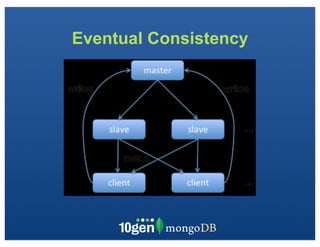
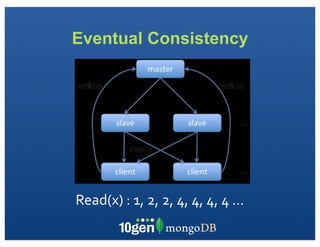
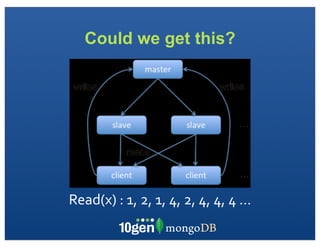
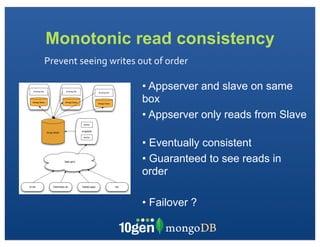
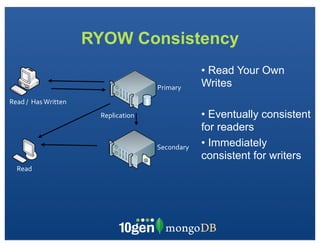
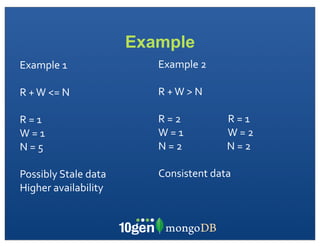
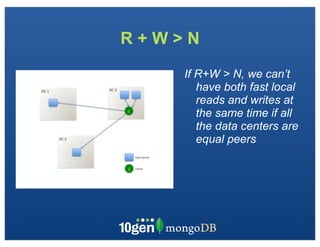
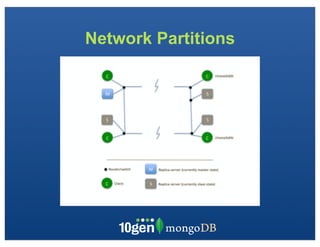
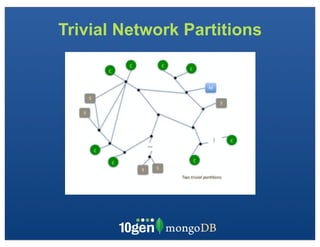
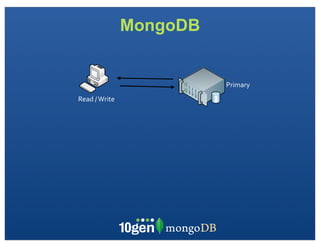
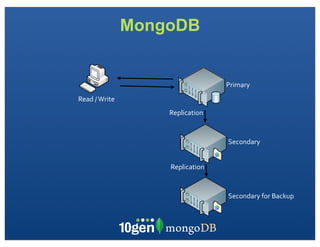
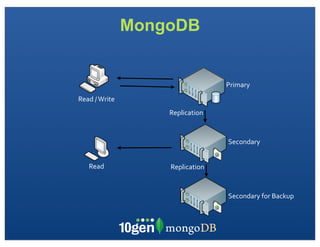
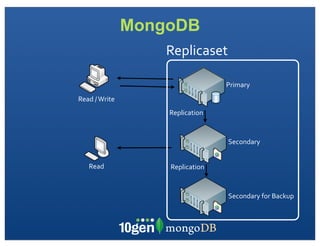
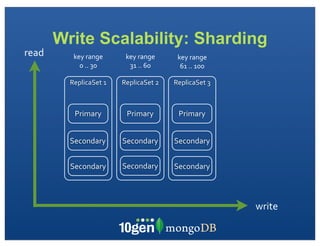
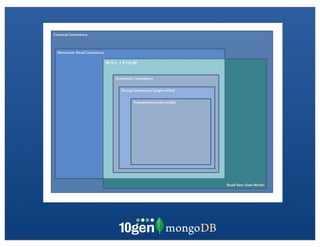
The document discusses transaction and consistency models in databases as the database world changes. It covers the CAP theorem and how it is impossible to guarantee availability, consistency and partition tolerance simultaneously in an asynchronous distributed system. It then discusses various consistency models including eventual, monotonic read, and read your own writes (RYOW). Examples are provided of eventually consistent systems. The document also discusses Amazon Dynamo's consistency model and how MongoDB supports different consistency levels and strategies for handling transactions and writes in distributed systems.