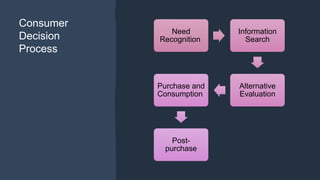
Consumer behavior studies how consumers make purchase decisions by examining their psychological, functional, physical, and economic needs. The consumer decision process involves need recognition, information search, alternative evaluation, purchase, and post-purchase evaluation. Maslow's hierarchy of needs argues that people are motivated to satisfy lower level needs like food and shelter before higher level needs like esteem and self-actualization. Understanding consumer behavior allows marketers to tailor products, services, marketing strategies, and the consumer experience to better satisfy consumer needs and wants.