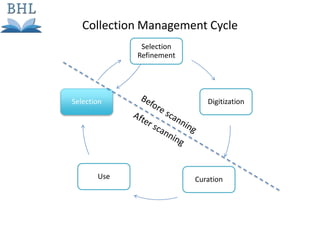
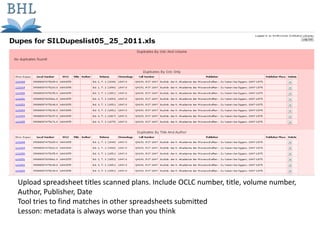
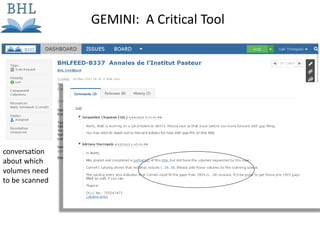
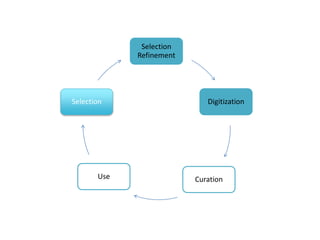
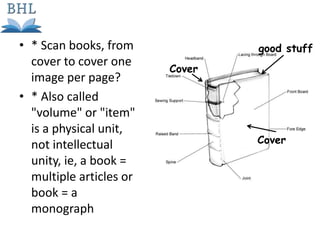
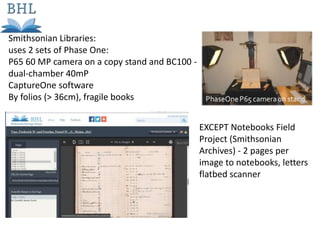
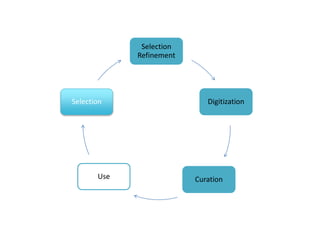
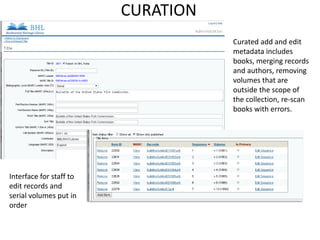
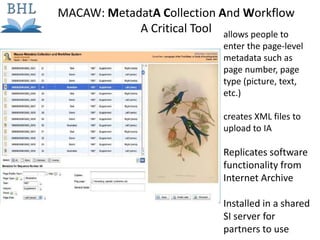
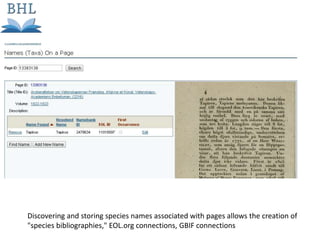
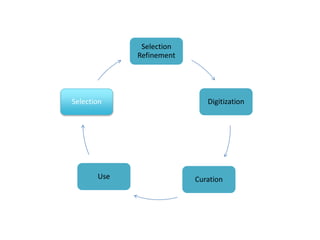
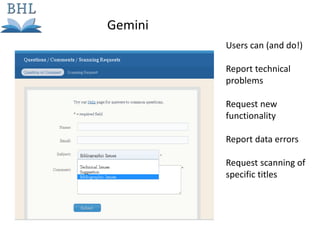
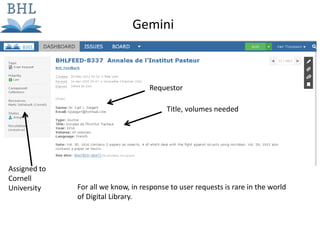
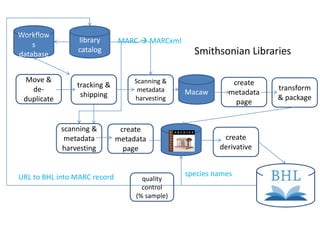
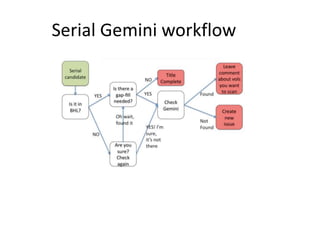
The document outlines the complexities of the digitization workflow for libraries, highlighting challenges such as the selection of scan-friendly books, metadata management, and the importance of accurate digital representations. It discusses the use of tools like Gemini and Macaw for curation and metadata collection, emphasizing their role in enhancing library processes. Additionally, it mentions collaborative efforts through shared resources like the Internet Archive to facilitate the scanning and preservation of library materials.