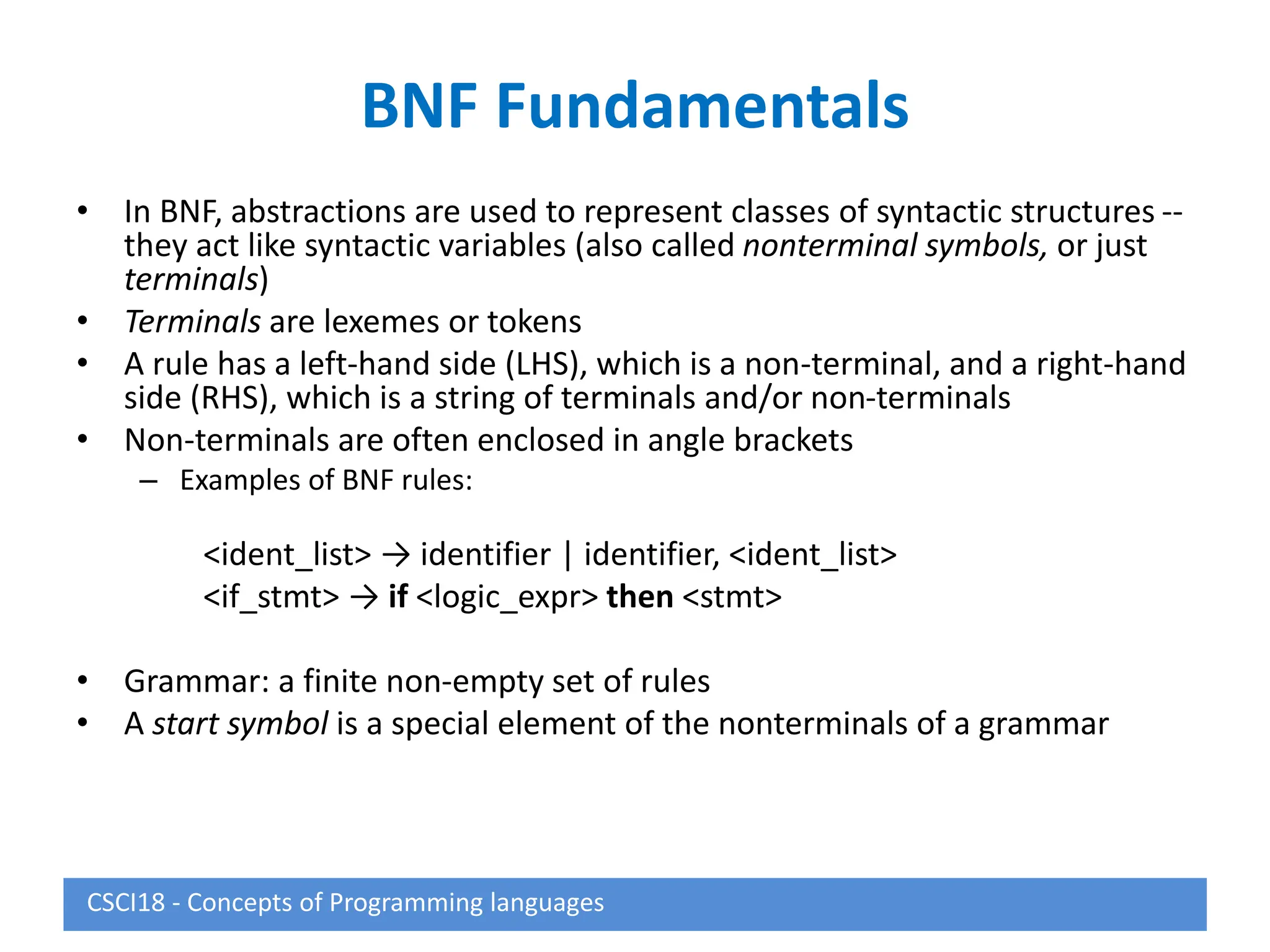
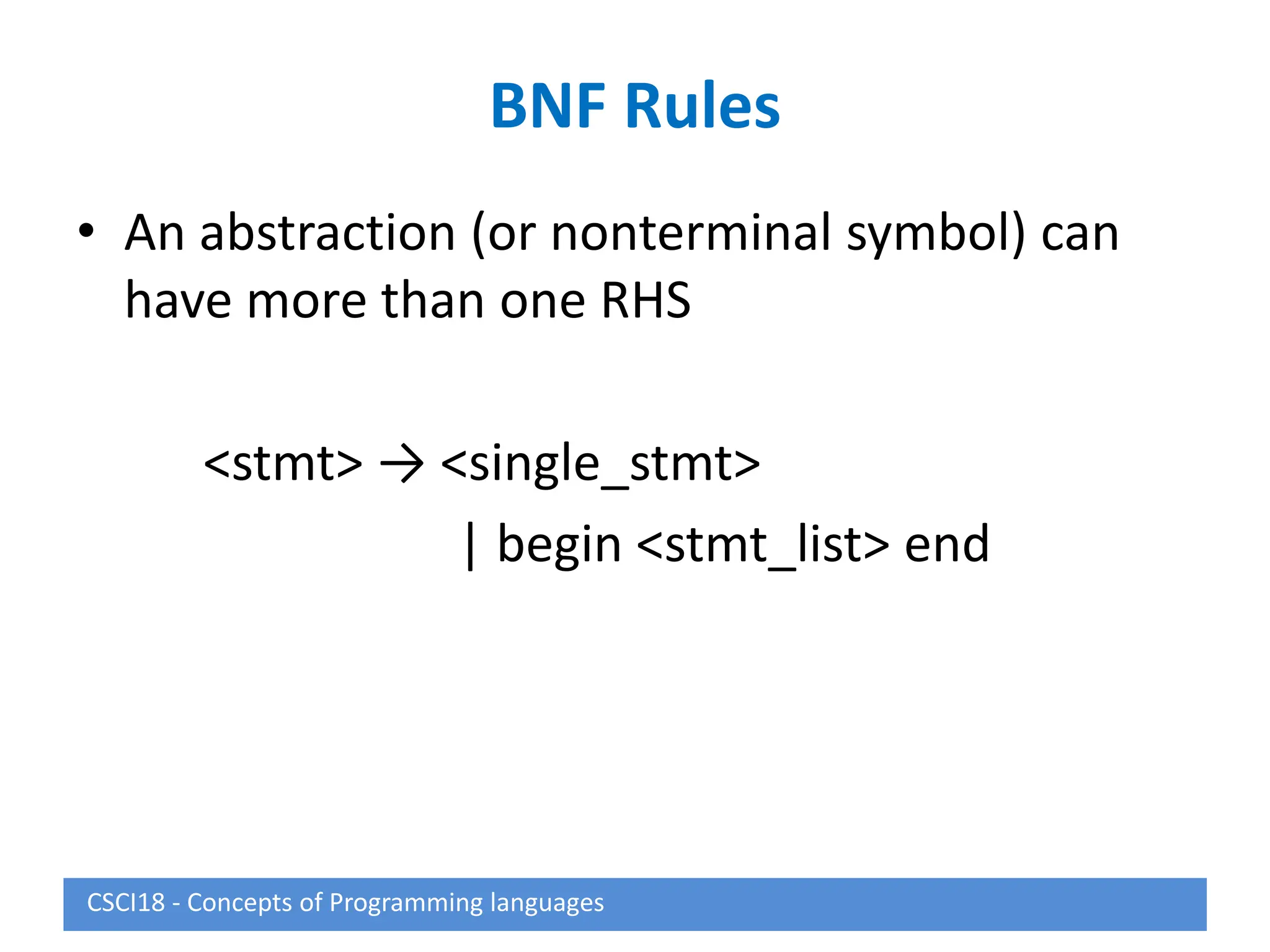
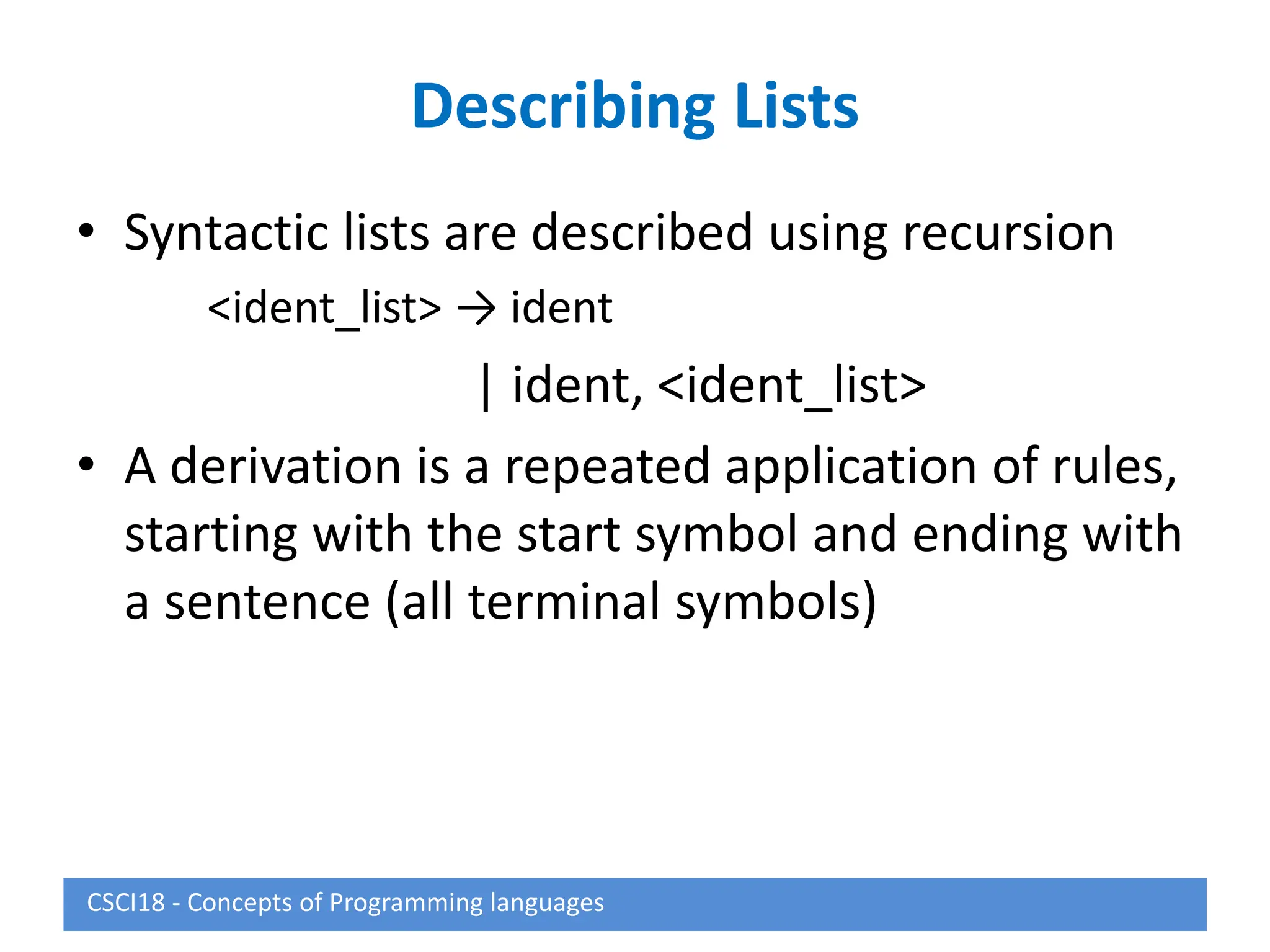
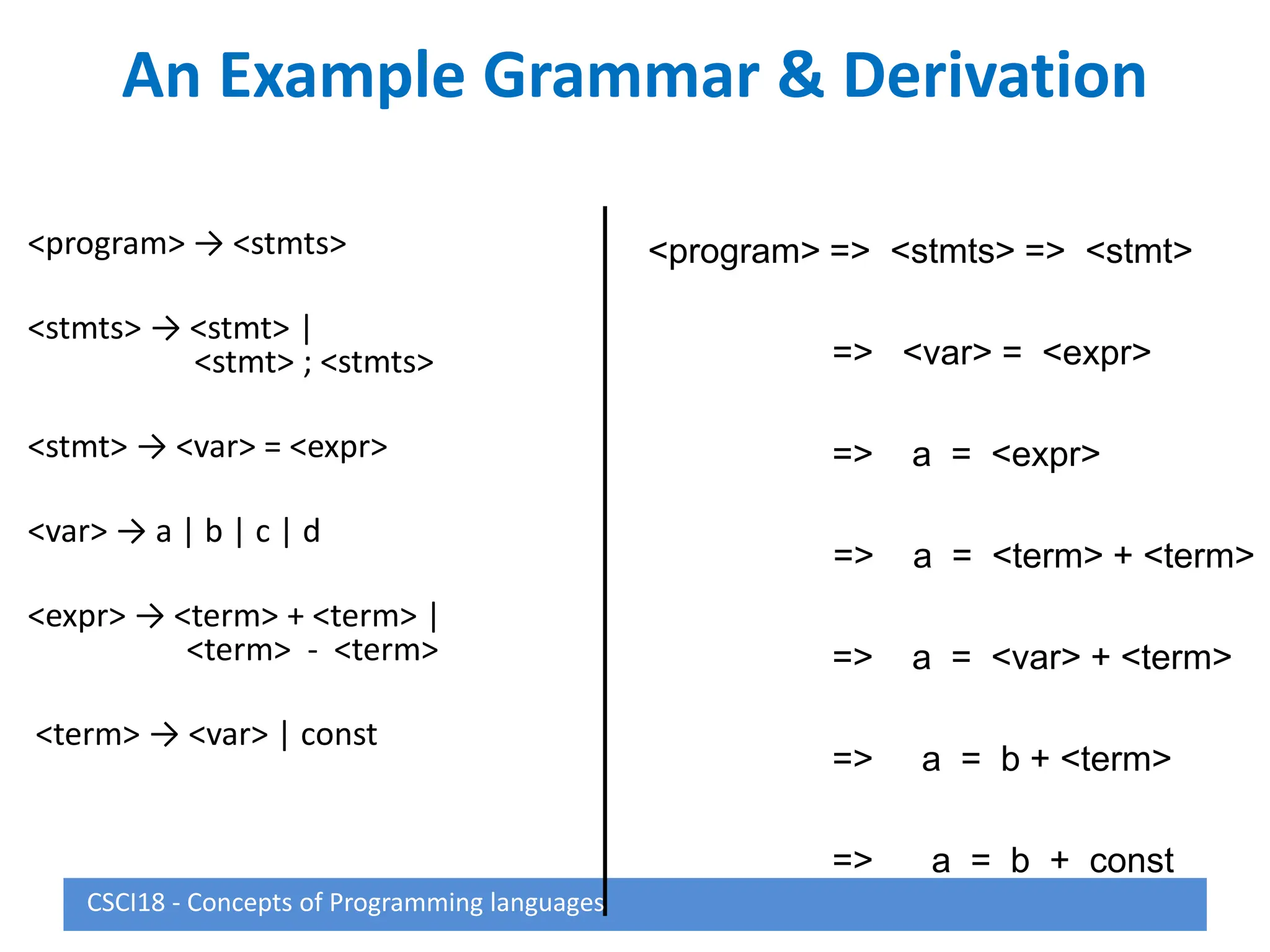
This document describes syntax and semantics for programming languages. It begins by defining syntax as the form or structure of a language and semantics as the meaning. Formal methods for describing syntax include context-free grammars, Backus-Naur Form (BNF), and attribute grammars. Semantics can be described through operational semantics which defines meaning through state changes during execution or denotational semantics which provides an abstract definition using recursive functions. The document provides examples of BNF rules, derivations, and attribute grammars.










![Extended BNF
• Optional parts (0 or one) are placed in
brackets [ ]
<proc_call> → ident [(<expr_list>)]
• Alternative parts of RHSs are placed inside
parentheses and separated via vertical bars
<term> → <term> (+|-) const
• Repetitions (0 or more) are placed inside
braces { }
<ident> → letter {letter|digit}
CSCI18 - Concepts of Programming languages](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8074448-231019015815-7ec2bda7/75/8074448-ppt-18-2048.jpg)






![Attribute Grammar (continued)
• Syntax rule: <expr> <var>[1] + <var>[2]
Semantic rules:
<expr>.actual_type <var>[1].actual_type
Predicate:
<var>[1].actual_type == <var>[2].actual_type
<expr>.expected_type == <expr>.actual_type
• Syntax rule: <var> id
Semantic rule:
<var>.actual_type lookup (<var>.string)
CSCI18 - Concepts of Programming languages](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8074448-231019015815-7ec2bda7/75/8074448-ppt-25-2048.jpg)

![Attribute Grammars (continued)
<expr>.expected_type inherited from parent
<var>[1].actual_type lookup (A)
<var>[2].actual_type lookup (B)
<var>[1].actual_type =? <var>[2].actual_type
<expr>.actual_type <var>[1].actual_type
<expr>.actual_type =? <expr>.expected_type
CSCI18 - Concepts of Programming languages](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8074448-231019015815-7ec2bda7/75/8074448-ppt-27-2048.jpg)