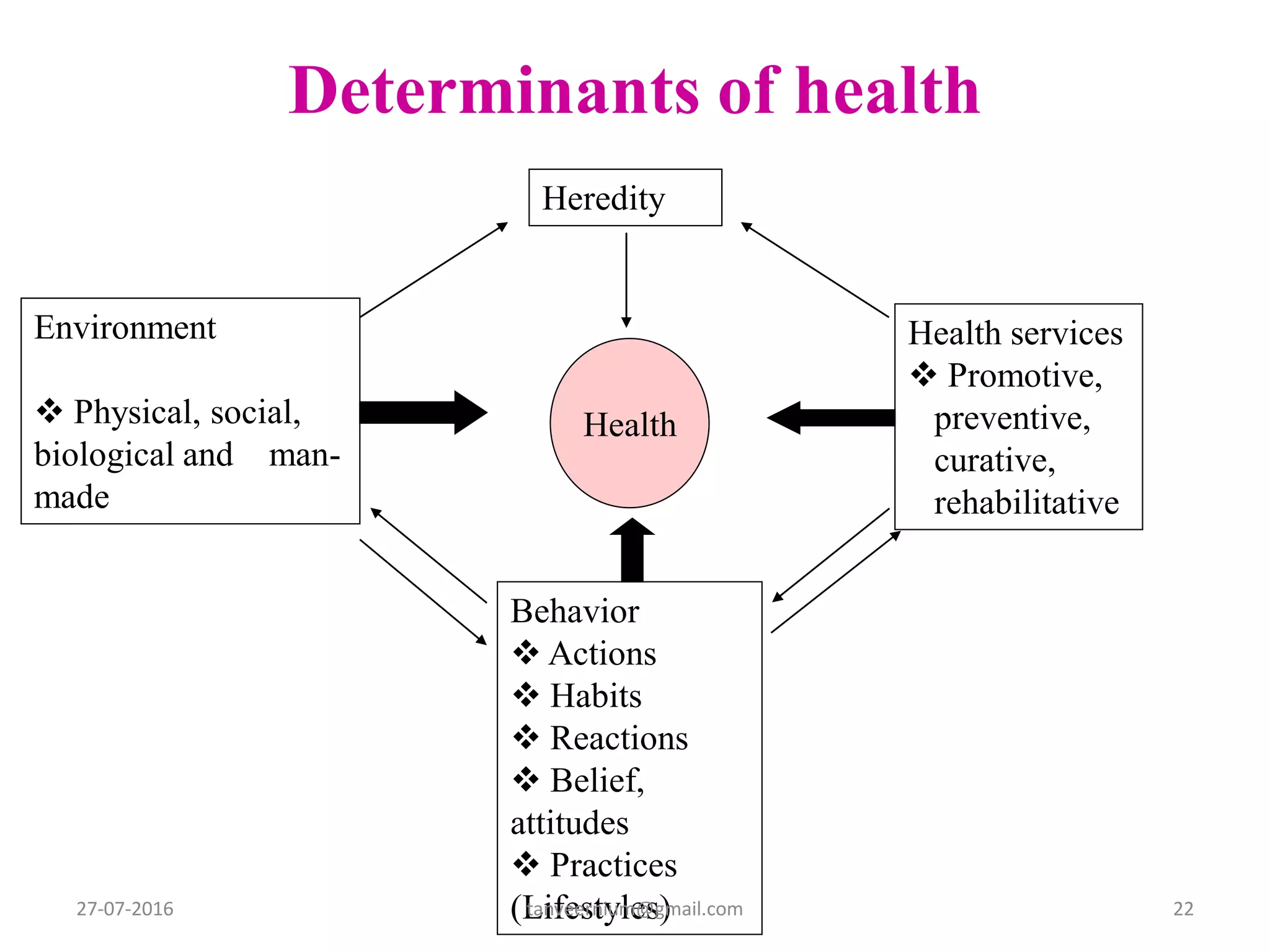
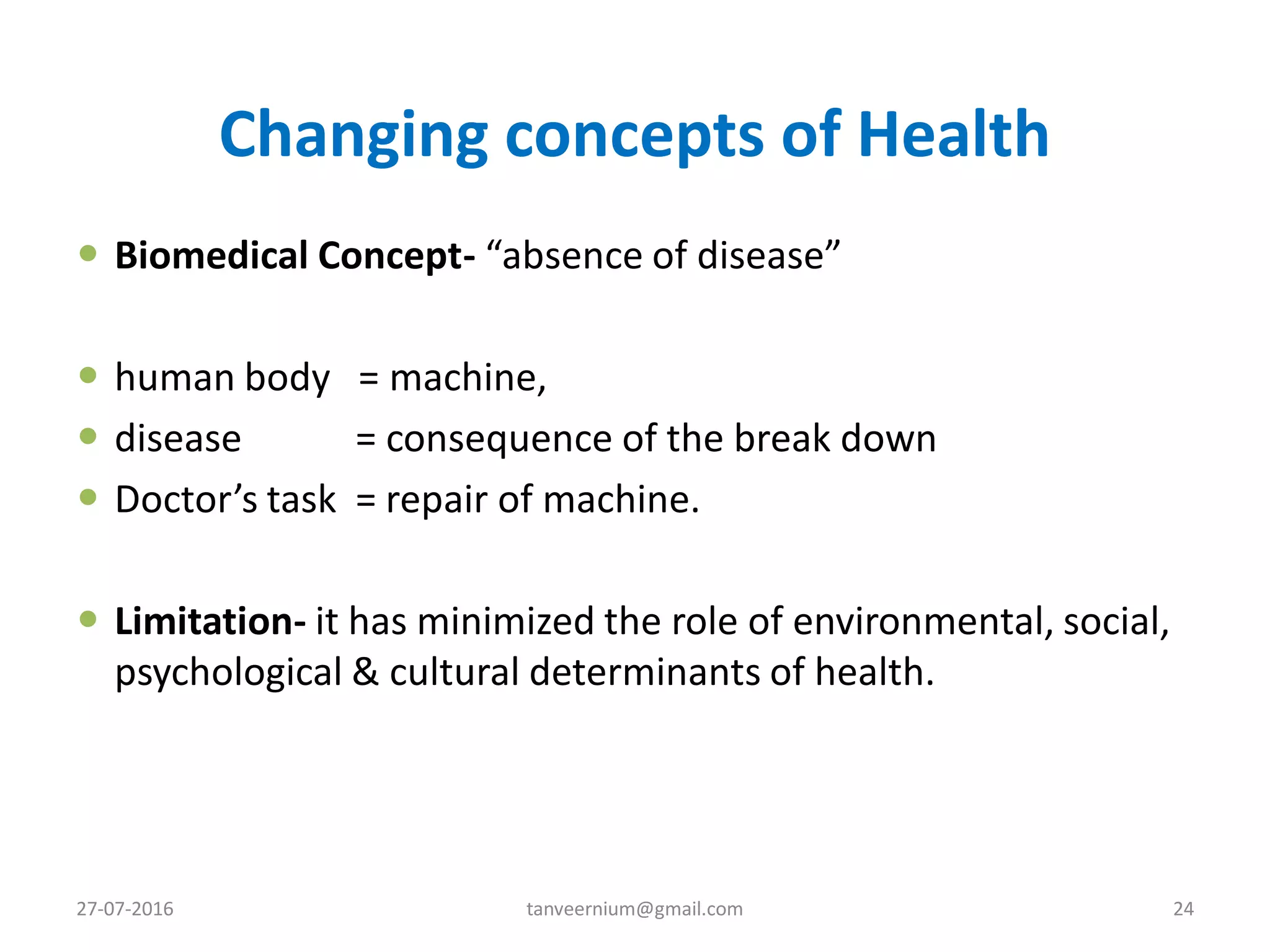
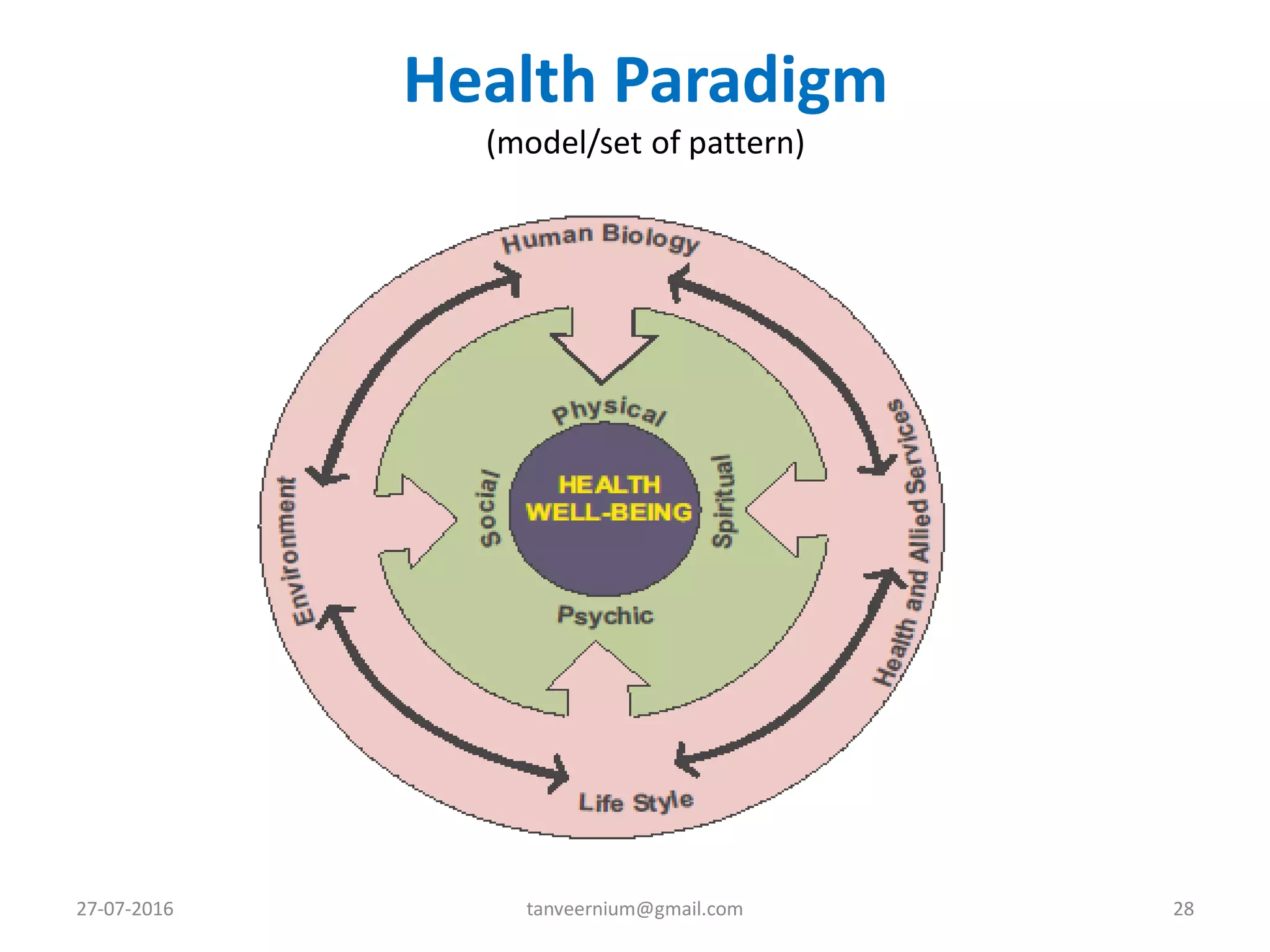
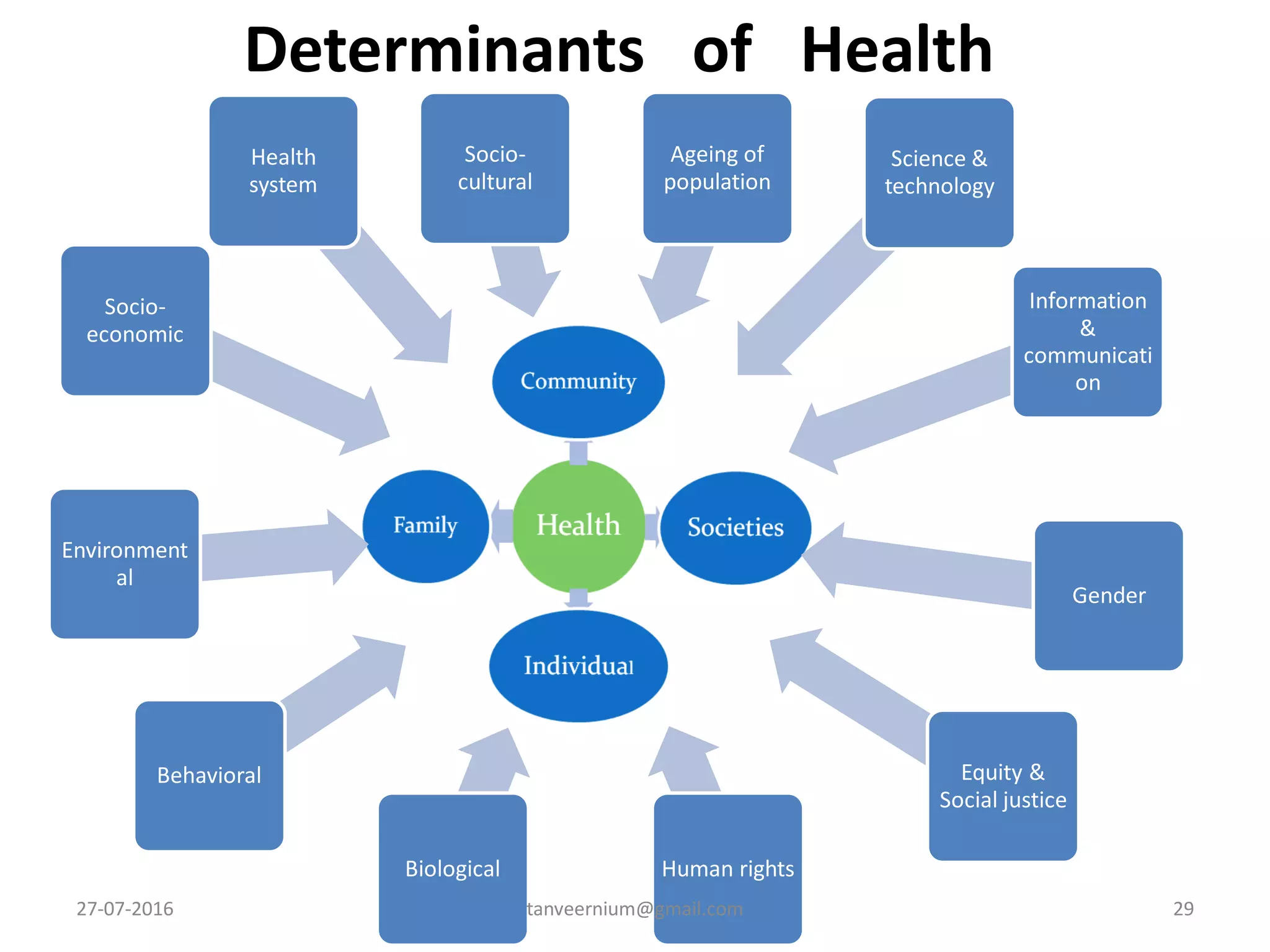
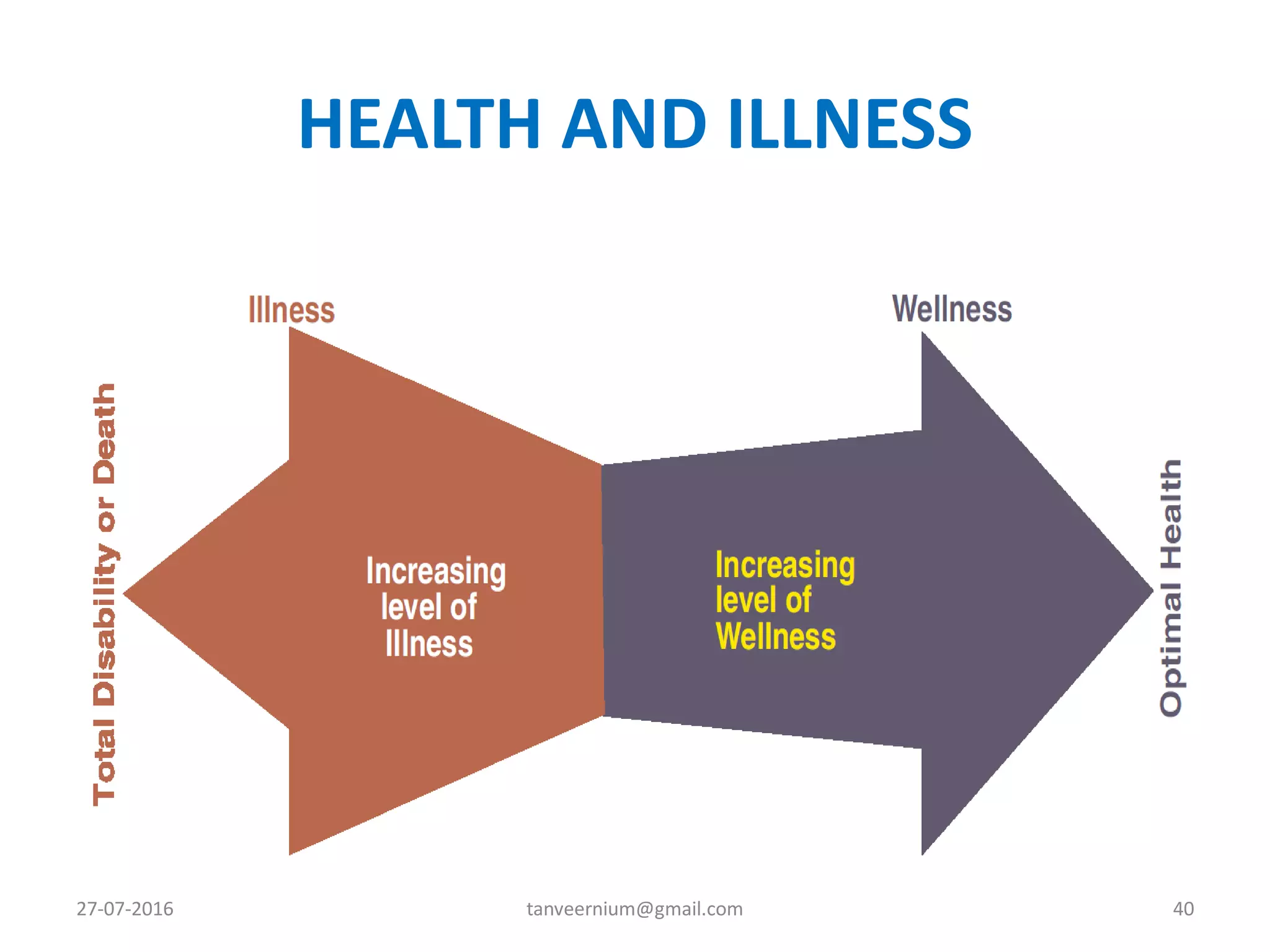
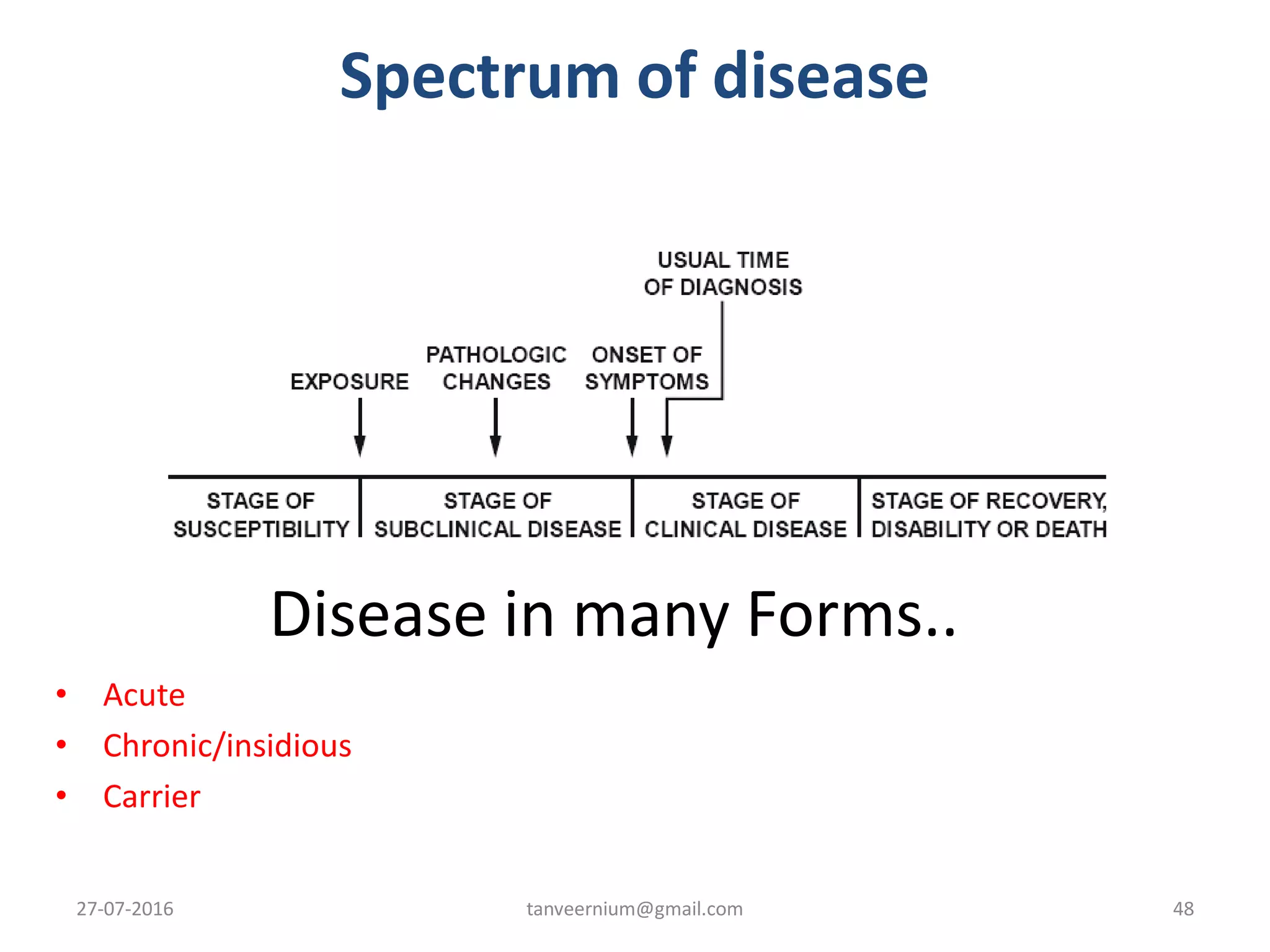
The document discusses various concepts and dimensions of health. It defines health according to different perspectives such as medical professionals and organizations. Health is a complex, multidimensional concept involving physical, mental, social, and spiritual well-being. The World Health Organization defines health as a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being, not just the absence of disease. Other topics covered include components of health, determinants of health, concepts of disease, and indicators used to measure population health.