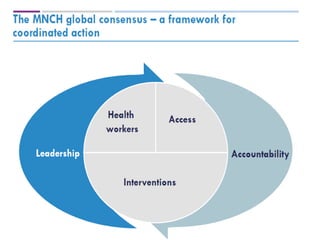
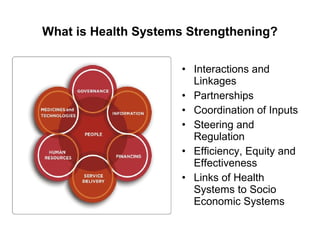
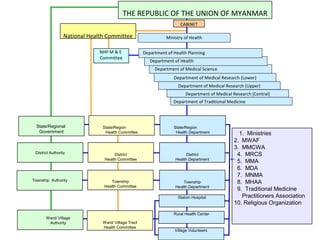
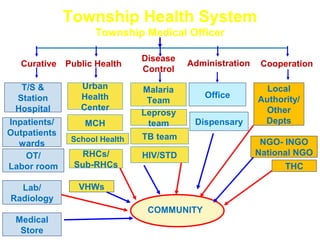
This document discusses several concepts related to coordination, collaboration, and strengthening health systems. It defines coordination as organizing different people or activities to achieve goals. Collaboration is working together to achieve a shared goal through knowledge sharing and consensus building. Cooperation is working harmoniously together, unlike competition. Community refers to a group sharing something in common and community participation involves empowering individuals and communities through ownership and involvement in health services. Health systems strengthening involves coordination of inputs, partnerships, and links between the health system and socioeconomic factors to improve efficiency, equity and effectiveness.