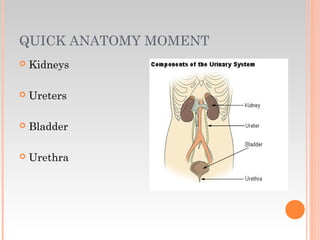
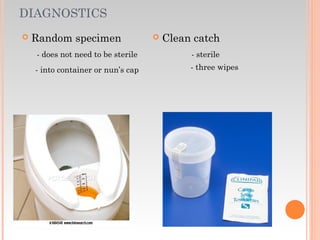
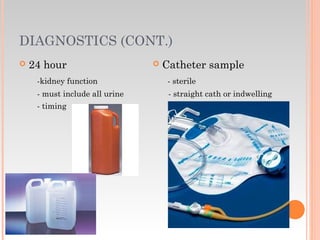
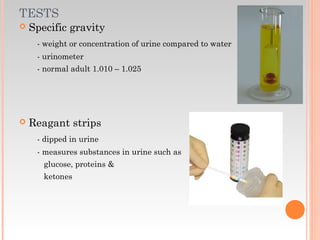
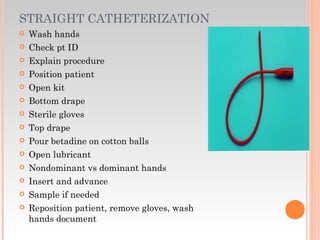
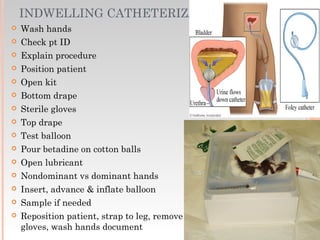
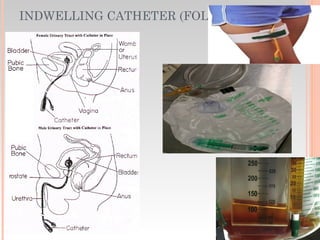
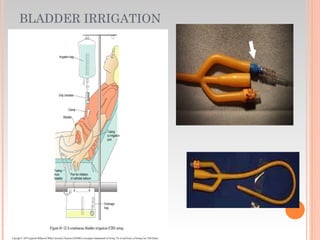
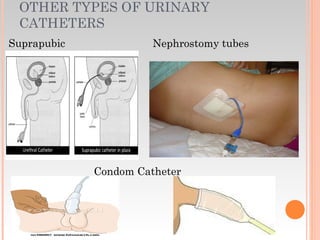
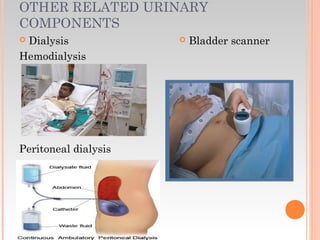
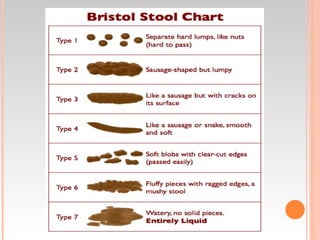
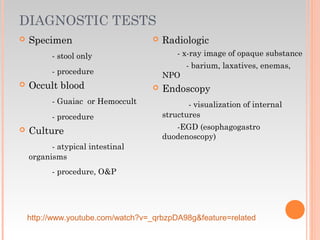
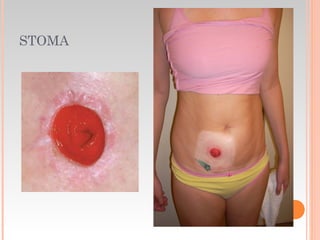
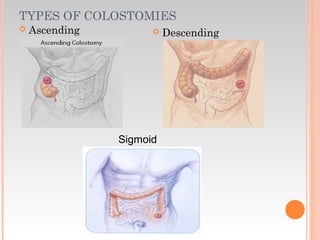
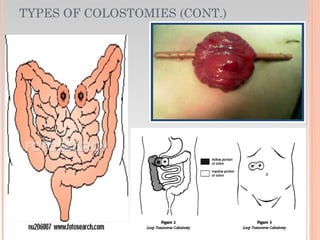
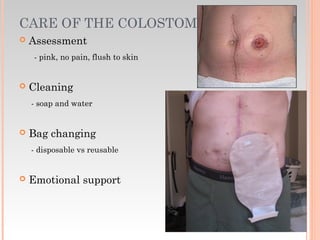
This document provides information about urinary and bowel elimination. It begins with anatomy and normal functions of the urinary system. It then discusses factors that can affect urination and signs of altered urinary function. It also covers incontinence, diagnostics, urinary health promotion, and urinary catheters. For bowel elimination, it discusses factors affecting function, signs of alteration, diagnostics including specimens and endoscopy, enemas, and fecal diversion including ostomies and their care.