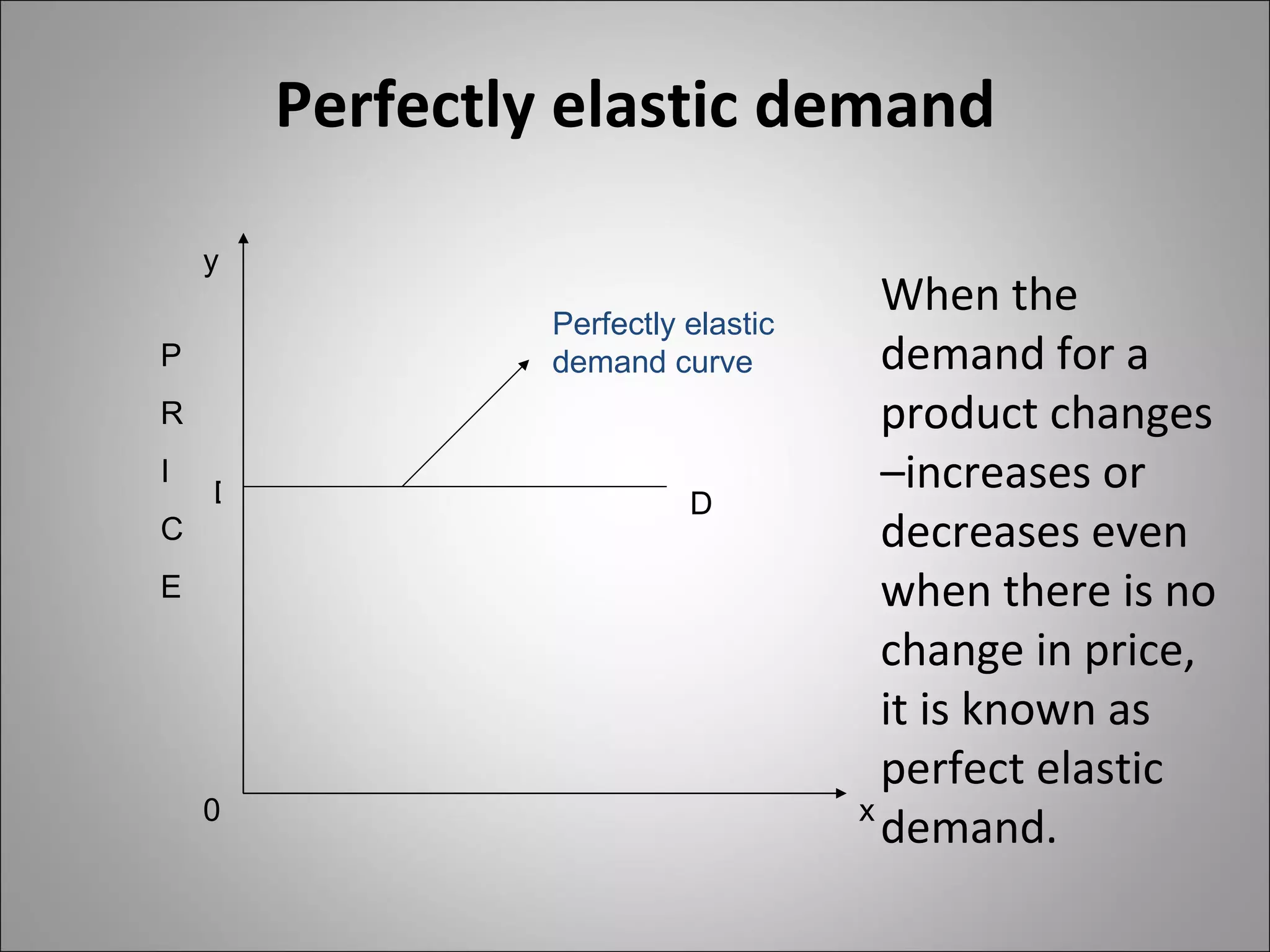
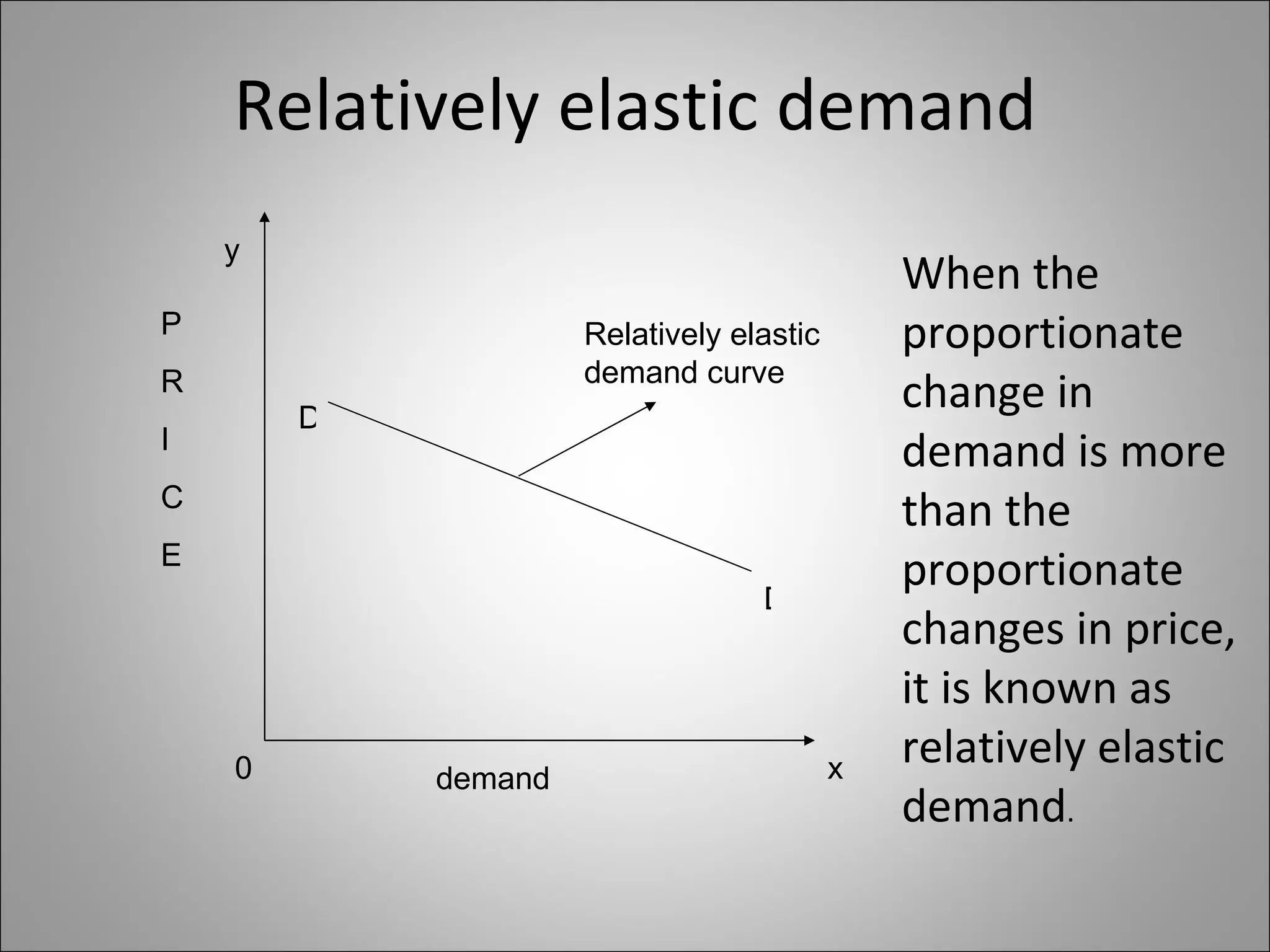
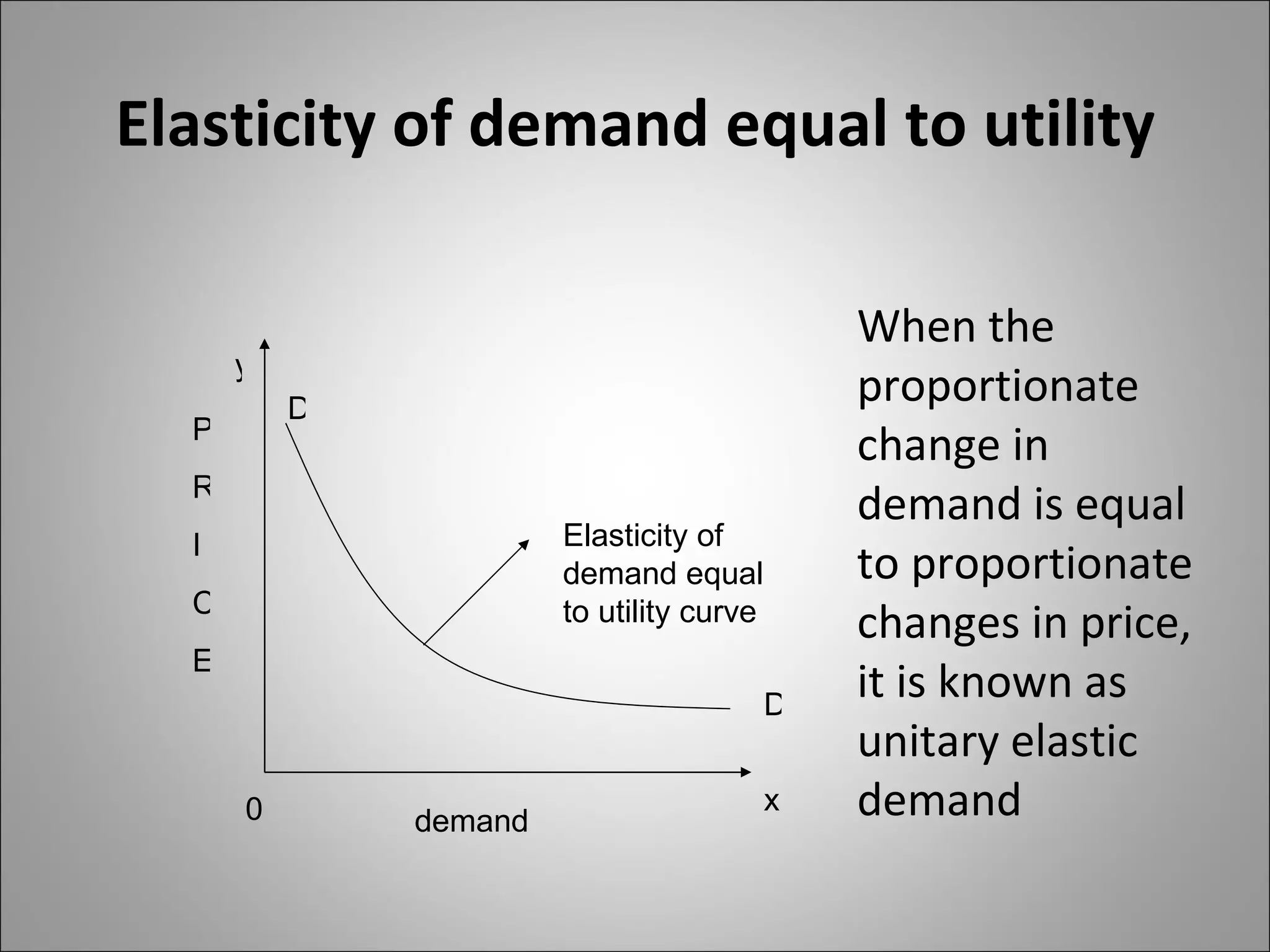
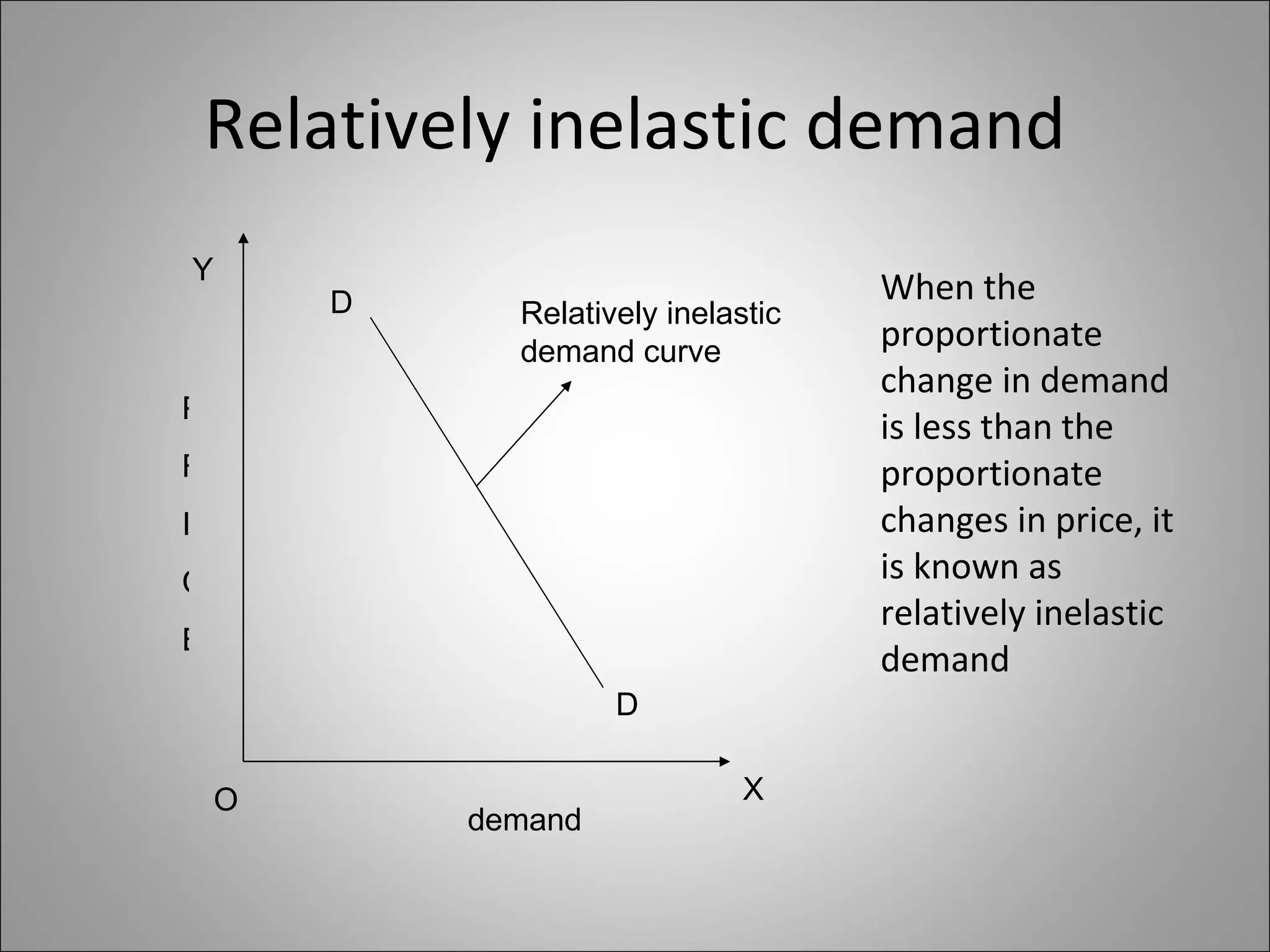
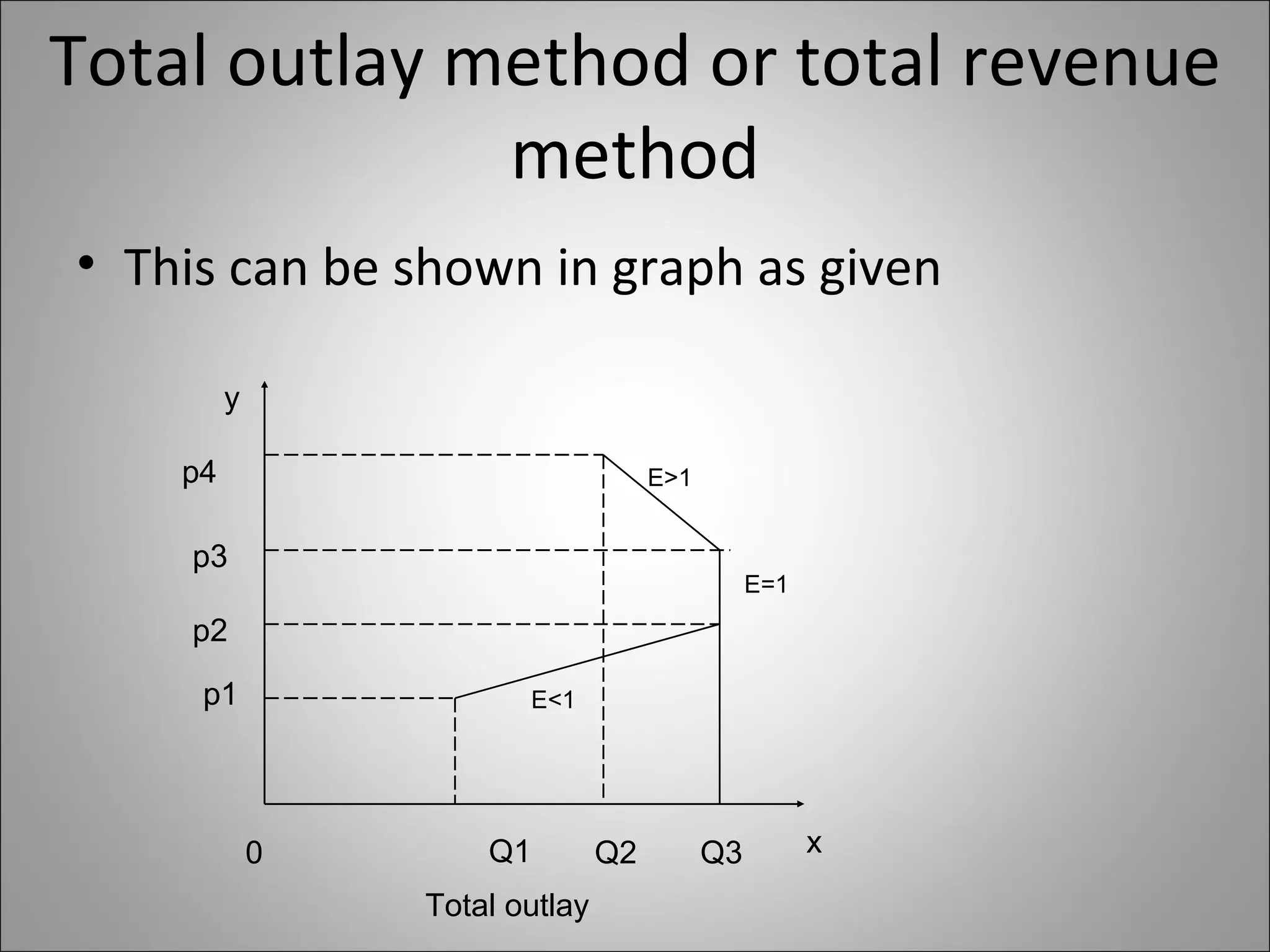
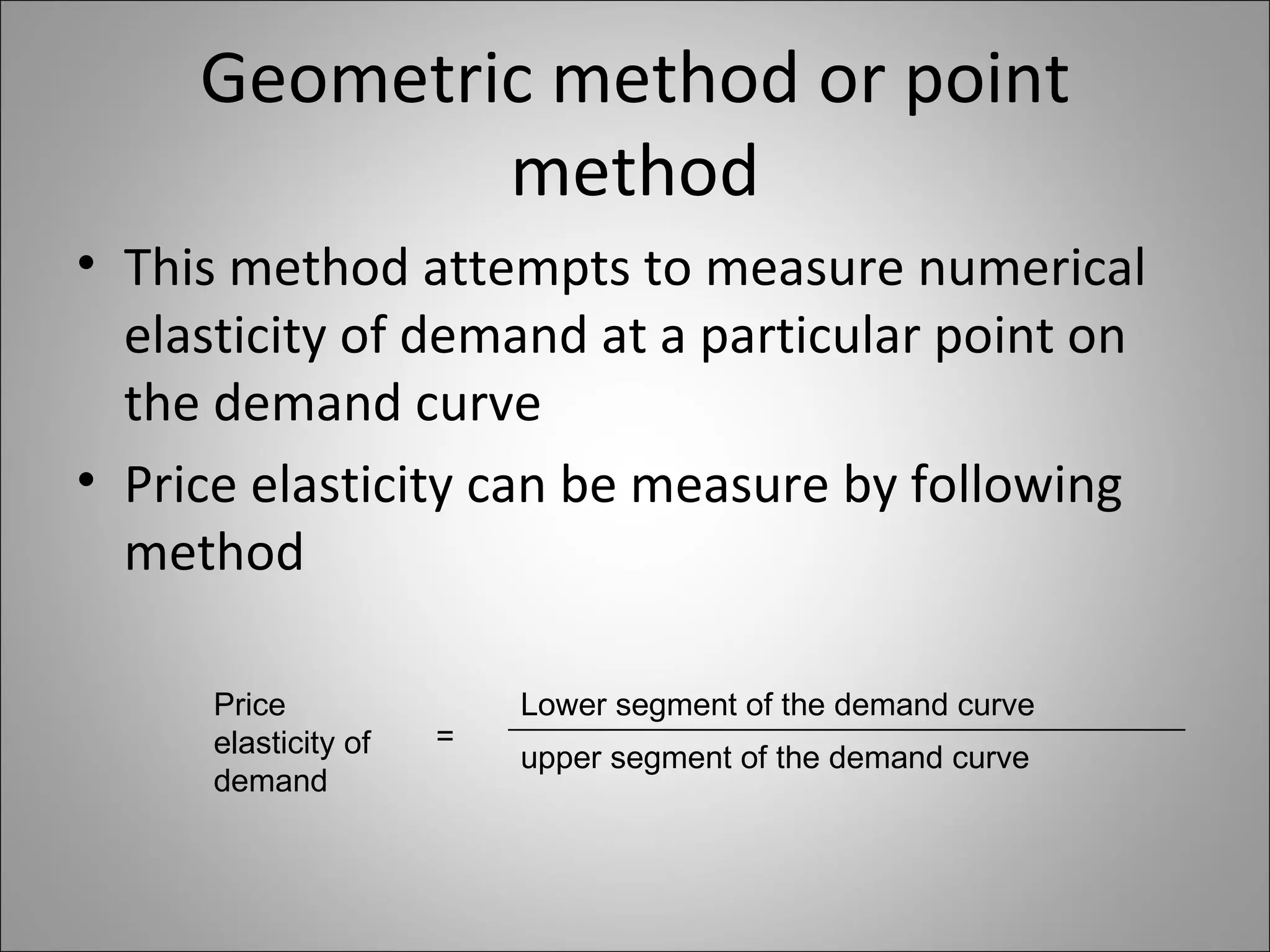
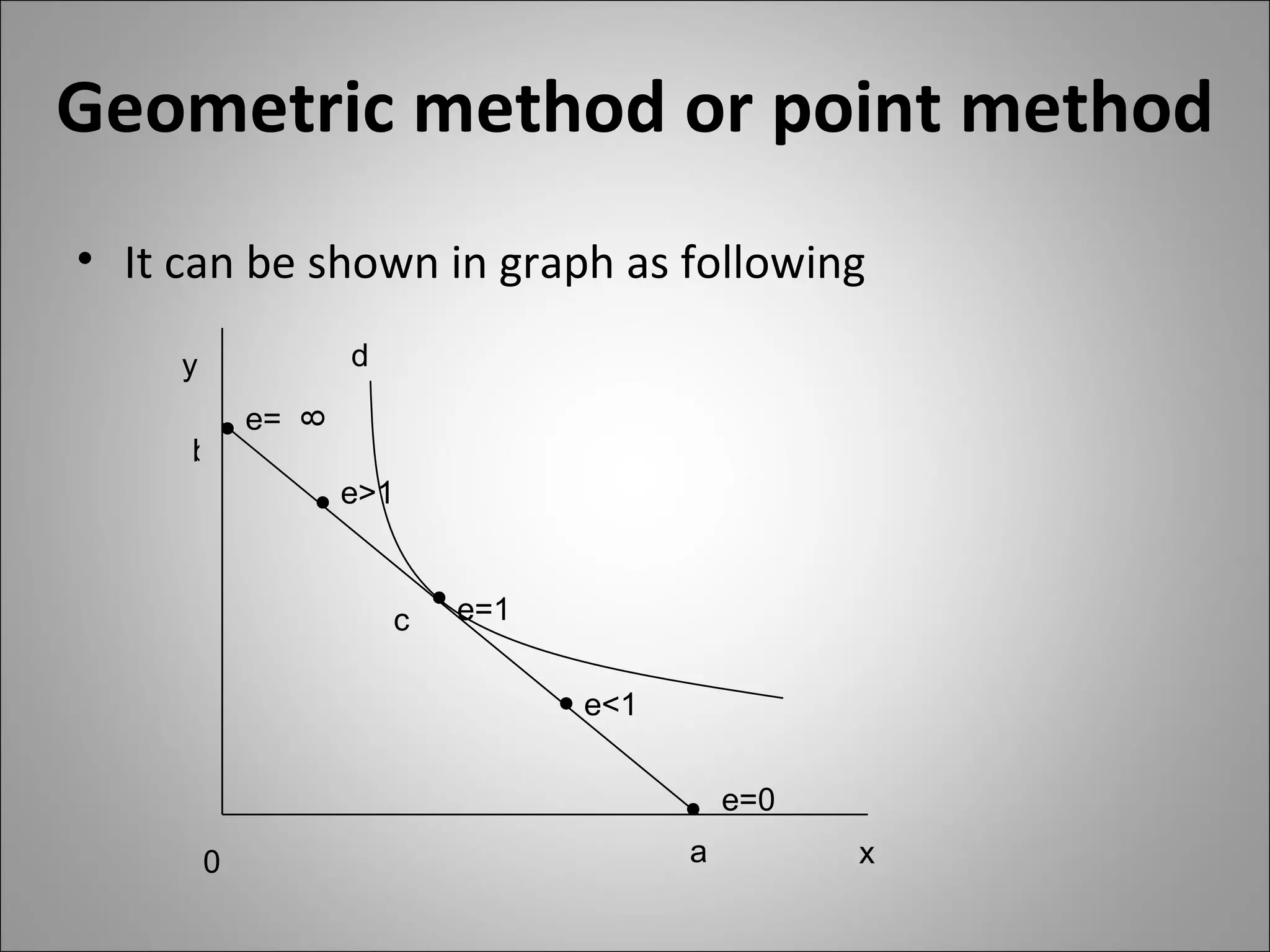
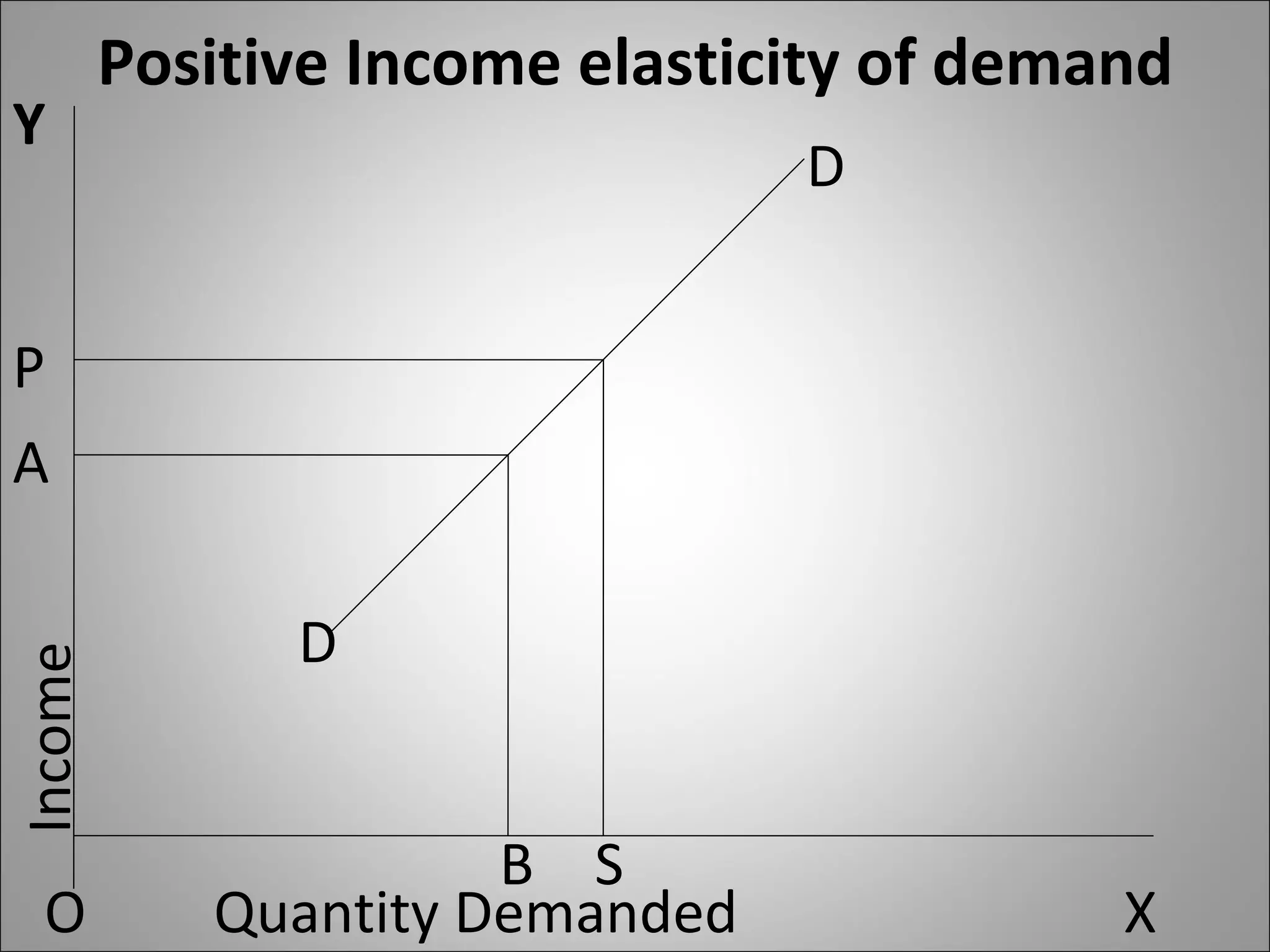
The document discusses different types of elasticity of demand including price elasticity, income elasticity, cross elasticity, substitution elasticity, and advertising elasticity. It defines each type and provides formulas for measuring elasticity. Some key points include:
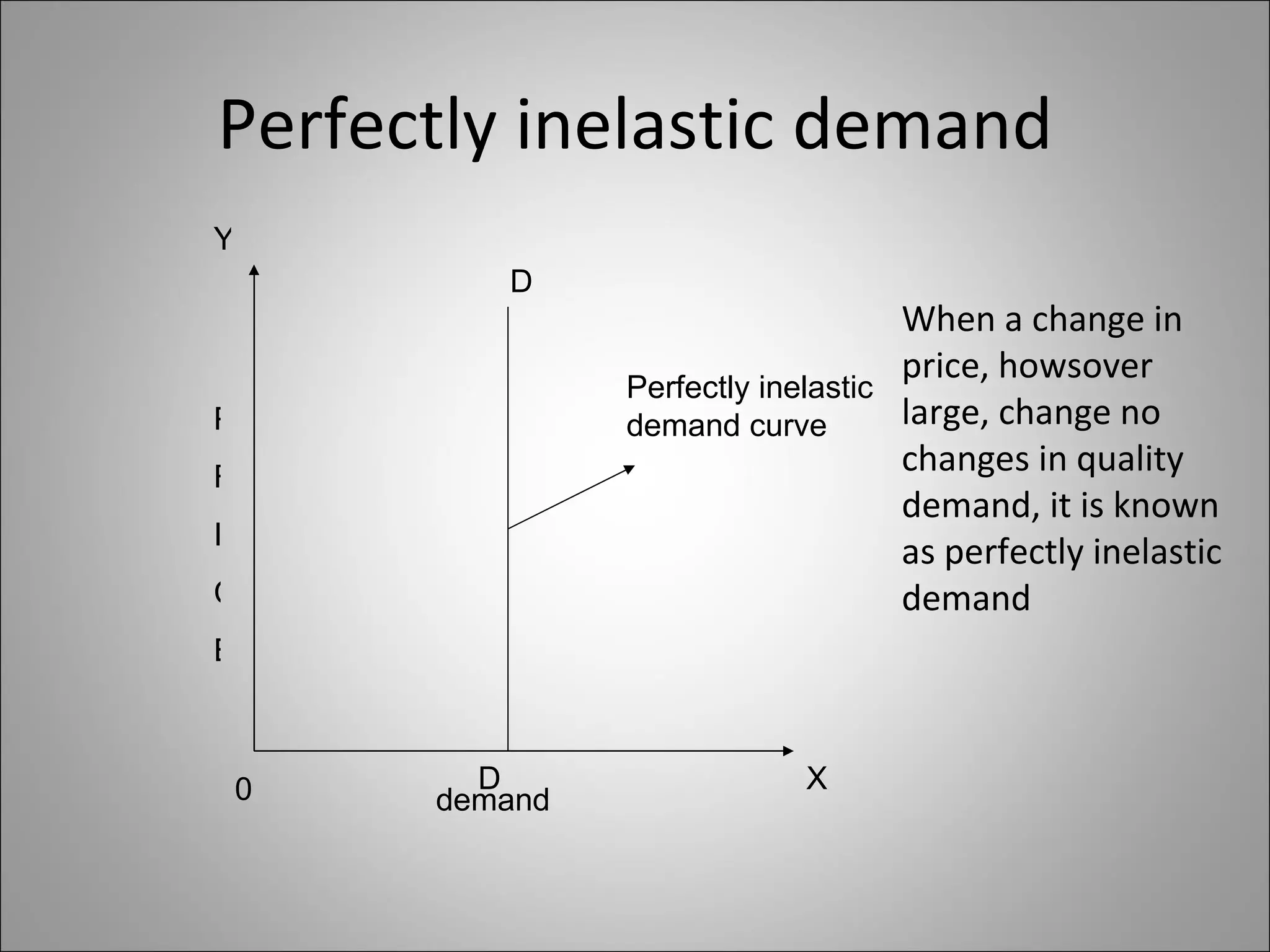
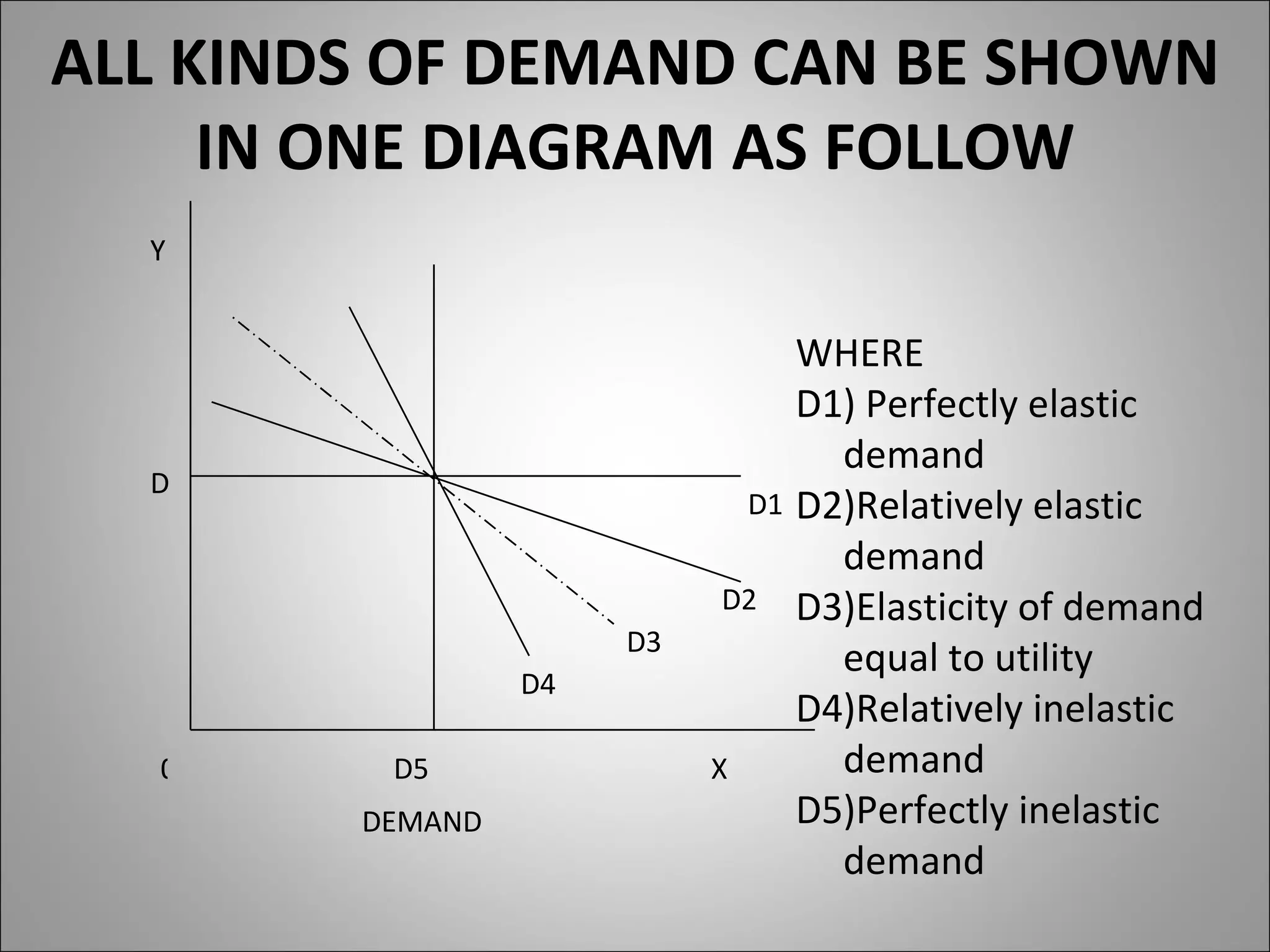
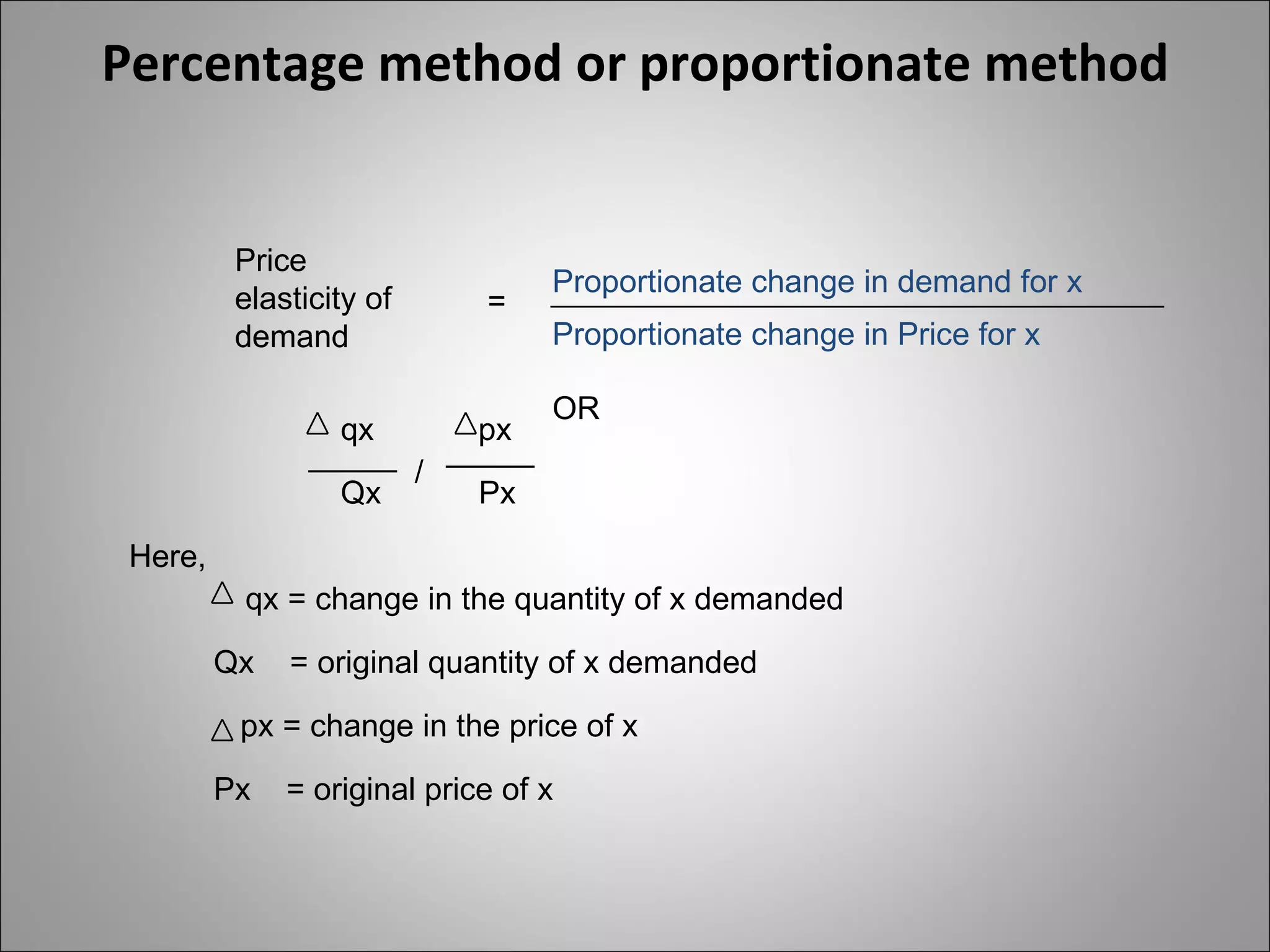
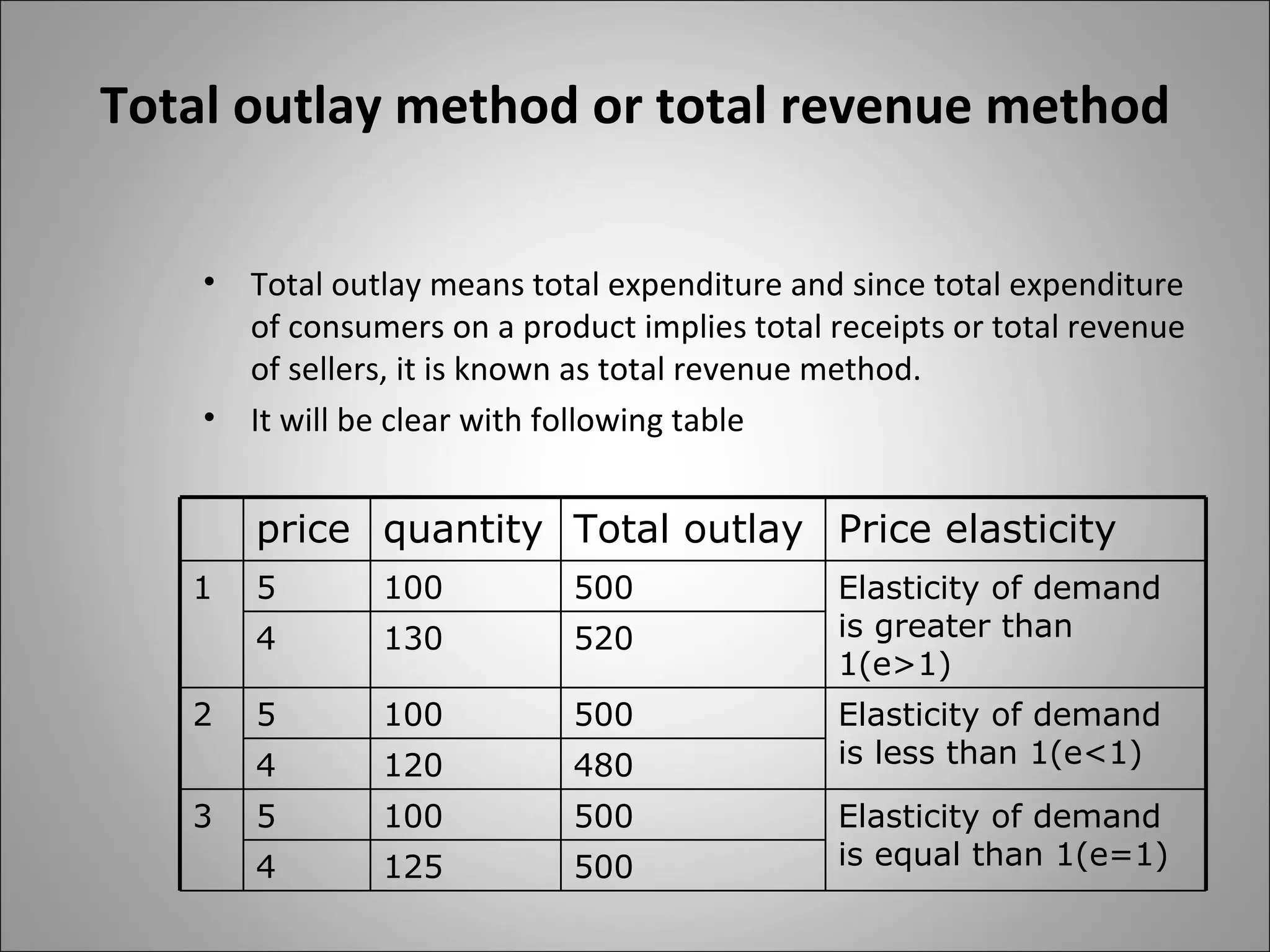
- Price elasticity measures the responsiveness of demand to a change in price. It can be perfectly elastic, unitary, or perfectly inelastic.
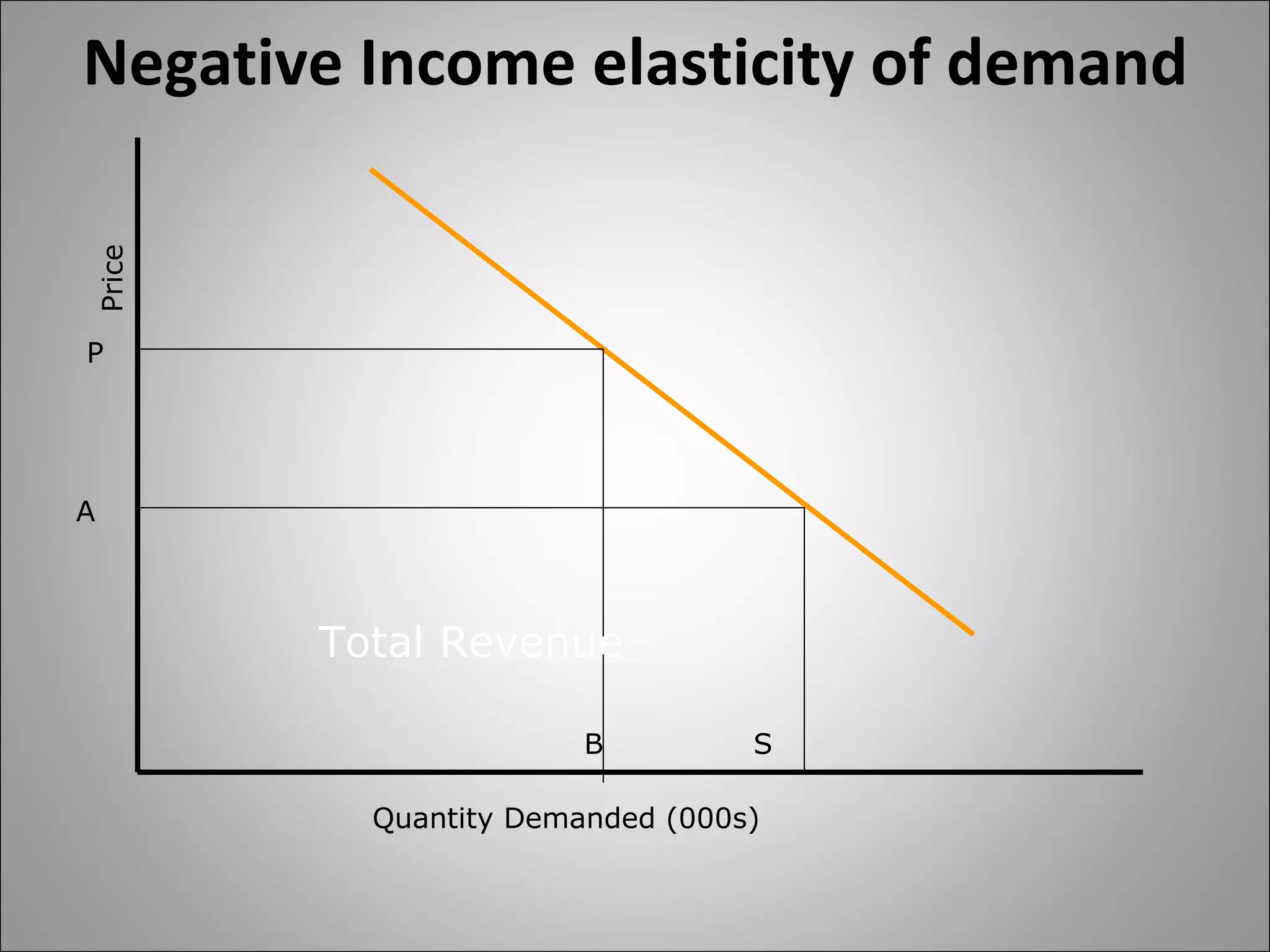
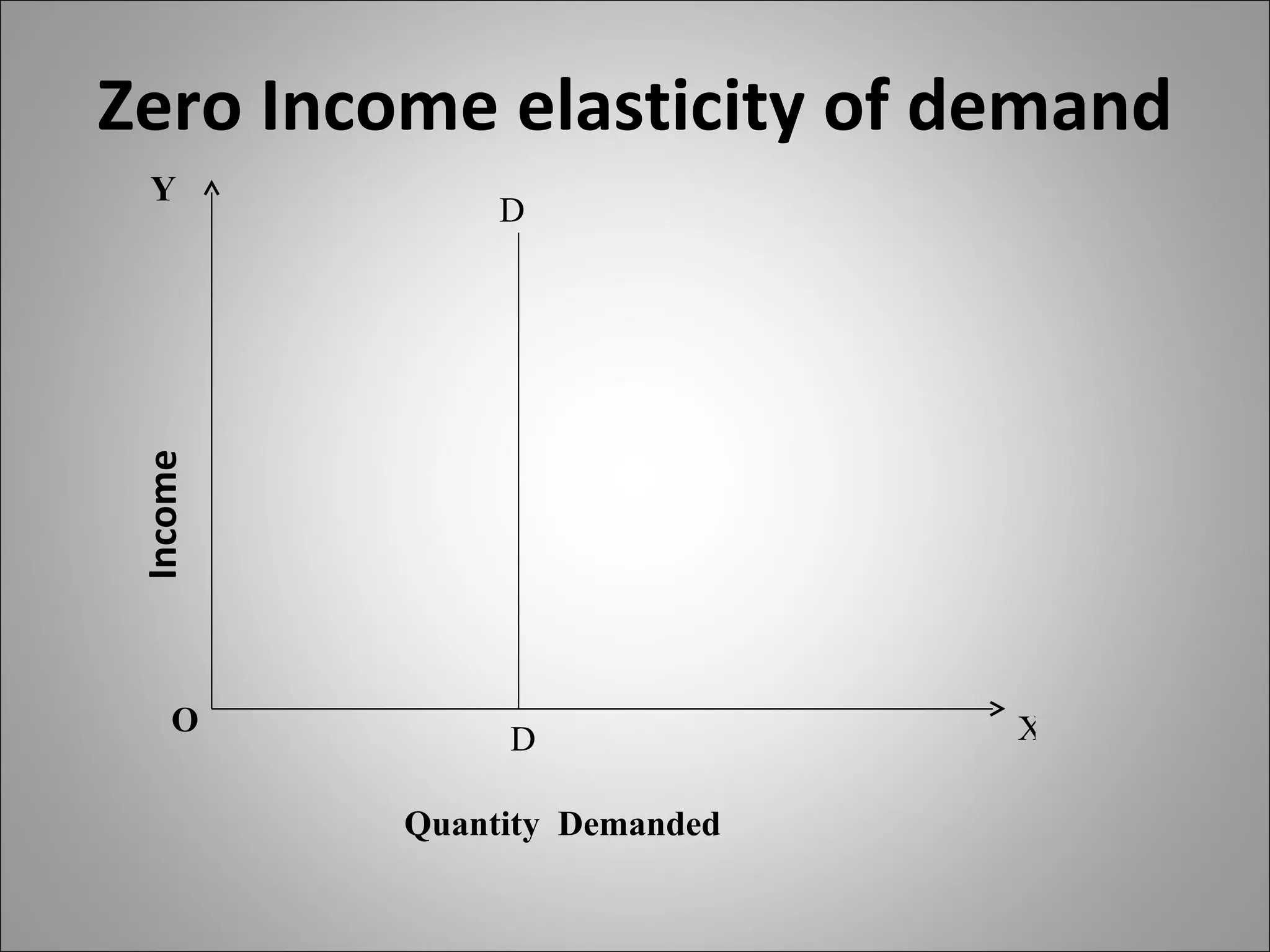
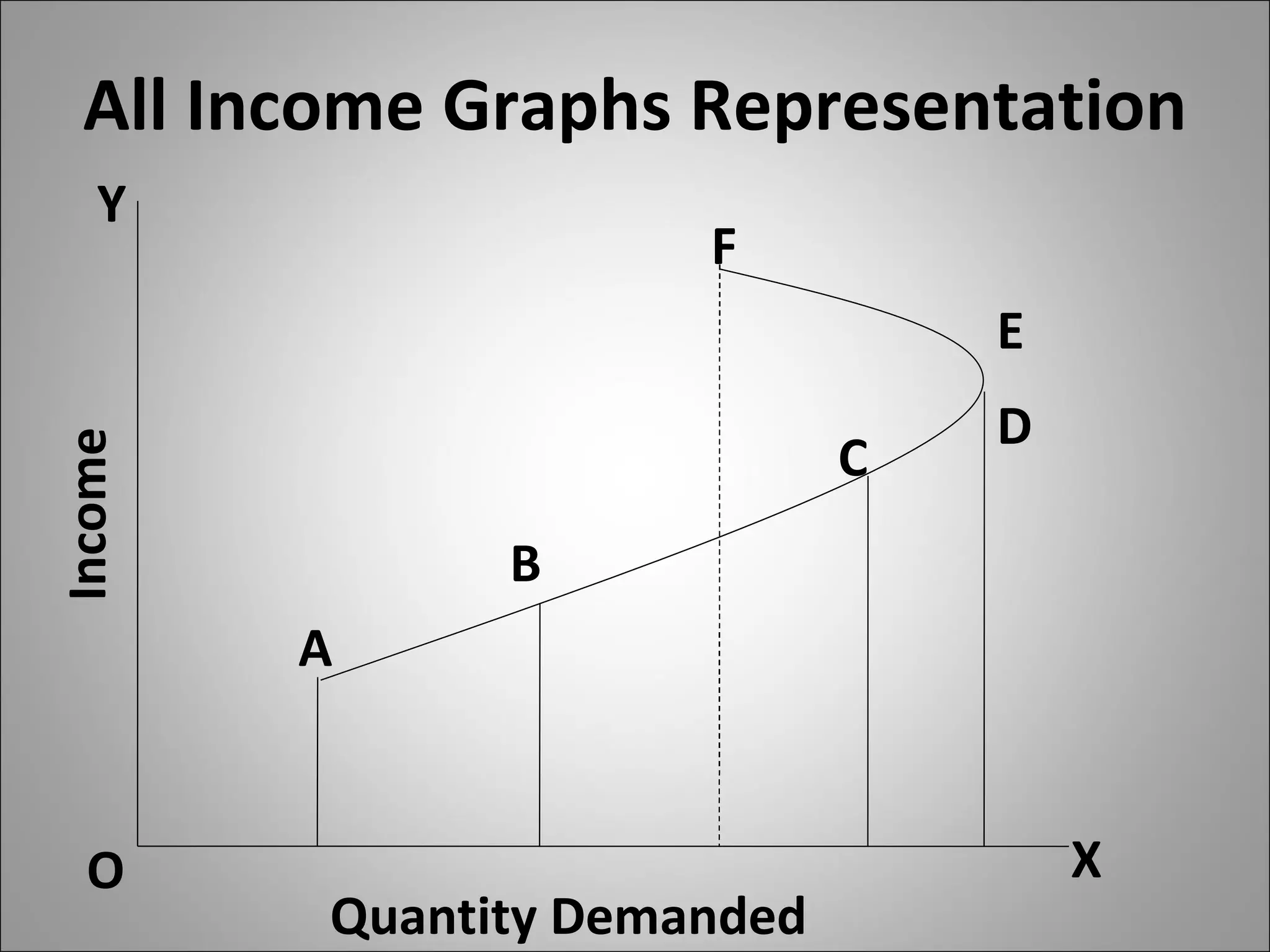
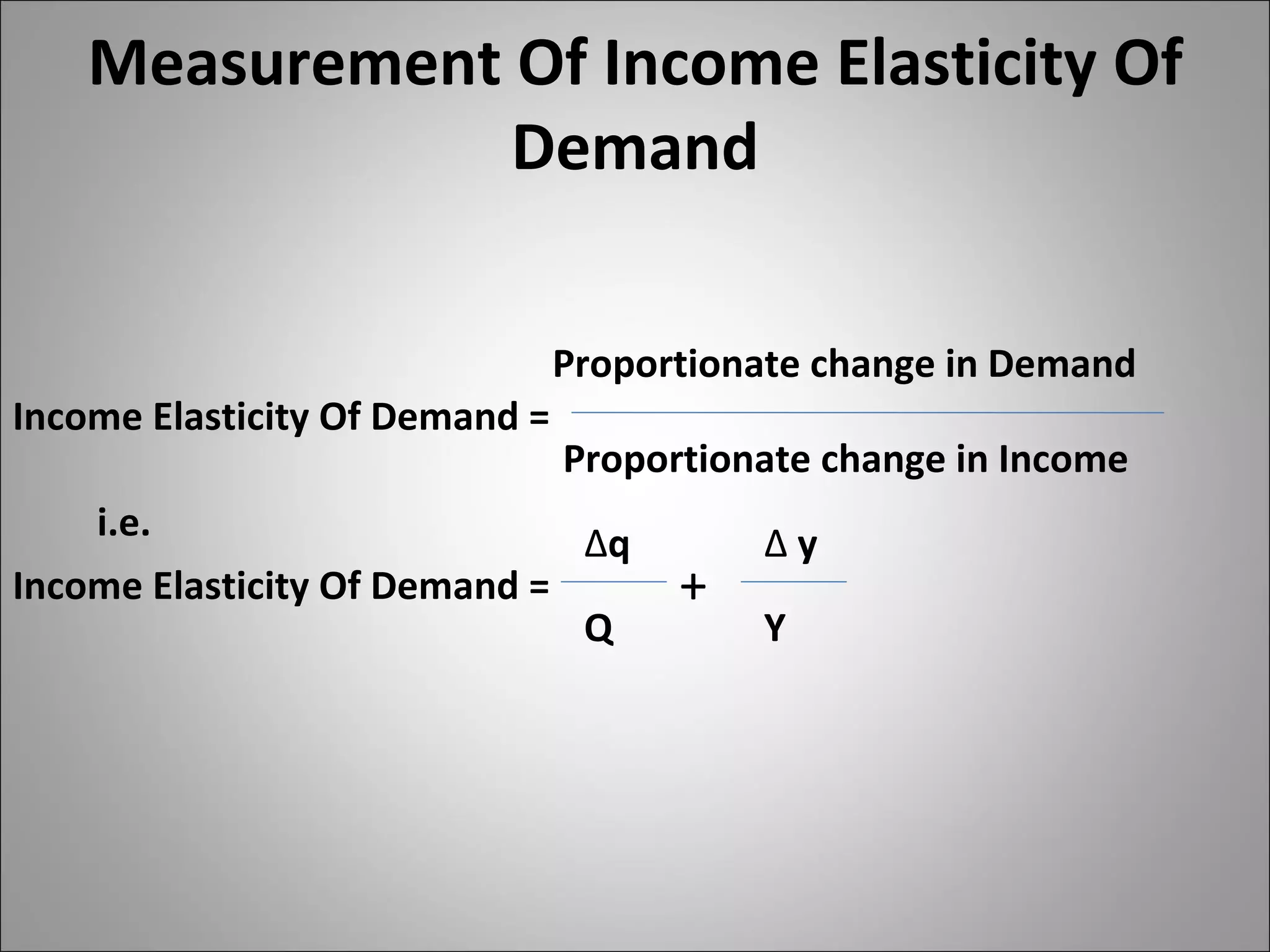
- Income elasticity indicates whether a good is a necessity or luxury based on whether demand increases or decreases with income.
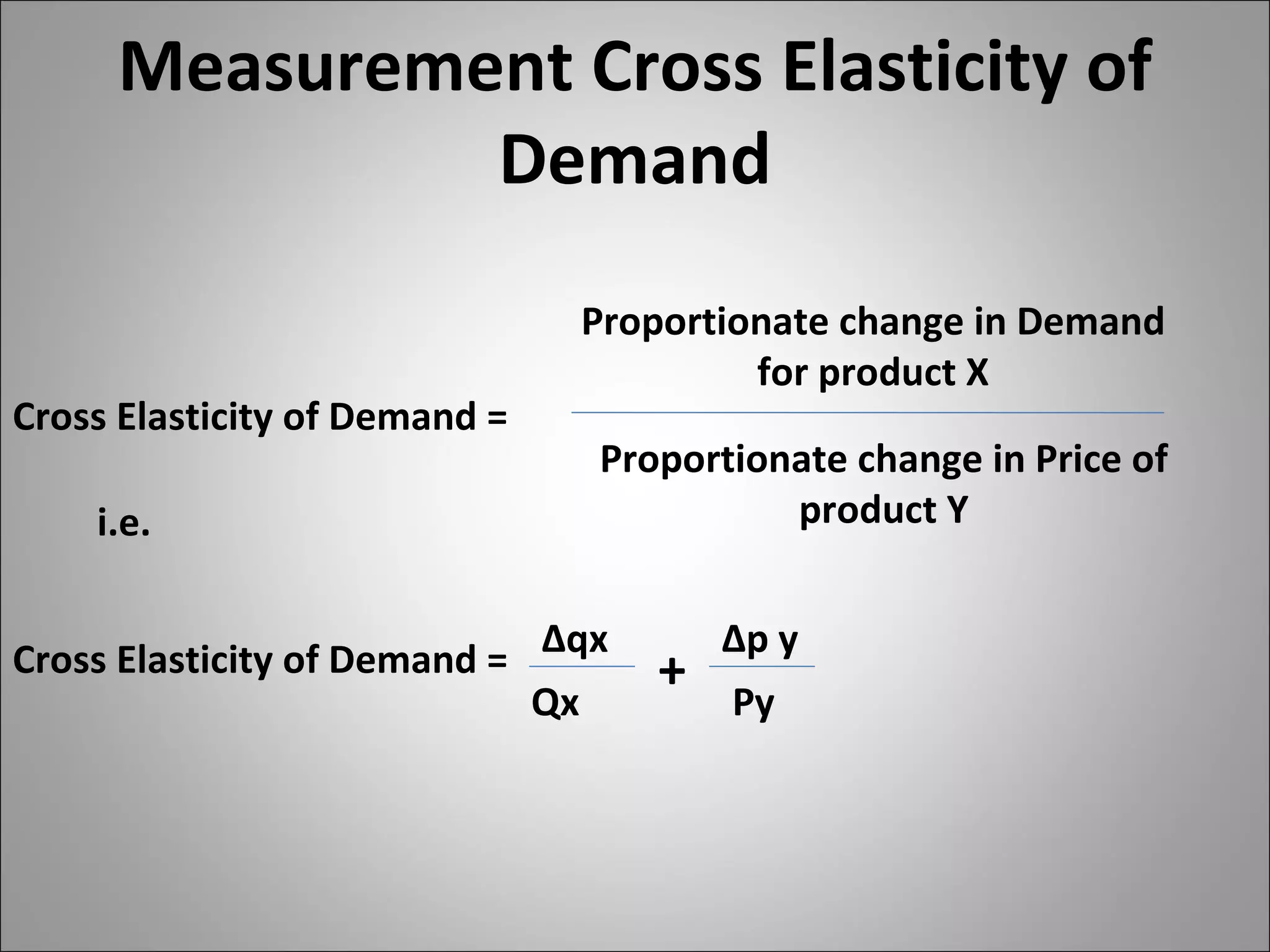
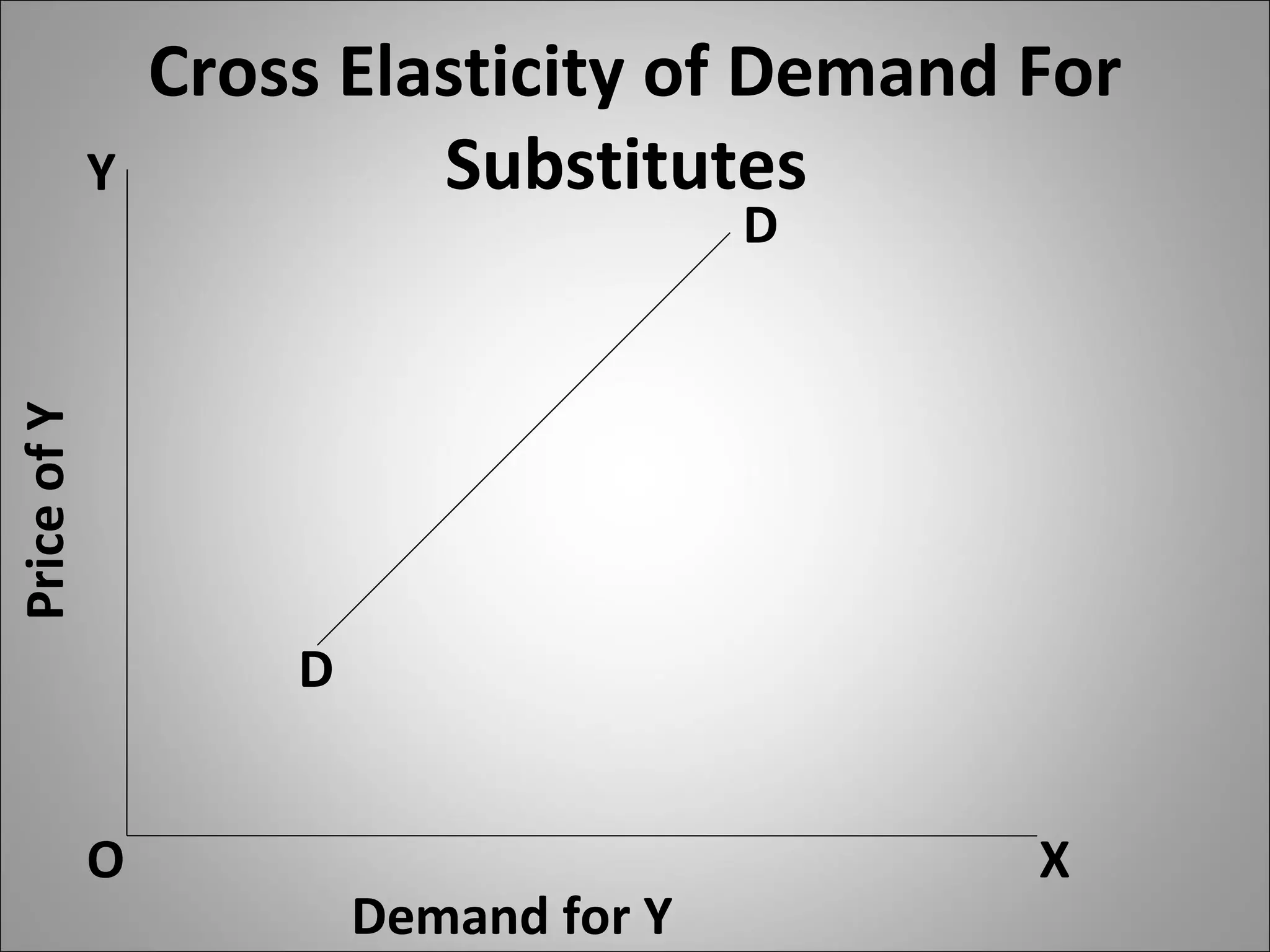
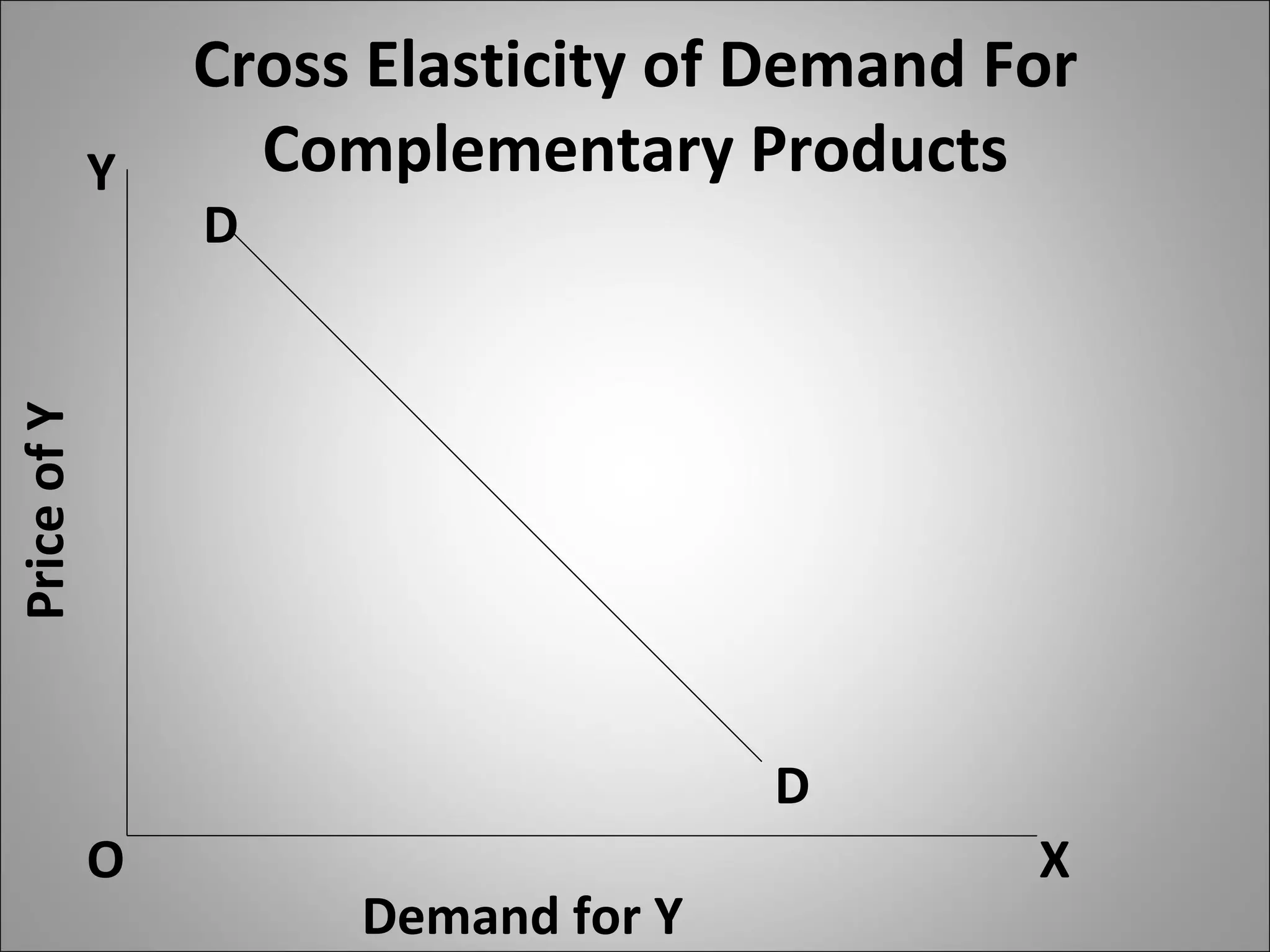
- Cross elasticity captures the relationship between the demand for one good and the price of another good, such as substitutes or complements.
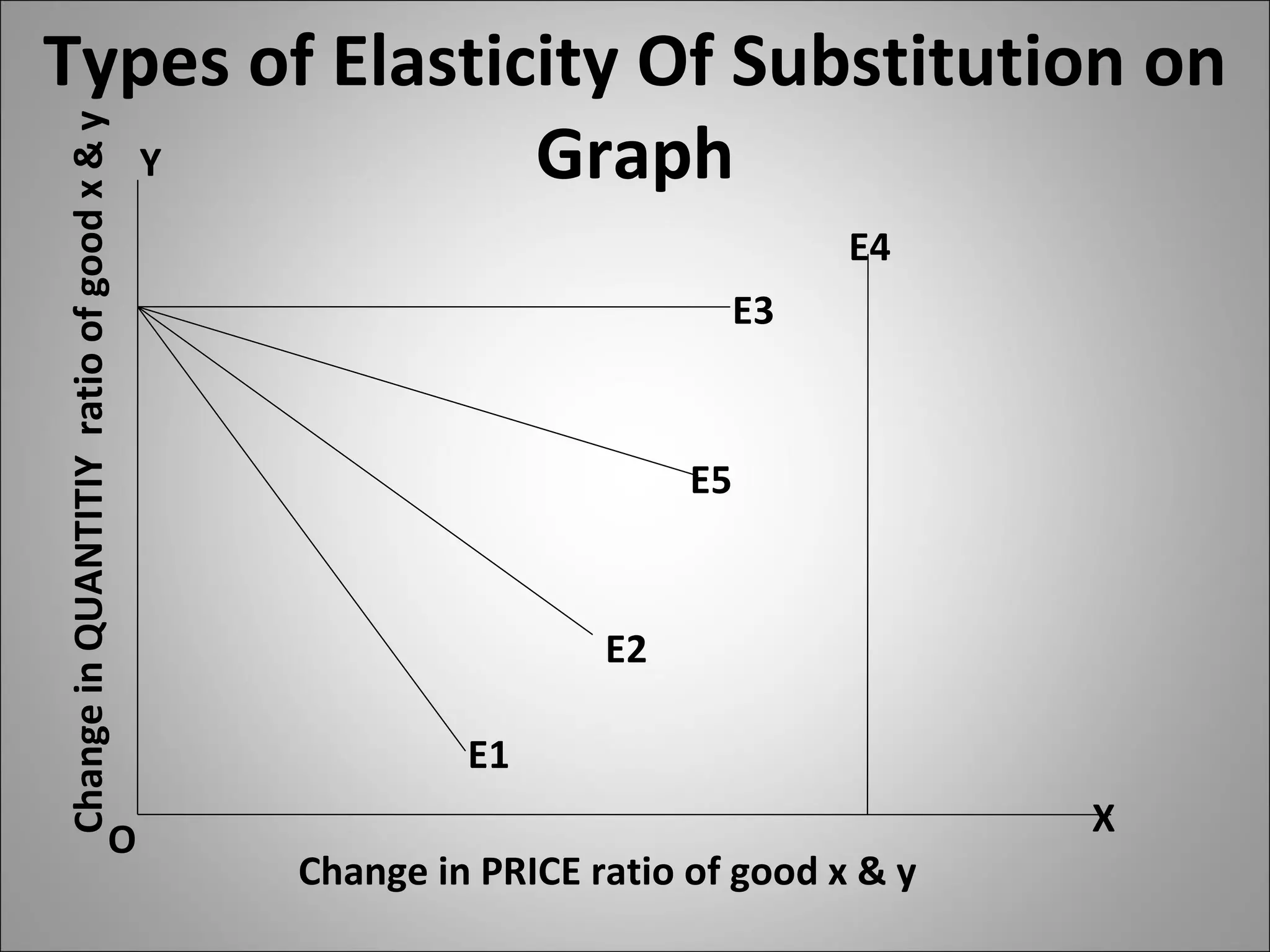
- Substitution elasticity measures how easily consumers can substitute one