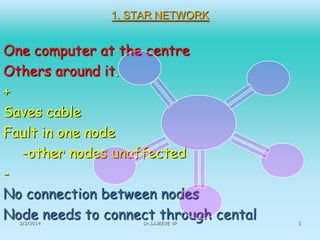
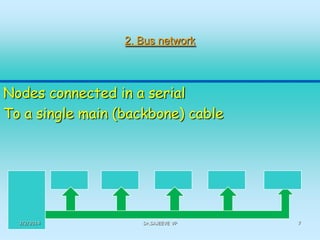
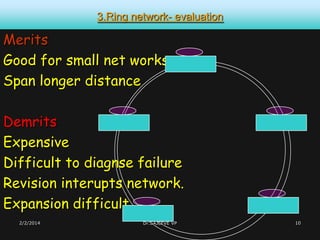
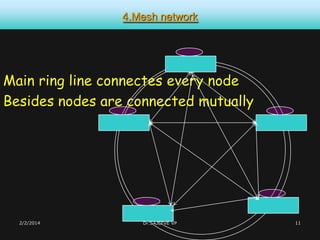
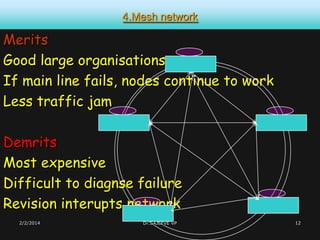
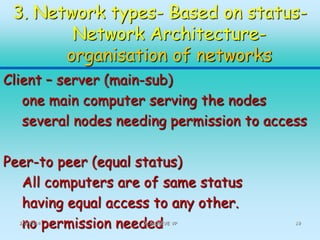
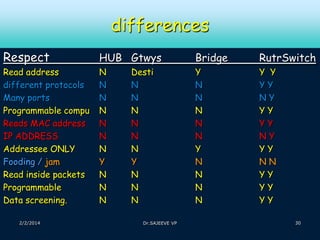
This document discusses different types of computer networks. It describes four common network structures (topologies): star, bus, ring, and mesh. It also discusses different network types based on area covered (LAN, MAN, WAN), connection model (client-server, peer-to-peer), and purpose (storage area network, wireless network). For each topology, the key characteristics and advantages/disadvantages are provided. Different network devices like hubs, bridges, routers and switches are also explained along with their functions.