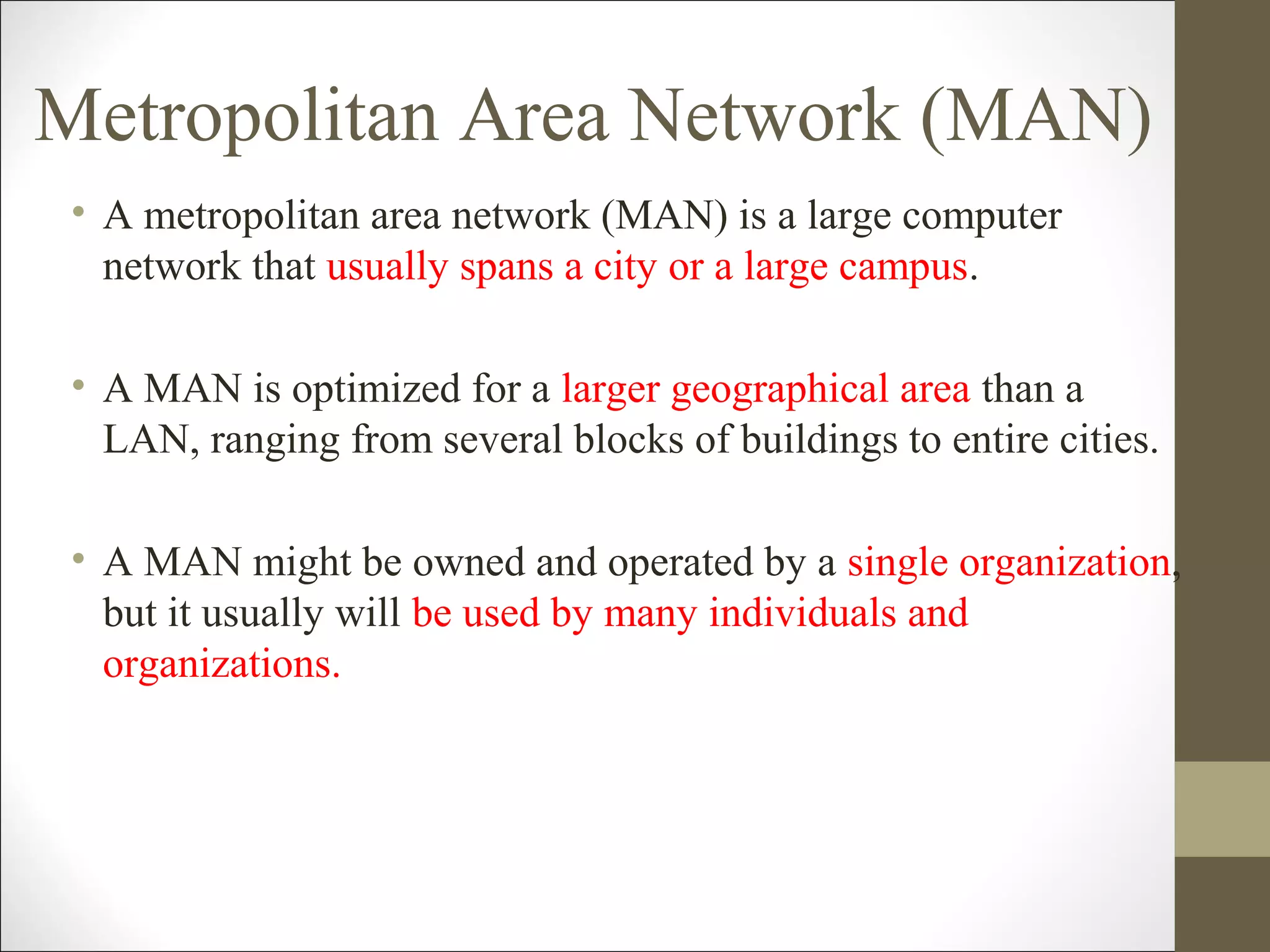
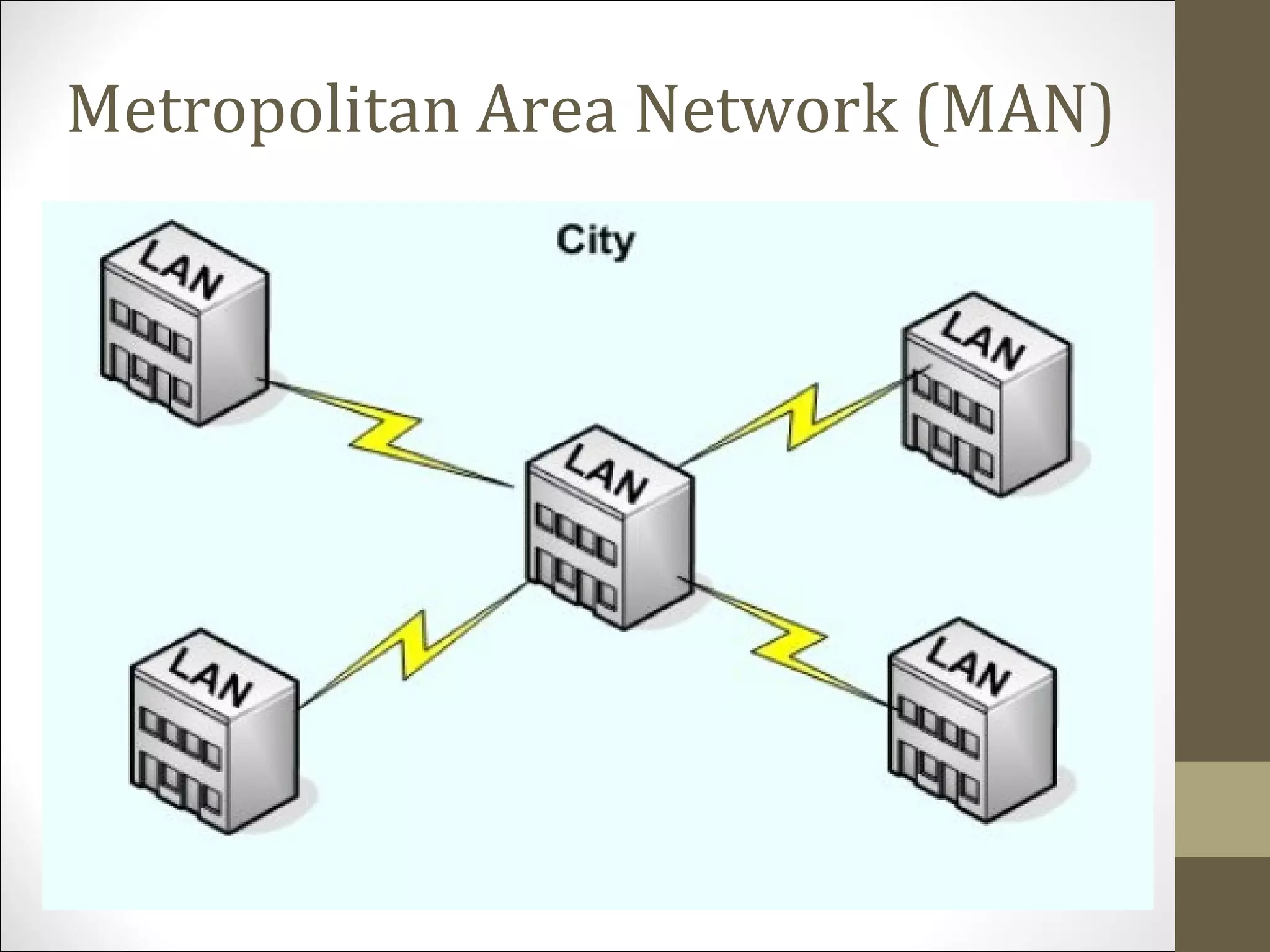
This document defines and describes different types of computer networks. It discusses Local Area Networks (LANs) that connect devices within a building using cables or wireless technology. Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs) span a larger area like a city using higher speed connections. Wide Area Networks (WANs) connect LANs over long distances using technologies like the internet. Personal Area Networks (PANs) wirelessly connect devices within a few meters of an individual.