Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX

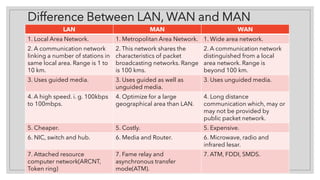
LANs connect devices within a small local area like a home or office using guided media like Ethernet cables. MANs connect devices within a larger metropolitan area of about 100 km using both guided and unguided media like fiber optics and communicate at speeds from 100 kbps to 100 mbps. WANs connect devices across geographic areas over 100 km using unguided media like microwave transmission or satellite and provide long distance communication through public or private networks at higher costs than LANs or MANs.

