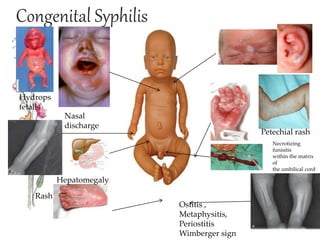
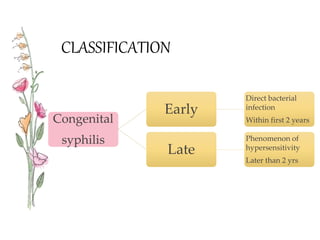
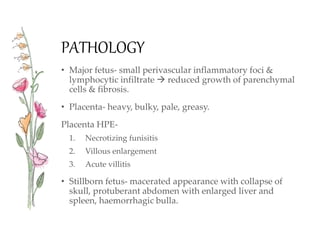
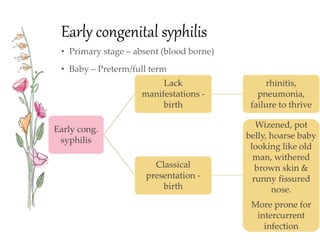
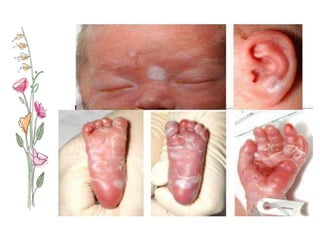
Congenital syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease transmitted from mother to fetus that can cause serious long term effects if left untreated. It is classified as either early or late disease, with early disease presenting within the first 2 years of life with symptoms like rash, fever, nasal discharge, and hepatitis. Late disease presents after 2 years with signs of damage to organs like the eyes, bones, and nervous system. Diagnosis involves tests of the mother and child along with examinations. Treatment is with intravenous penicillin or erythromycin antibiotics to prevent disability or death in the infant from this untreated infection.