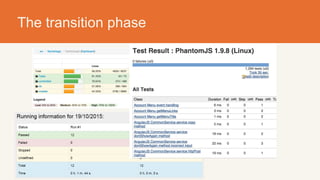
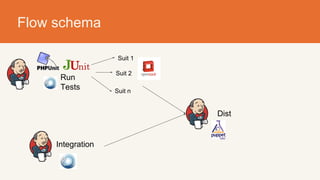
The document discusses MyHeritage's transition to continuous deployment (CD) to enhance their software development process, addressing challenges faced with their previous weekly service pack system. Key benefits of adopting CD include fast feedback loops, risk reduction, improved coding quality, and increased velocity in delivering updates. The transition involved implementing new engineering practices, automation tools, and improved error handling, resulting in higher efficiency, fewer bugs, and increased satisfaction among teams.