1. Consumer behavior involves the processes individuals and groups go through to select, purchase, and use goods and services.
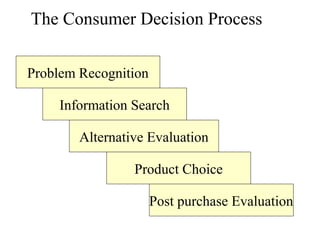
2. The consumer decision process includes problem recognition, information search, alternative evaluation, product choice, and post-purchase evaluation.
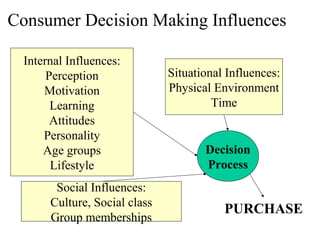
3. Consumer behavior is influenced by internal factors like perception, motivation, attitudes, and lifestyle as well as situational factors such as physical environment, time, and social influences including culture, social class, and reference groups.