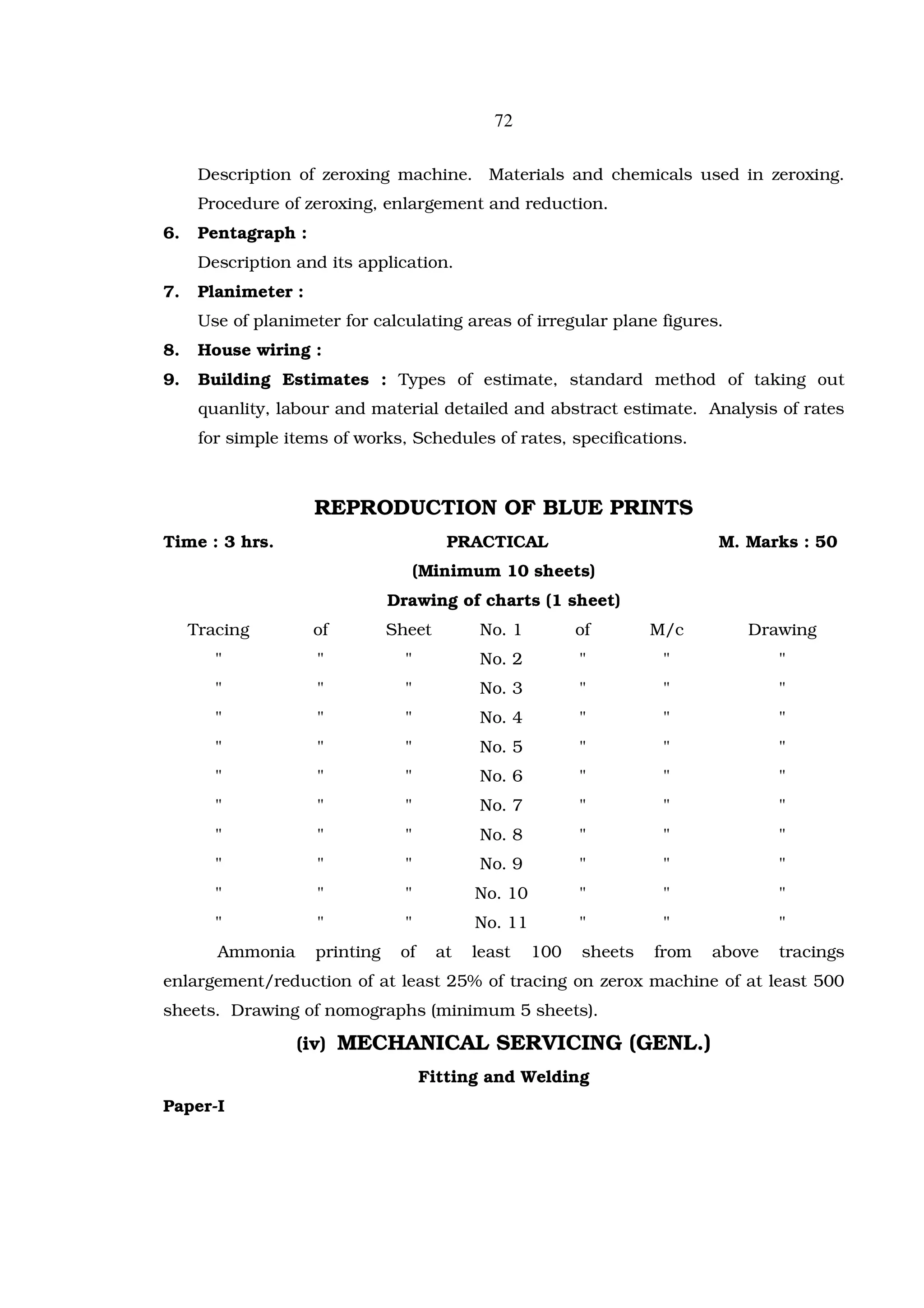
The document outlines the scheme of studies for the 12th class vocational stream examination. It details the compulsory and elective subjects students can choose. For compulsory subjects, students must take General English, General Punjabi, Environmental Education, Computer Science, and a General Foundation Course. Elective subjects allow students to choose one of five groups - Agriculture, Business/Commerce, Home Science, Engineering/Technology, or Humanities. Each elective subject has three theory components worth 80 marks total and a practical component worth 60 marks. Overall, the scheme of studies provides the framework for subject distribution, duration of exams, grading system, and time allotment for vocational stream students.










































![41
(uksV % fx;kjoha d{kk esa 'kkVZgSaM dh fl[kykbZ ds i<+s gq, fu;eksa dh nksgjkbZA)
Hkkx&I
1- milxZ&izU;;A
2- dkVoha fof/A
3- 'kkVZgSaM fy[kus ds fy, lkeku&iSUu] iSafUly] dkihA
4- Jqrys[k fy[kus dh fof/A
5- xyfr;k¡ ,o mUgsa lq/kjus dh fof/A
Hkkx&II
6- fyfi&varj fof/ (Transciption)
7- vke izpfyr 'kCnksa dk la{ksi :Ik@okD;ka'k (Pharasecgraphy)
8- ipsZ dk eqY;kadu] LVSuksa ds dk;ZA
9- nwljh Hkk"kkvksa (vaxzsth@iatkch) esa 'kkVZgSaM lEcU/h tkudkjhA
'kkVZgSaM (fgUnh)
iz;ksfxd ijh{kk
isij&II
le; % 3 ?kaVs vf/dre vad % 50
1- 200 'kCnksa dk iSjk] 80 'kCn izfr feUV dh xfr ls <kbZ (2½) feUV esa fy[kk;k tk,xk vkSj bls 20
feUVksa esa VkbZi e'khu ij fyfi&'kq¼ djus dks Hkh dgk tk,xkA
2- 200 'kCnksa dk ,d vkSj iSjk] 80 'kCn izfr feUV dh xfr ls <kbZ (2½) feUV esa fy[kk;k tk,xk vkSj
bls 20 feUVksa esa VkbZi e'khu ij fyfi&'kq¼ djus dks Hkh dgk tk,xkA
(uksV % fn, x, nksuksa iSjksa esa ,d feUV dk fojke fn;k tk,xkA)
3- lS'ku ds nkSjku fo|kfFkZ;ksa }kjk iwjs o"kZ esa fd;s x, dk;Z dh de ls de 100 i`"Bksa dh QkbZy rS;kj dh tk,xhA
TYPEWRITING-ENGLISH
Paper-III
Time : 2 hours Theory M. Marks : 30
Part-I
1. Correspondence-Memorandum, D.O., U.O., Circular letter.
2. Typing systematically, Typing heading, Typing addresses on envelopes,
Typing in margins, typing sub-headings.
3. Tabulation-Importance, methods.
4. Use and types of carbon paper, making duplicate copies, making corrections
on carbon copies, care of carbon papers.
Part-II
5. Stencil paper-Importance, use, method of cutting, methods of making
corrections, use of fluid, stylus pen, stencil plate.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/contents-pages958/75/CONTENTS-Pages-45-2048.jpg)

![43
a2 .kDNZe b;A?N; uZtf Nzwf 02 kd osZg hoscd
a3 .kBoe ghJkN uZtf KNzwf 03 {zB NA?wN/N; hd Kwbke 4
a4 hd KnBfzg 001 NZx-'NZx hd wze /Jr /she Bko"d bk; A'bZt KnhEokndftf Bko"d hJkby;f
./tki hshe oknsf bhJkc
VkbZi&jkbfVax (fgUnh)
fyf[kr ijh{kk
isij&III
Le; % 2 ?kaVs vf/dre vad % 30
Hkkx&I
1- i=kkpkj&eSeksjSaMe] v/Z&ljdkjh i=k (D.O. Letters), xLrh i=k (U.O.)] xSj&ljdkjh i=k
(Circular Letters) vkfn ds ckjs esa KkuA
2- lgh <ax ls VkbZi djuk&'khZ"kd VkbZi djuk fyQkQksa ij irk VkbZi djukA
3- lkj.khdj.k&egRo ,ao fof/A
4- dkcZu isij dh fdLesa] iz;ksx] MqIyhdsV dkih rS;kj djuk] dkcZu dkfi;ksa dh 'kks/] dkcZu isij dh laHkkyA
Hkkx&II
5- LVSaly isij&bldk egRo] iz;ksx] dkVus dh fof/] v'kqf¼;k¡ lq/kjus ds <ax] dqjSd'ku Qy;wM
(Correction Fluid) dk iz;ksx] LVkbZySl (Stylus) iSUu] LVSaly IysV dk iz;ksxA
6- MqIyhdsV e'khu] jksVjh MqIyhdsVjA
7- lkfgrd ,ao dkuwuh nLrkostksa dks lgh <ax ls VkbZi djukA
8- VkbZi isij dh eqY;kadu fof/] i:Q jhfMaxA
VkbZi&jkbfVax (fgUnh)
iz;ksxh ijh{kk
le; % 3 ?kaVs vf/dre vad % 50
1- 300 'kCnksa dk iSjk (Paragraph) 30 feUVksa esa VkbZi djus ds fy, fn;k tk,xkA
2- nÝrjh i=k dk 20 feUVksa esa LVSaly dkVukA
3- pkj dkye dh LVsVeSaV dks 30 feUVksa esa VkbZi djukA
4- lS'ku nkSjku fo|kfFkZ;ksa }kjk iwjs o"kZ esa fd;s x, dk;Z dh de ls de 100 iUuksa dh QkbZy rS;kj dh tk,A
(ii) ACCOUNTANCY & AUDITING
Fundamentals of E-Business
Paper-I
Time : 2 hrs. Theory M. Marks : 30
Part-I](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/contents-pages958/75/CONTENTS-Pages-47-2048.jpg)