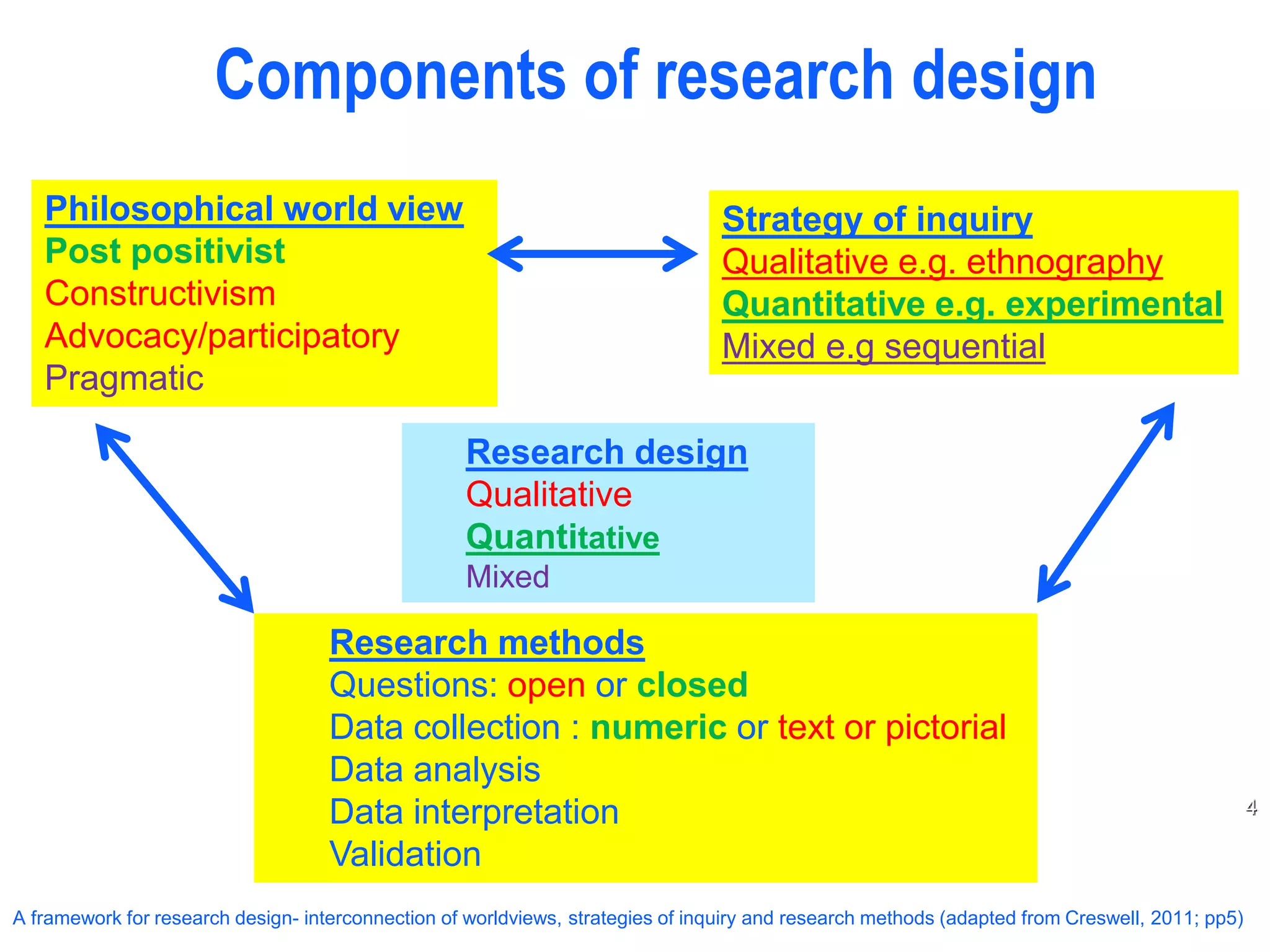
This document discusses quantitative research design. It defines research design as the conceptual structure and plan for conducting research, including assumptions, strategies, data collection and analysis. Quantitative research is objective and systematic, utilizing numerical data to study social problems. It tests hypotheses deductively and looks for cause-and-effect relationships between variables. Quantitative research is rooted in postpositivism and employs experimental or survey strategies to quantify trends, attitudes or relationships, allowing results to generalize to populations. Methods involve predetermined questions, performance/attitude measurement, and statistical analysis and interpretation to test theories.