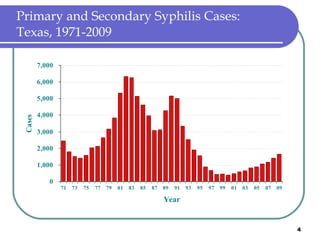
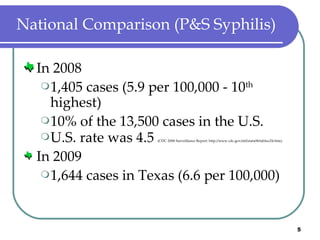
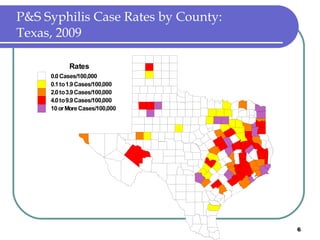
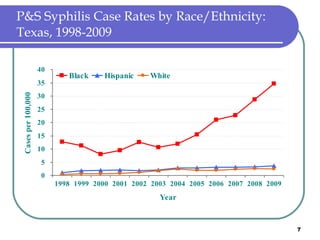
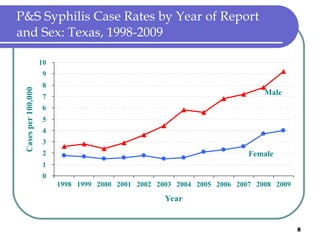
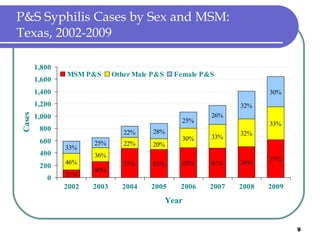
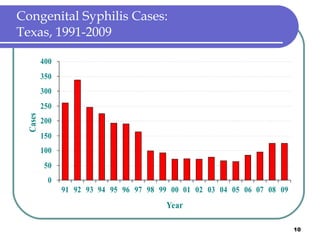
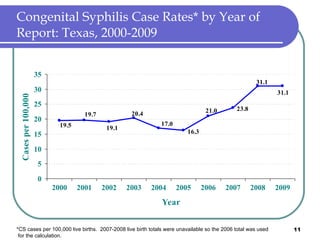
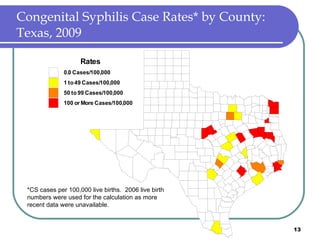
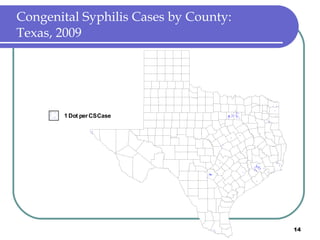
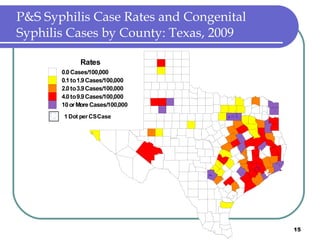
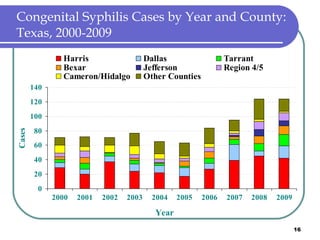
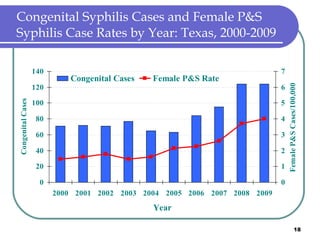
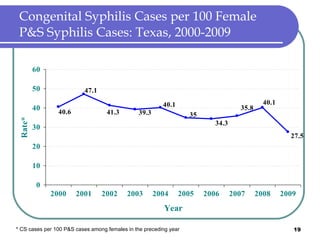
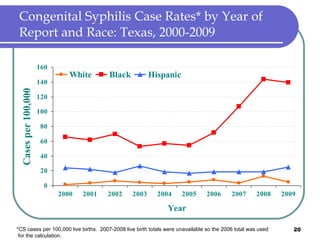
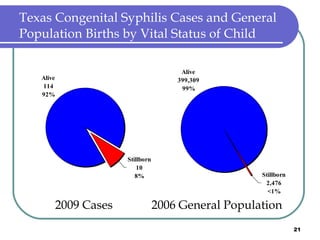
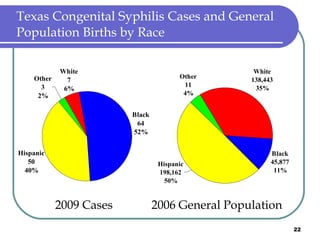
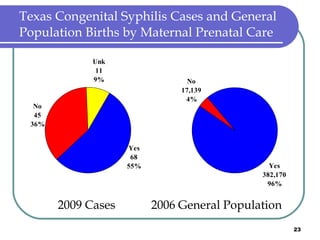
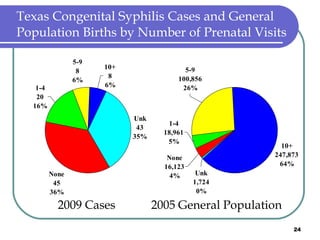
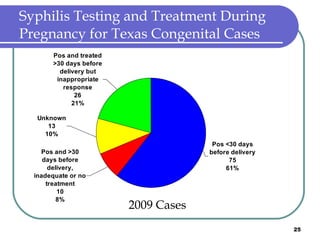
Congenital syphilis occurs when a pregnant woman with syphilis passes the infection to her fetus. If untreated, it can cause stillbirth, neonatal death, deafness, neurological impairment, or bone deformities in the infant. The document discusses epidemiological data on congenital syphilis and syphilis cases in Texas from 1991-2009 which show high rates compared to national levels. It outlines Texas' plan to reduce congenital syphilis cases by 25% in 5 years through improved surveillance, targeting high-risk populations, promoting screening, and ensuring treatment.