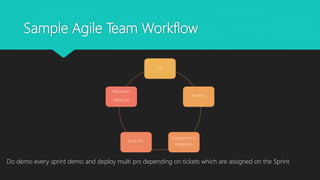
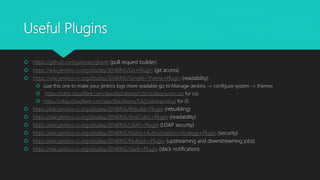
This document discusses CI/CD workflows and best practices using Jenkins. It explains that Jenkins helps automate the software development process by building code whenever commits are pushed to version control. Good CI practices include integrating with source control, running all tests, and providing feedback via chat systems. The document provides examples of basic, agile team, and advanced CI workflows and recommendations for configuring Jenkins, including using plugins, securing authentication, and proxying Jenkins within a VPN.