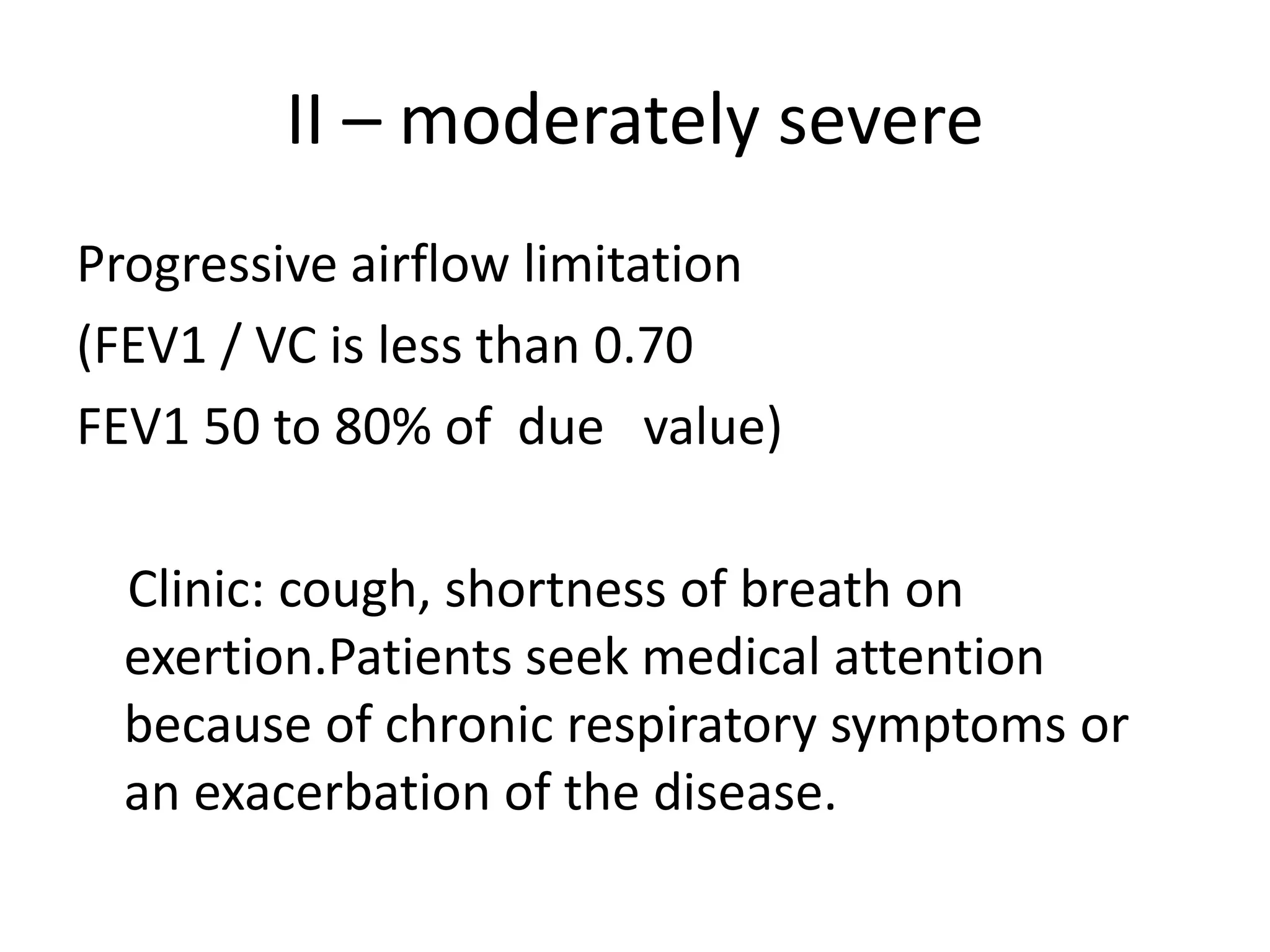
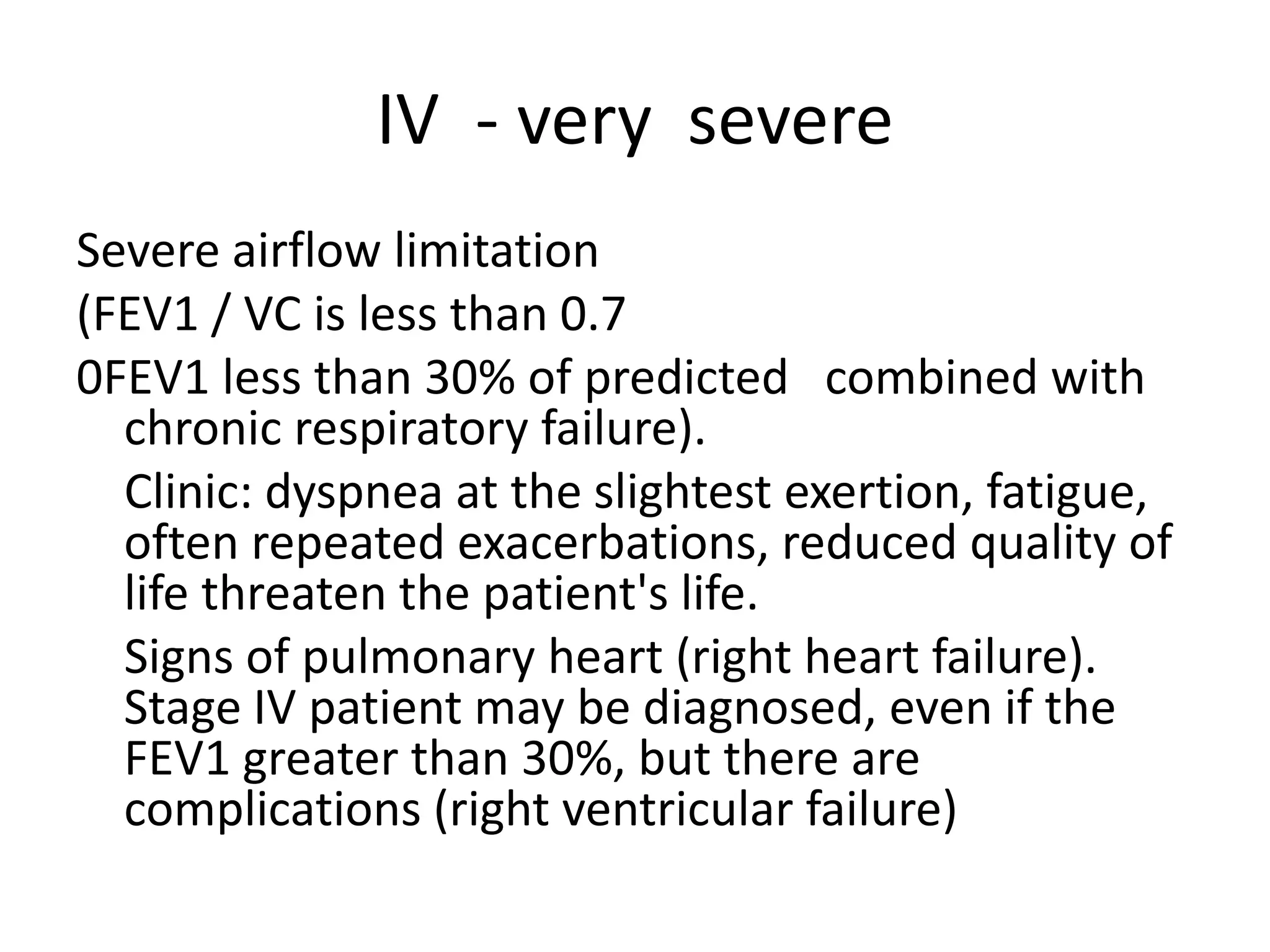
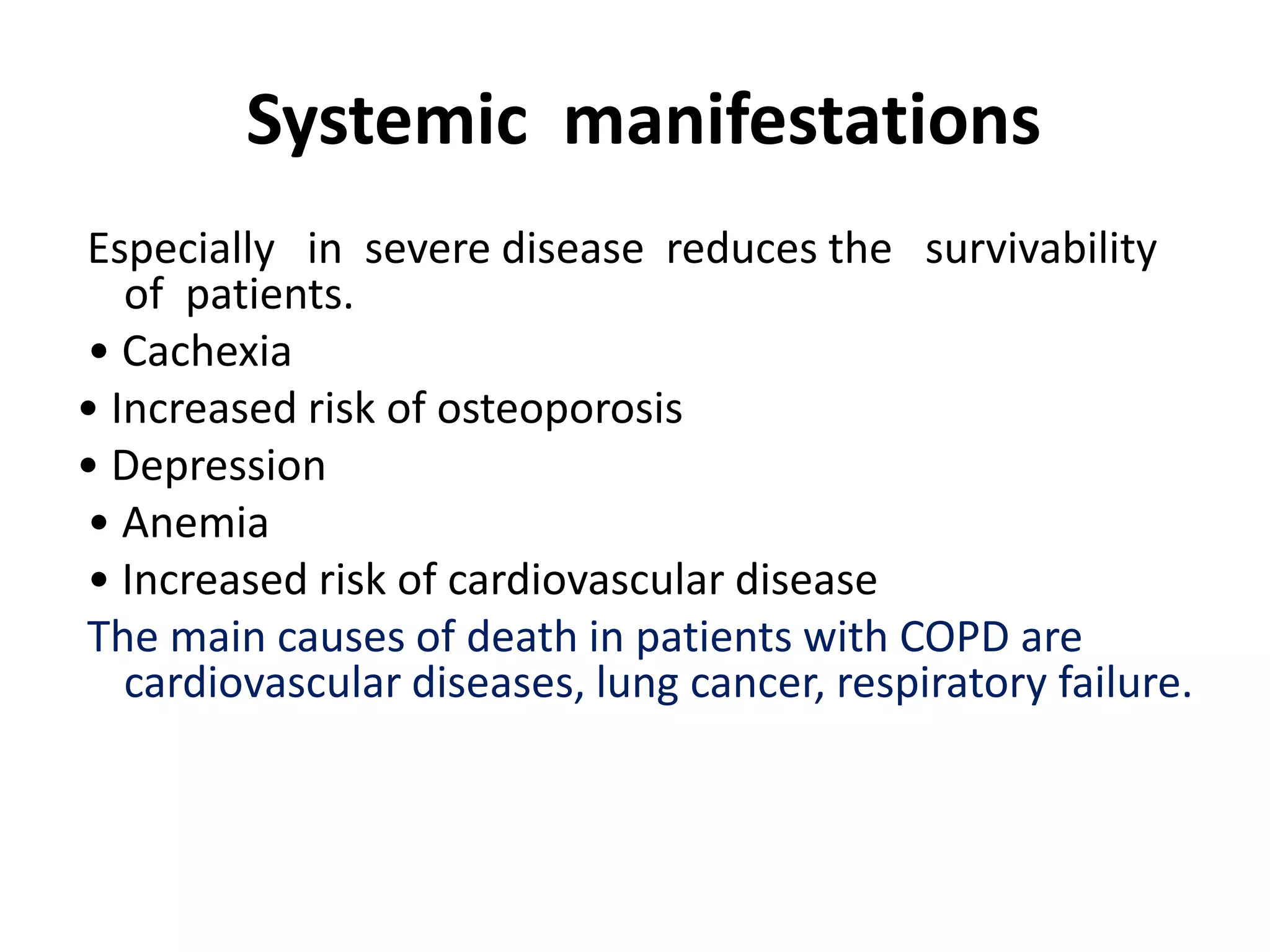
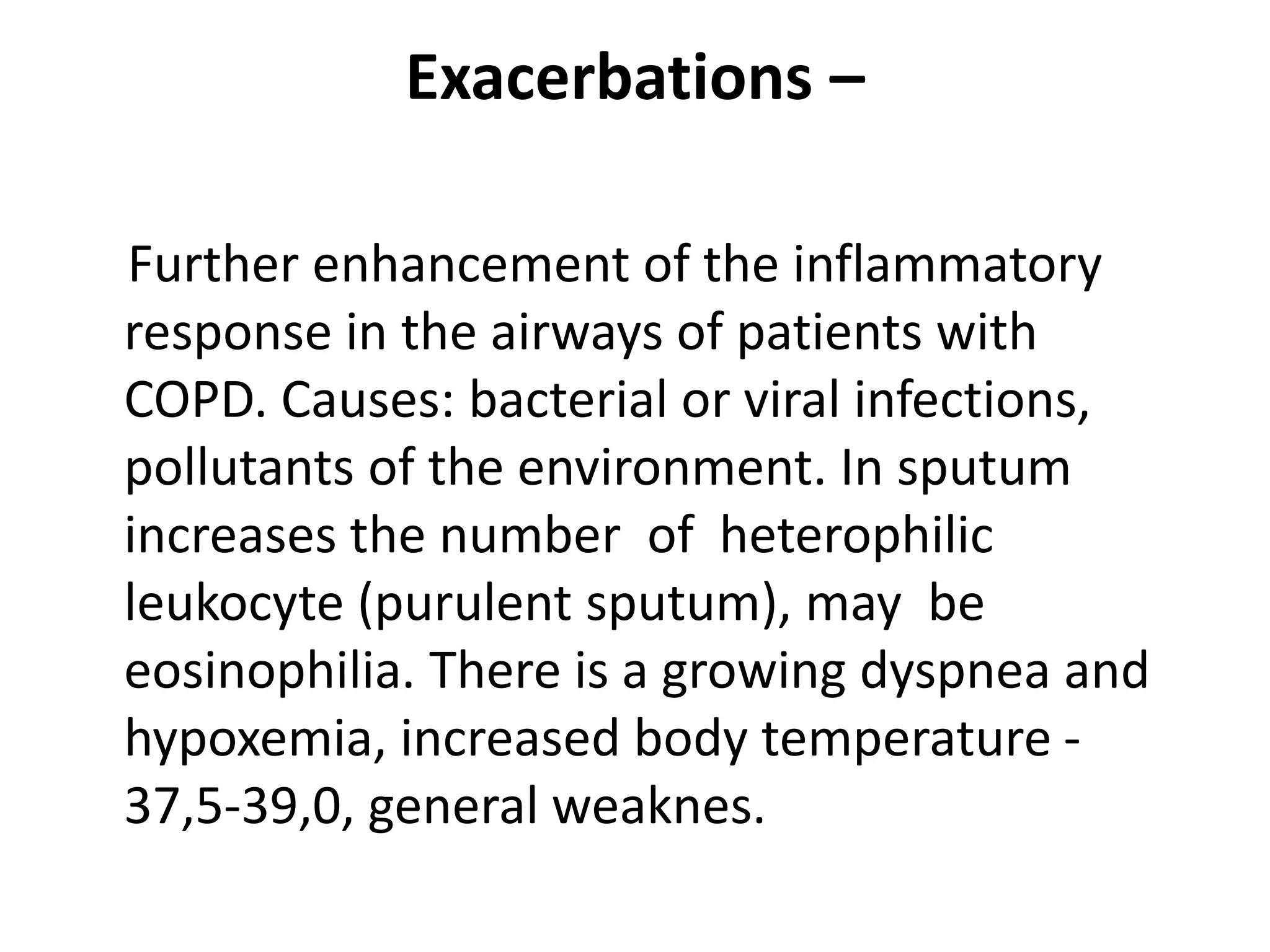
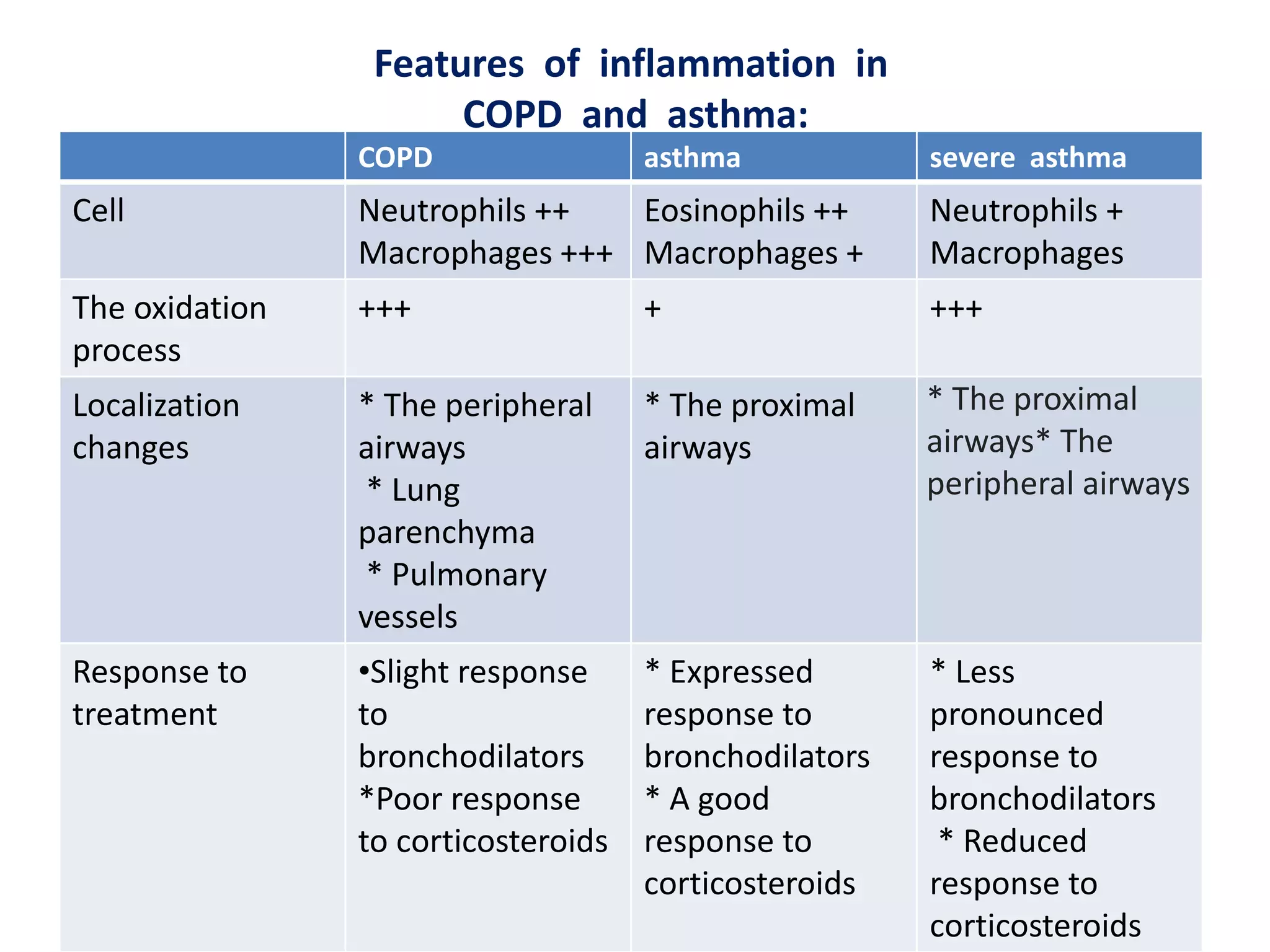
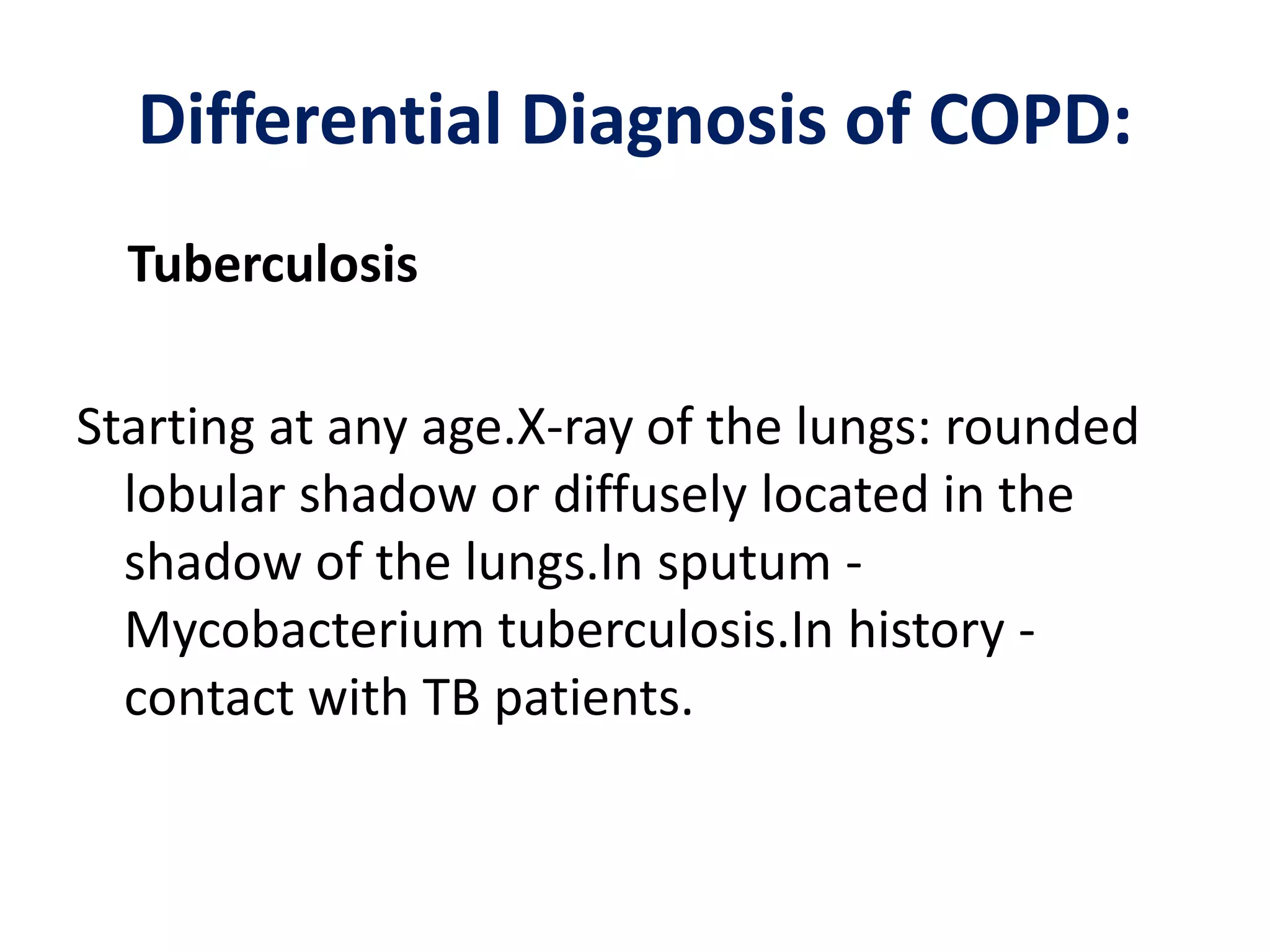
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a chronic lung disease characterized by airflow limitation caused by damage to the lungs, usually from smoking. It involves emphysema and small airway fibrosis leading to trapped air in the lungs. Symptoms include shortness of breath and cough. Diagnosis involves assessing risk factors, symptoms, and lung function tests showing airflow limitation that is often only partially reversible with bronchodilators. Treatment focuses on stopping smoking and using bronchodilators and inhaled corticosteroids to relieve symptoms and reduce exacerbations.