimental. The presentation also highlights the relevance of statistical analysis in quantitative research while contrasting it with qualitative methods.