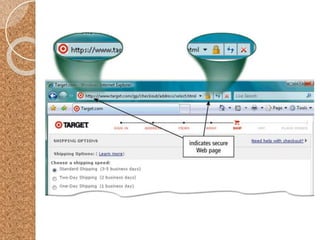
The document discusses the various computer security risks, categorizing perpetrators of cybercrime into seven groups, including hackers and cyberterrorists. It also outlines techniques used for cyber attacks such as botnets, denial of service attacks, and spoofing, while suggesting protective measures like firewalls and encryption. Important security protocols like TLS and the use of virtual private networks (VPNs) are highlighted as essential for safe data transmission.