Embed presentation
Download to read offline

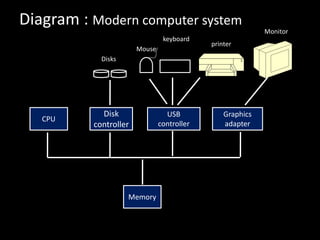


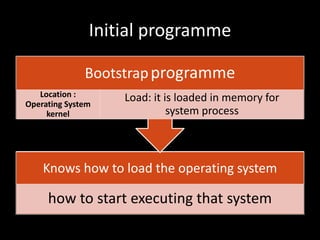

The document summarizes the components and organization of a modern computer system. It consists of a CPU connected through a common bus to various device controllers that provide access to shared memory. Each controller manages a specific device type, like disks or graphics. The CPU and controllers can run in parallel competing for memory access. The initial bootstrap program stored in ROM loads the operating system kernel into memory to start system processes. Hardware and software can trigger interrupts that stop CPU execution and transfer it to a fixed location.





