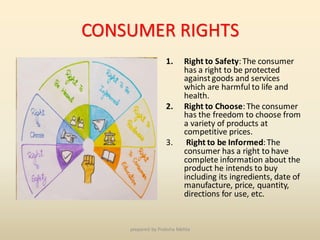
This document discusses consumer protection in India. It outlines the importance of consumer protection from both the consumer and business perspective. It describes ways to protect consumers, including self-regulation, consumer awareness programs, and government intervention. The document also details consumer rights such as the right to safety, choice, and education. Corresponding consumer responsibilities are provided. The three-tier system for consumer grievance redressal at the district, state, and national level is explained. Finally, the various reliefs available to consumers are outlined.