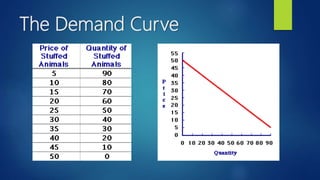
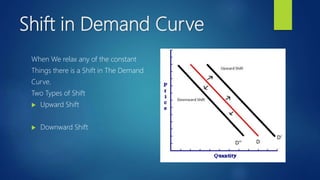
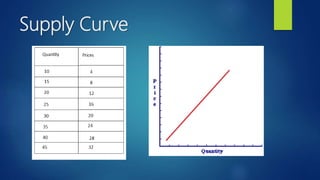
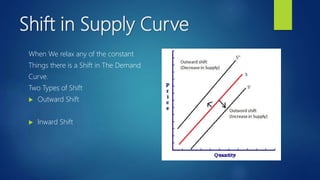
The document outlines the fundamental concepts of demand and supply, including the laws of demand and supply, the demand curve, and elasticity. It explains how various factors such as price, income, and population affect demand and supply, as well as the methods for calculating elasticities. Additionally, it describes shifts in demand and supply curves due to changing conditions.