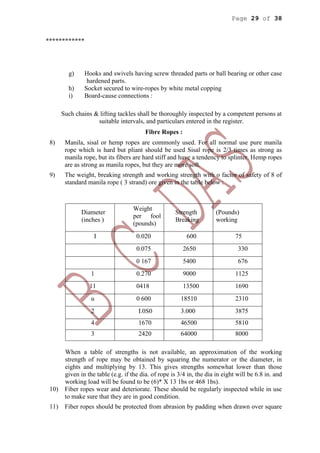
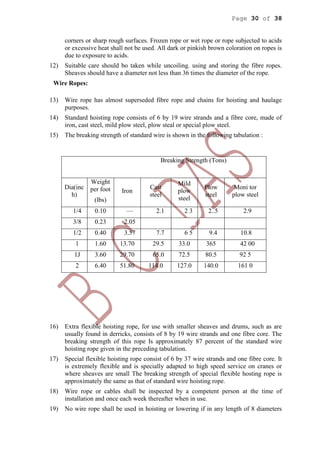
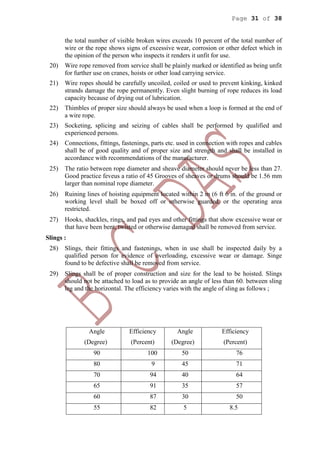
This document provides health and safety guidelines for various construction activities including excavation, blasting, construction processes, and plant/machinery use. It discusses hazards associated with open excavations, tunneling, shaft excavation, coffer dams, demolition, transportation and storage of explosives, blasting procedures, and more. The document aims to ensure the safety of workers involved in these various operations at construction sites.