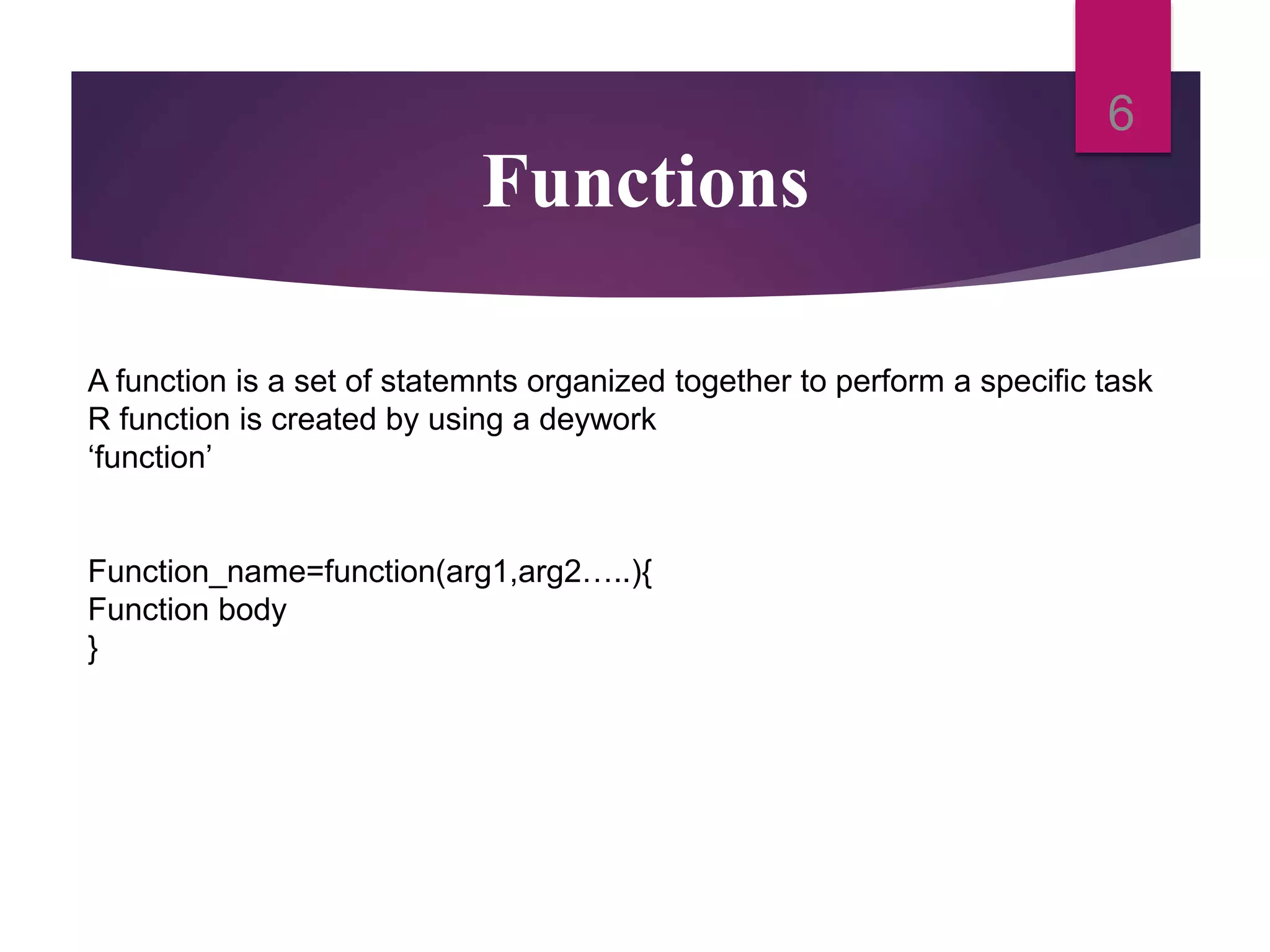
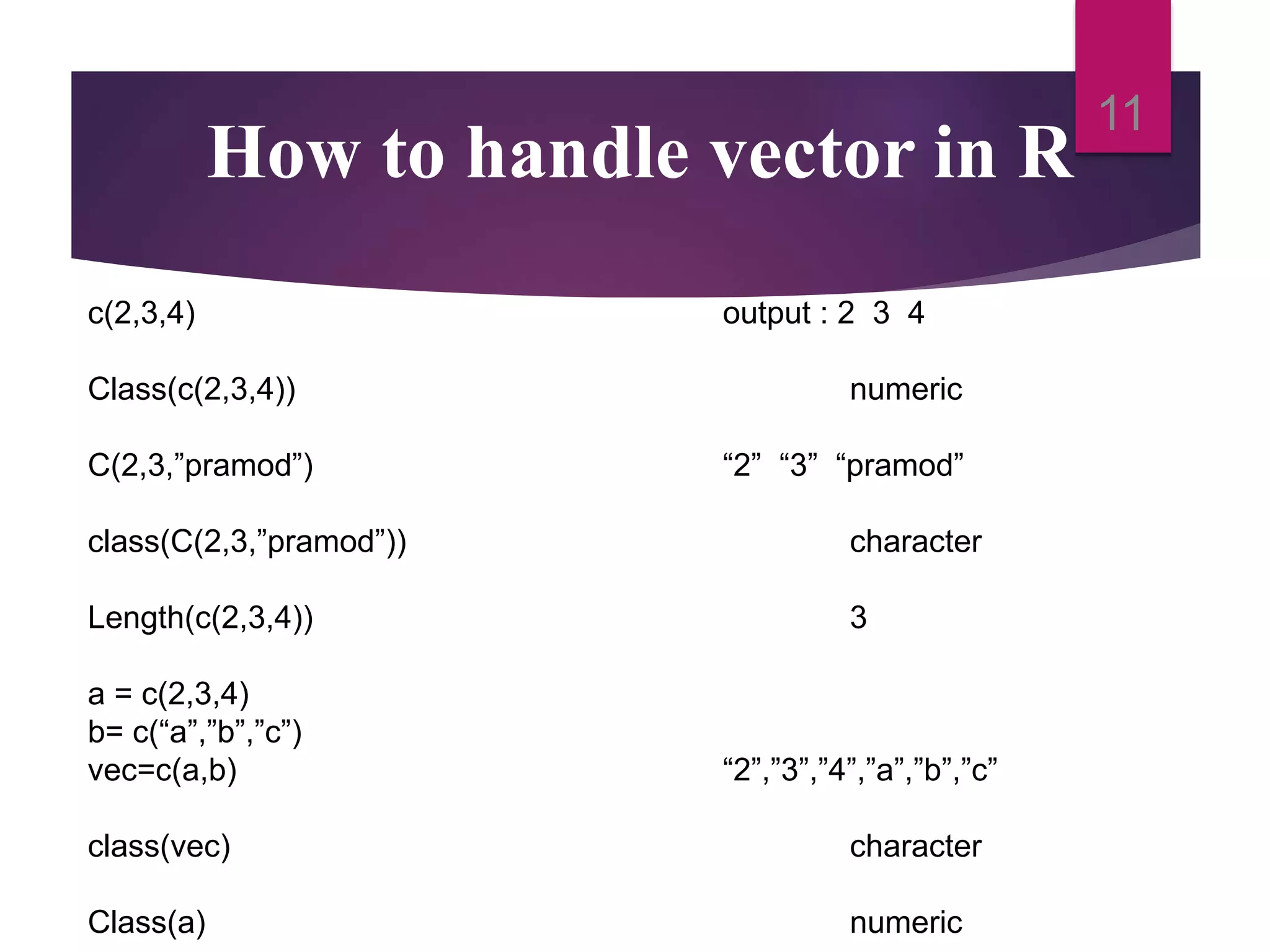
Control structures allow programmers to control the flow of execution of code in R. This document discusses various control structures like if-else loops, for loops, while loops, and functions. It also covers various data types in R like vectors, lists, data frames, factors and how to handle vectors through operations like addition, indexing, etc. It provides examples for each concept discussed.




![If…else
7
data(“iris”)
View(iris) inbuilt dataset
str(iris)
#mean,median,standard deviation
Desc_setosa=matrix(nrow=5,ncol=4,
dimnames=list(c(“mean”,”median”,”mode”,”standard deviation”,”no
ofcases”),colnames(iris)[1:4]))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/controlstatements-200418061138/75/Control-statements-7-2048.jpg)



![How to handle vector in R
13
v4= c(1:10)
v4[5] 5
V4[-5] 1 2 3 4 6 7 8 9 10
V4(3:5) 3 4 5
V4[c(3:5),10] 3 4 5 10 range indexing](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/controlstatements-200418061138/75/Control-statements-13-2048.jpg)


