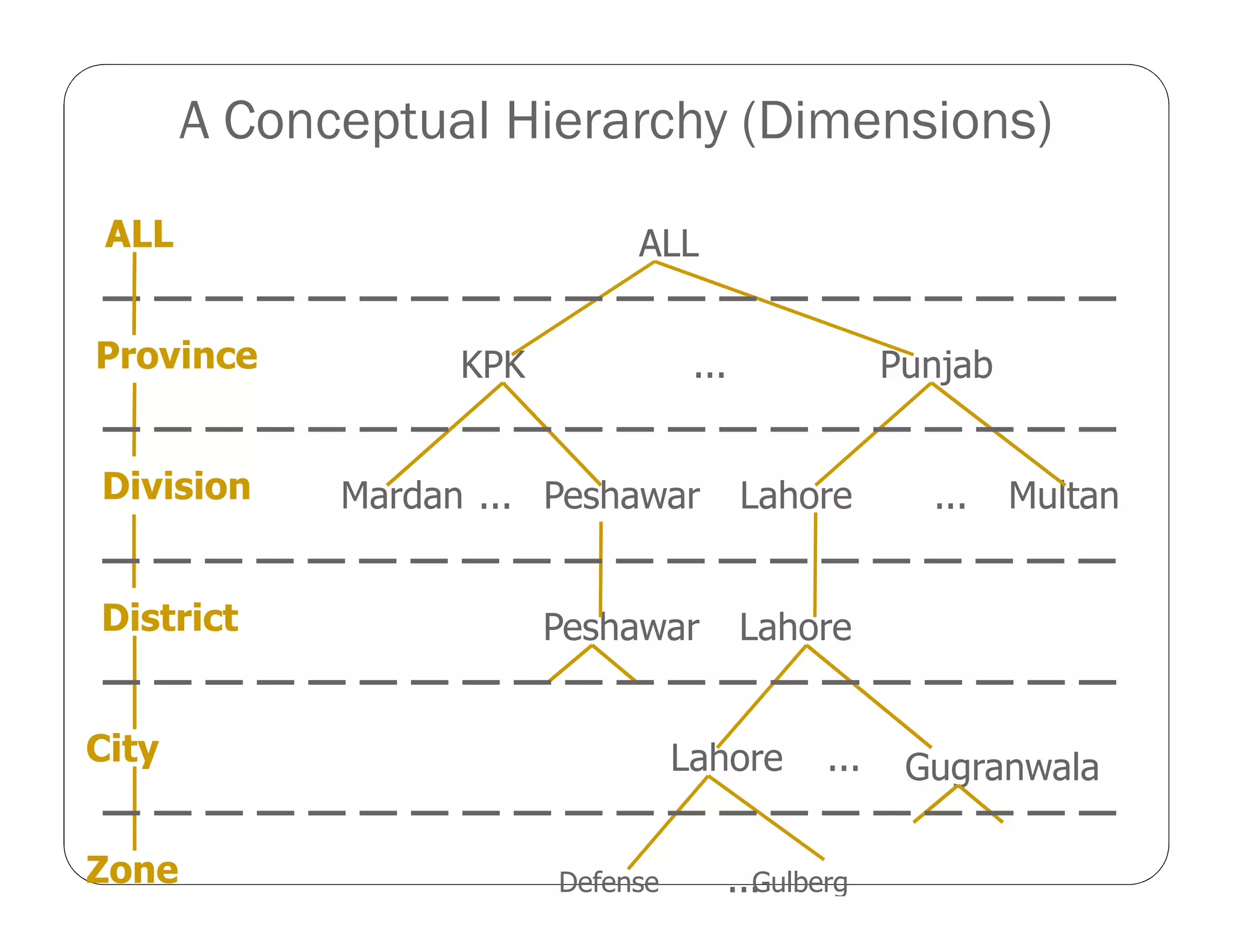
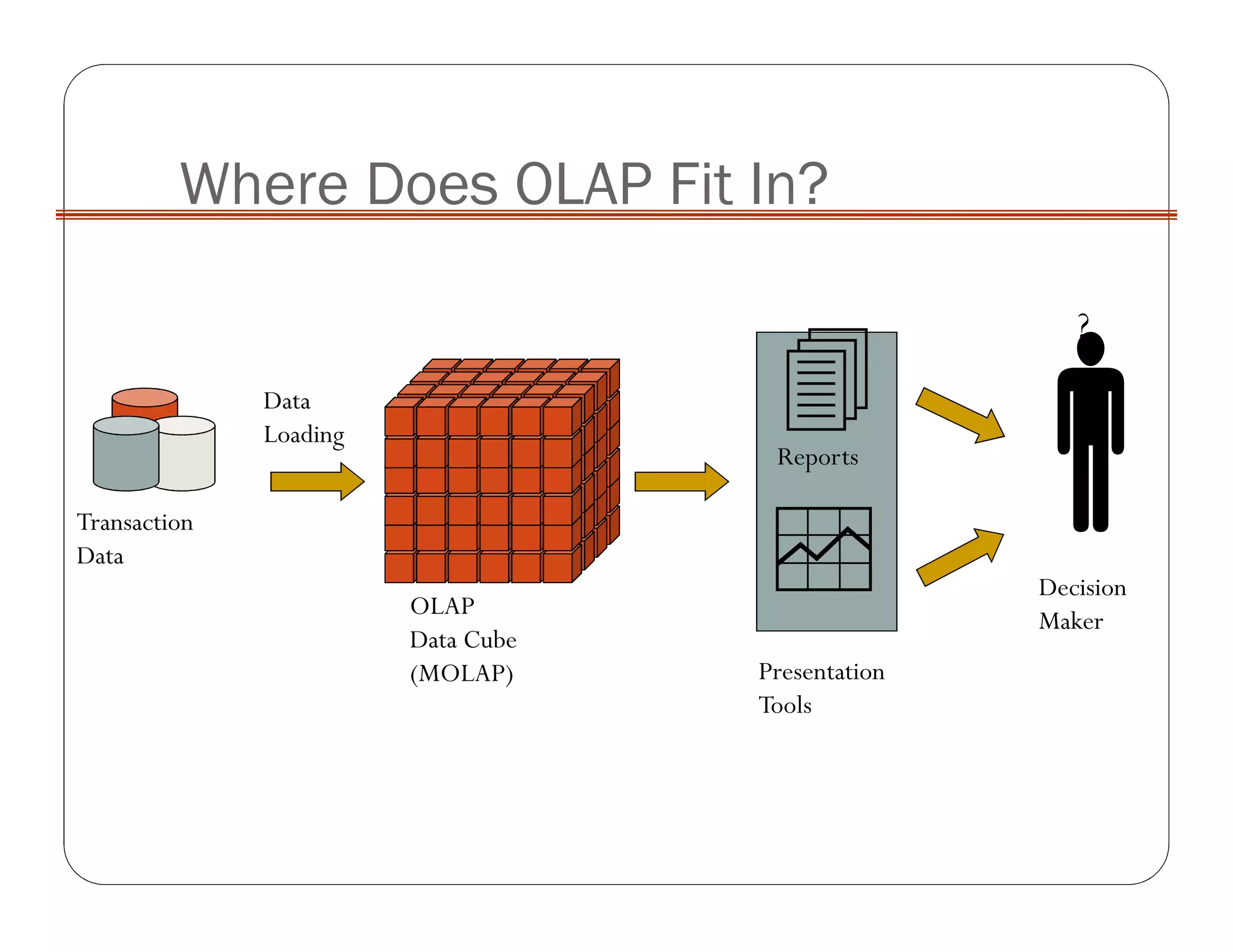
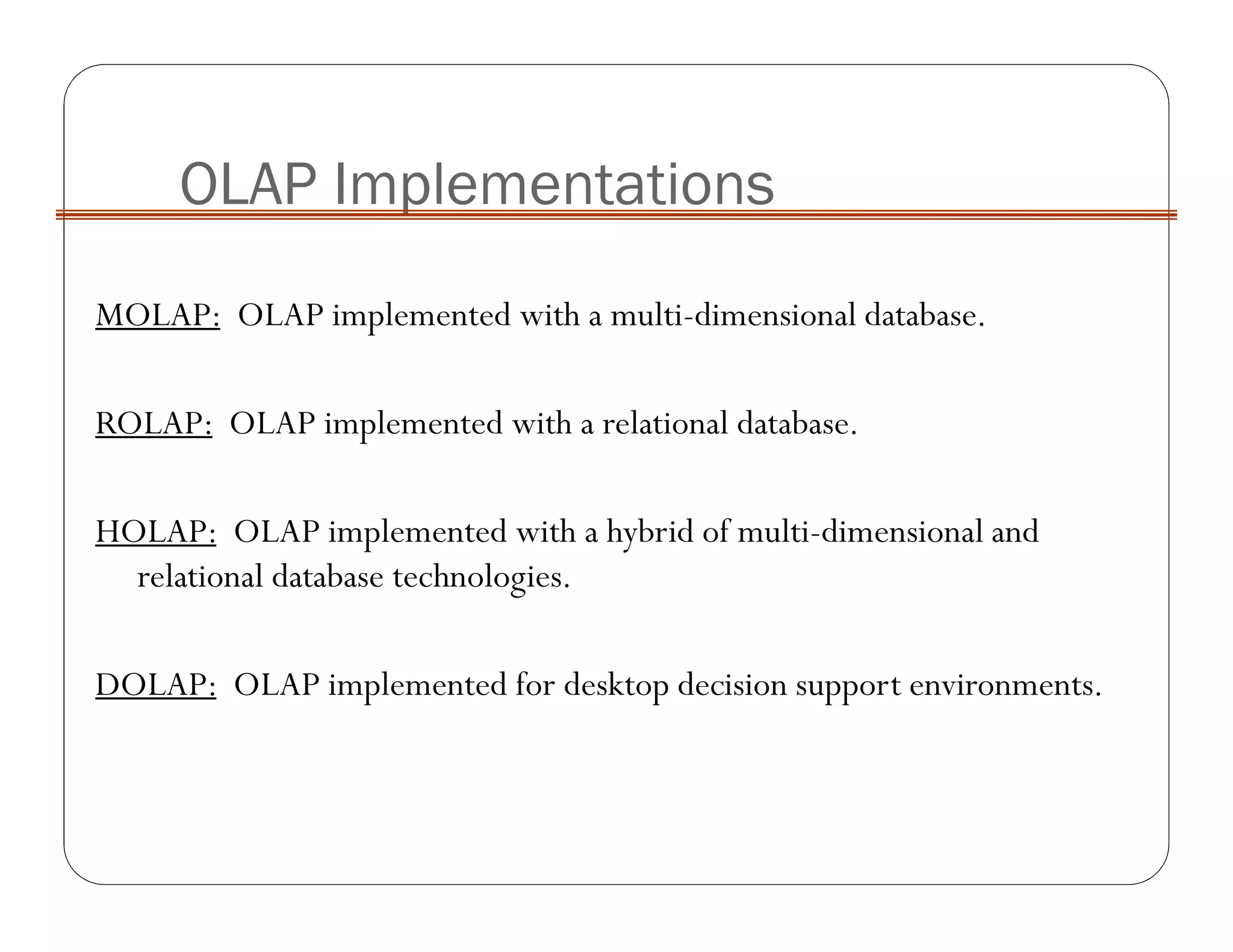
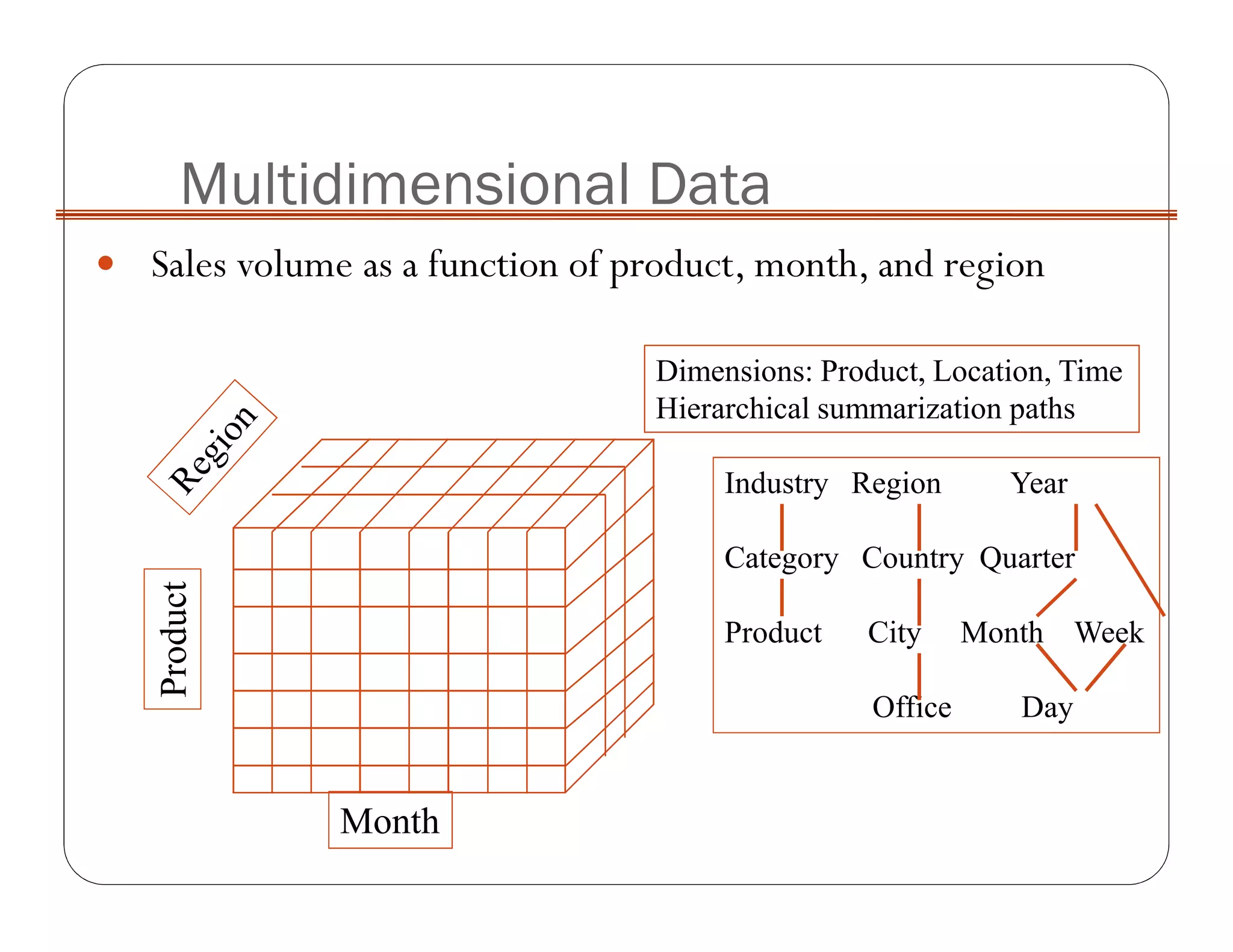
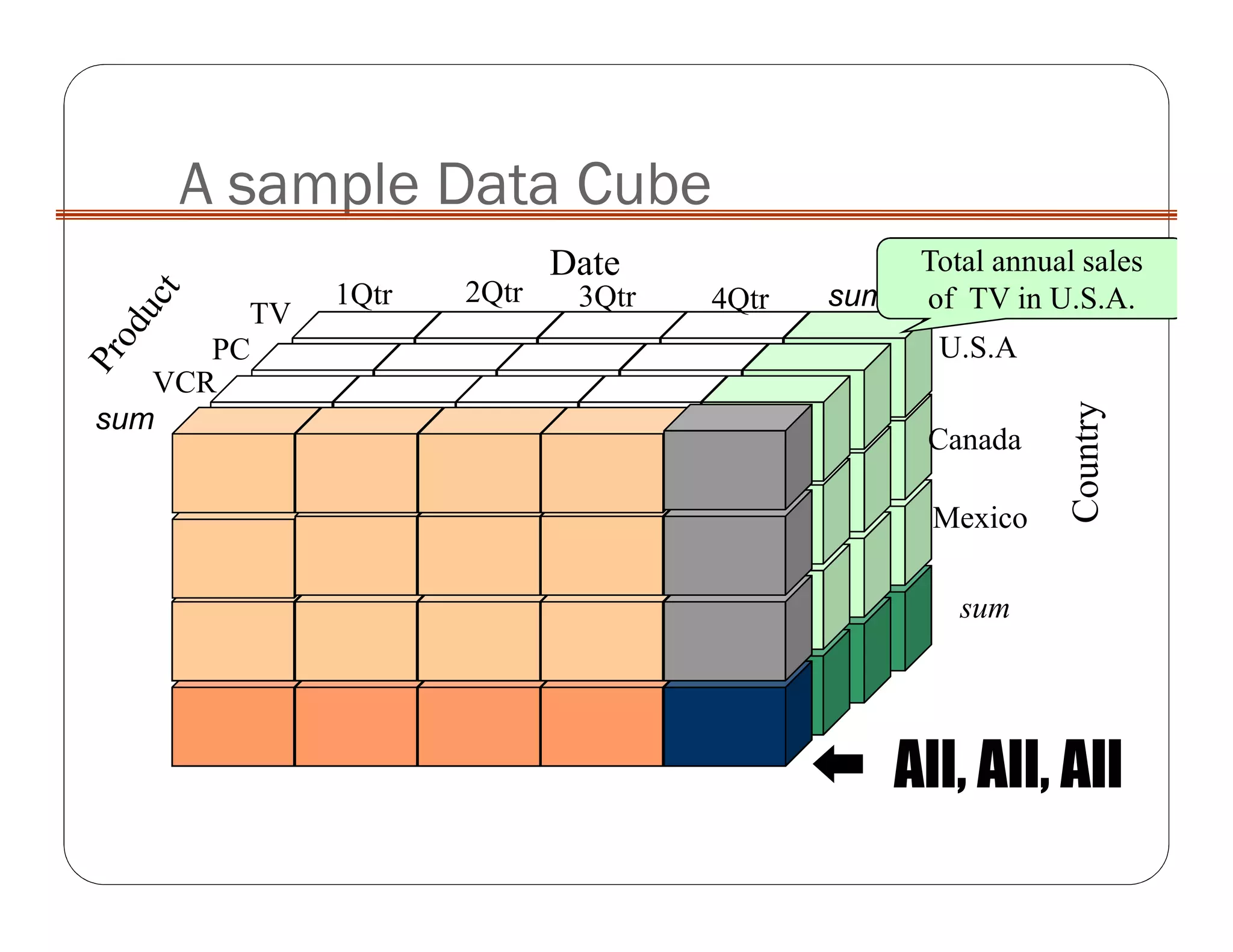
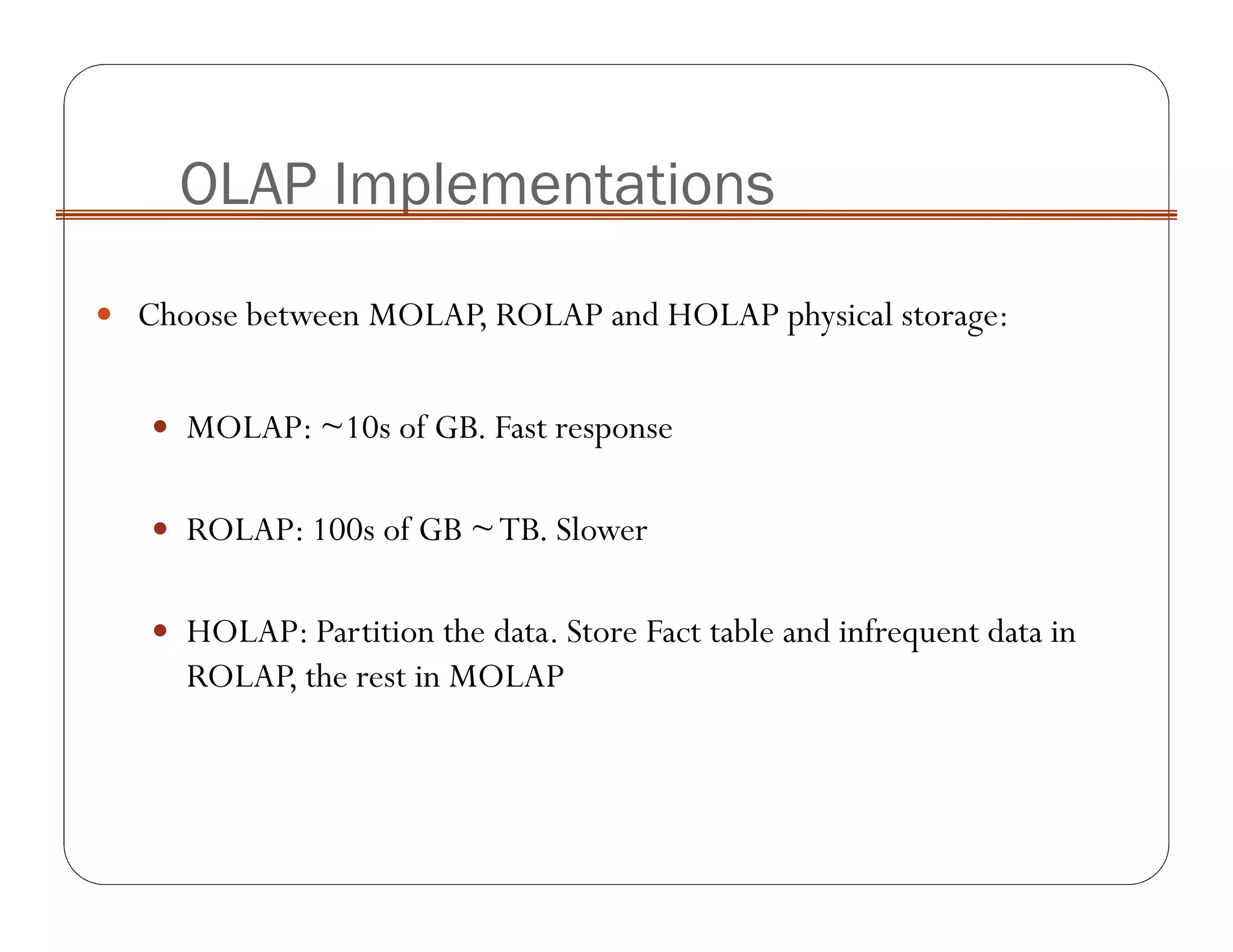
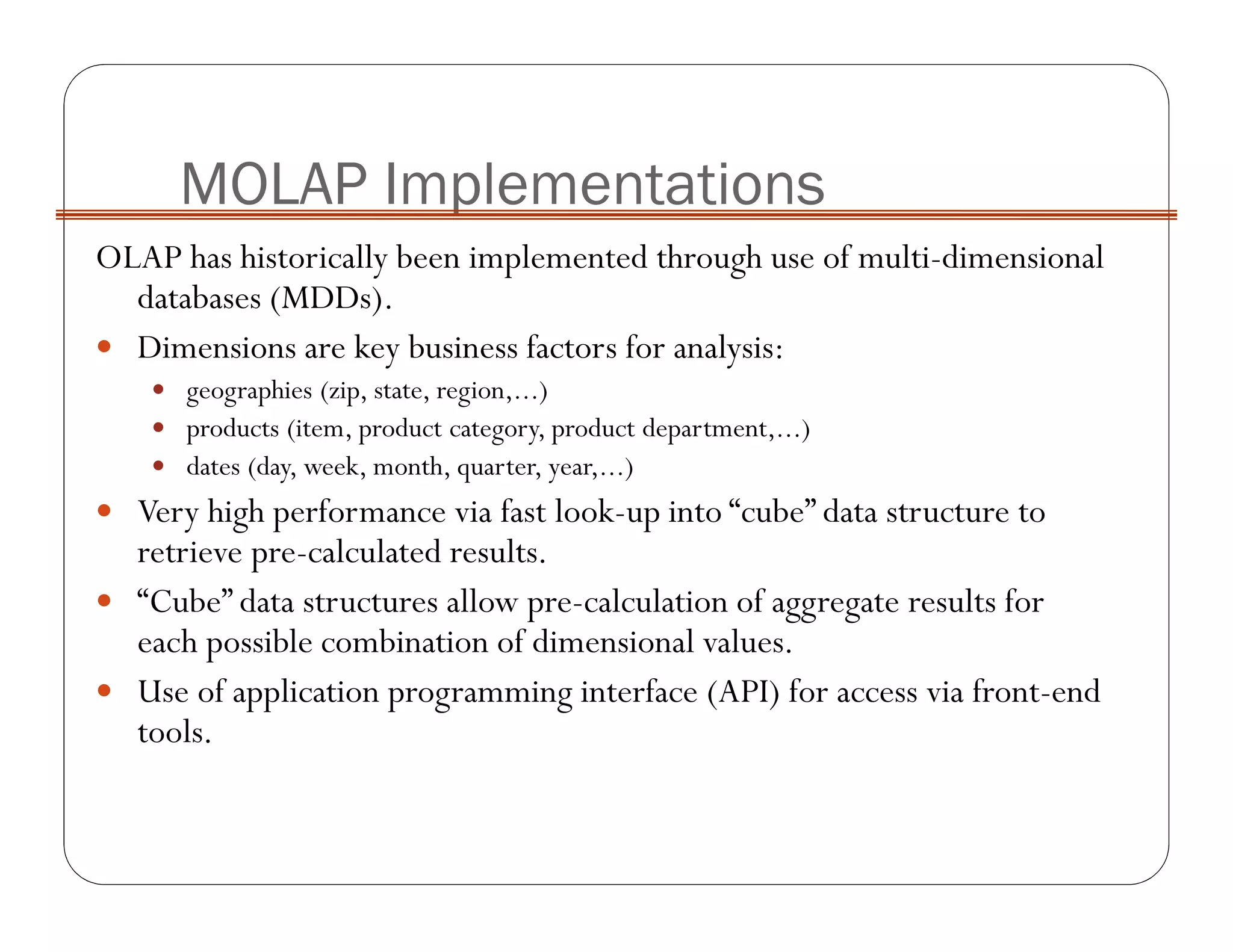
OLAP implementation techniques include MOLAP, ROLAP, HOLAP, and DOLAP. MOLAP implements OLAP using a multi-dimensional database with pre-calculated results stored in cube data structures for very fast retrieval. ROLAP uses a relational database, which can store larger volumes of data but provides slower response. HOLAP is a hybrid approach that partitions data between MOLAP and ROLAP.