Computer Network Introduction full
- 1. Slides Prepared by Aneeb.A Assiatant Professor HM College of Science and Technology Manjeri
- 4. Slides Prepared by Aneeb.A Assiatant Professor HM College of Science and Technology Manjeri
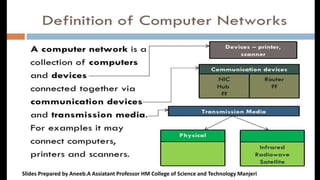
- 5. FILE SHARING – Networks offer a quick and easy way to share files directly. RESOURCE SHARING – All computers in the as and network printers, modems. can fax share resources such machines, scanners, COMMUNICATION –Those on the network can communicate with each other via e-mail, instant messages, etc.
- 6. Flexible Access - Networks allow their users to access files from computers throughout the network. - share Sharing of Information Computer networks enable us the to data that and areinformation with computers located geographically large distance apart.
- 11. P2P Stands for "Peer to Peer." In a P2P network, the "peers" are computer systems which are connected to each other via the Internet. Files can be shared directly between systems on the network without the need of a central server. In other words, each computer on a P2P network becomes a file server as well as a client.
- 14. DifferentTypes of Networks • Depending upon the geographical by a network, it is classified as: area covered – Local Area Network (LAN) – Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) – Wide Area Network (WAN) – Personal Area Network (PAN)
- 15. Local Area Network (LAN) A LAN is a network that is used for communicating among computer devices, usually within an office building or home. • • LAN’s enable the sharing of resources such as files or hardware devices that may be needed by multiple users • • Is limited in size, typically spanning a few hundred meters, and no more than a mile • Is fast, with speeds from 10 Mbps to 10 Gbps • Requires little wiring, typically a single cable connecting to each device • Has lower cost compared to MAN’s or WAN’s
- 16. Local Area Network (LAN) LAN’s can be either wired or wireless.Twisted pair, coax or fibre optic cable can be used in wired LAN’s. • • Every LAN uses a protocol – a set of rules that governs how packets are configured and transmitted. • Nodes in a LAN are linked together with a certain topology.These topologies include: – – – Bus Ring Star • LANs are capable of very high transmission rates (100s Mb/s to G b/s).
- 17. Local Area Network (LAN)
- 18. Advantages of LAN • Speed • Cost • Security • E-mail • Resource Sharing
- 19. Disadvantages ExpensiveTo Install of LAN • • Requires Administrative Time • File Server May Fail • Cables May Break
- 20. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) A metropolitan area network (MAN) is a large computer network that usually spans a city or a large campus. • • A MAN is optimized for a larger geographical area than a LAN, ranging from several blocks buildings to entire cities. of • A MAN might be owned and operated by a single organization, but it usually will be used by many individuals and organizations.
- 21. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) A MAN often acts as a high speed network to allow sharing of regional resources. • • A MAN typically covers an area of between and 50 km diameter. 5 • Examples of MAN:Telephone company network that provides a high speed DSL to customers and cable TV network,Networks of Banks like institution which cover a district
- 22. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
- 23. Wide Area Network (WAN) WAN covers a large geographic area such as country, continent or even whole of the world. • • AWAN is two or more LANs connected together.The LANs can be many miles apart. • To cover great distances,WANs may transmit data over leased high-speed phone lines or wireless links such as satellites.
- 24. Wide Area Network (WAN) Multiple LANs can be connected together using devices such as bridges, routers, or gateways, which enable them to share data. • • The world's most popularWAN is the Internet. Slides Prepared by Aneeb.A Assiatant Professor HM College of Science and Technology Manjeri
- 25. Wide Area Network (WAN)
- 27. Personal Area Network (PAN)
- 28. Personal Area Network (PAN) A PAN is a network that is used for communicating among computers and computer devices (including telephones) in close proximity of around a few meters within a room • • It can be used for communicating between the devices themselves, or for connecting to a larger network such as the internet. • PAN’s can be wired or wireless
- 29. Personal Area Network (PAN) A personal area network (PAN) is a computer network used for communication among computer devices, including telephones and personal digital assistants, in proximity to an individual's body. • • The devices may or may not belong to the person in question.The reach of a PAN is typically a few meters.
- 30. Personal Area Network (PAN)
- 31. It is the physical way in which computers are interconnected. Five basic network structures are :
- 32. Devices are connected to a central computer called HUB. A Star network is particularly appropriate for organizations that require a centralized data base or a centralized processing facility. For example, a star network may be used in banking for centralized record keeping in an on-line branch office environment.
- 34. It is easy to add new and remove nodes. A node failure does not bring let down the entire network. It is easier to diagnose network through a central hub. problems
- 35. If the central hub fails, the whole network ceases to function. It costs more to cable a star configuration than other topologies because more cable is required than other topologies.
- 36. In Bus topology a single network cable runs in the building or campus and all nodes are line or linked along with this communication with two endpoints called the bus backbone. This structure is very popular for local area networks
- 38. Slides Prepared by Aneeb.A Assiatant Professor HM College of Science and Technology Manjeri
- 39. Reliable in very small networks as well as easy to use and understand. Requires the least amount of cable to connect the computers together and therefore is less expensive than other cabling arrangements.
- 40. Heavy network traffic can slow a bus considerably. Each connection between cables weakens the electrical signal. If the common cable fails, then the whole system will crash down
- 41. In Ring topology the network cable passes from one node to another until all nodes are connected in the form of a “loop or ring”. Transmits in only one direction. Used in LAN’S and WAN’S.
- 43. 1.One station is known as monitor station which takes all the responsibility to perform the operations. 2.To transmit the data, station has to hold the token. After the transmission is done, the token is to be released for other stations to use. 3.When no station is transmitting the data, then the token will circulate in the ring.
- 44. Ring networks can span longer distances than other types of networks. Ring networks are easily extendable.
- 45. Relatively expensive and difficult to install. Failure of one computer on the network can affect the whole network. Adding or removing computers can disrupt the network.
- 46. In mesh network, there is random connection of nodes using communication links. Mesh topology is the general topology for wide area network. In mesh topology, every device is connected to another device via particular channel. In mesh topology, every device is connected to another device via particular channel.
- 47. Slides Prepared by Aneeb.A Assiatant Professor HM College of Science and Technology Manjeri
- 48. Figure 1 : Every device is connected with another via dedicated channels. These channels are known as links. •If suppose, N number of devices are connected with each other in mesh topology, then total number of ports that is required by each device is ? N-1. In the Figure 1, there are 5 devices connected to each other, hence total number of ports required is 4. •If suppose, N number of devices are connected with each other in mesh topology, then total number of dedicated links required to connect them is NC2 i.e. N(N-1)/2. In the Figure 1, there are 5 devices connected to each other, hence total number of links required is 5*4/2 = 10
- 49. The reliability is very high alternate paths available if as there are always direct link between two nodes is down. Yields the greatest amount of the of redundancy in the event that one can nodes fails where network node. traffic be redirected to another
- 50. The cost of installation and maintenance is high ( more cable is required than any other configuration).
- 51. A tree topology connects one star network the other star network. to It is an extension of star topology. Here, we divided the whole network into segment which can be easily managed and maintained.
- 53. In this the various secondary hubs are connected to the central hub which contains the repeater.
- 54. Each segment is provided with dedicated point-to-point wiring to central hub. Error detection and correction is easy. If one segment is damaged, other segment are not affected. Expansion of network is possible and easy.
- 55. As multiple segments are connected to a central hub, the networks depend heavily on the hub. Its failure affects the entire network. Maintenance is not easy and cost are high. With increase in size beyond a point, the management becomes difficult.
- 56. Hybrid Topology : This topology is a collection of two or more topologies which are described above. This is a scalable topology which can be expanded easily. It is reliable one but at the same it is a costly topology
- 57. INTERNETWORK/Internet Today, it is very rare to see a LAN, a MAN, or a LAN in isolation; they are connected to one another. When two or more networks are connected, they become an internetwork, or internet. As an example, assume that an organization has two offices, one on the east coast and the other on the west coast. The established office on the west coast has a bus topology LAN; the newly opened office on the east coast has a star topology LAN. The president of the company lives somewhere in the middle and needs to have control over the company from her horne. We can make communicate them using internet via switches and routers like network devices
- 60. NETWORK MODELS Computer Network Models : Introduction For data communication to take place and two or more users can transmit data from one to other, a systematic approach is required. This approach enables users to communicate and transmit data through efficient and ordered path. It is implemented using models in computer networks and are known as computer network models. Computer network models are responsible for establishing a connection among the sender and receiver and transmitting the data in a smooth manner respectively. There are two computer network models i.e. OSI Model and TCP/IP Model on which the whole data communication process relies.
- 61. Computer Network Models : The OSI Reference Model The OSI Model is one of the general purpose networking or communication model among computer network models, which is responsible for establishing connection in an open manner between all the communicable devices present across the globe. OSI stands for “Open System Interconnection” and the name of this reference model was given by an organization known as “International Organization for Standardization”. The ISO is responsible for generating and promoting industrial and commercial standards applicable for all the users or universally. Apart from OSI Model, another computer network models which is widely used is TCP/IP Model. OSI model having a layered architecture, allows easy data communication as each layer has predefined structured and functionalities. The functionalities are different for each layer and thus when combined together forms the OSI Model. There are in total seven layers in general purpose OSI model
- 64. Physical Layer The lowest layer of the OSI reference model is the physical layer. It is responsible for the actual physical connection between the devices. The physical layer contains information in the form of bits. It is responsible for transmitting individual bits from one node to the next. When receiving data, this layer will get the signal received and convert it into 0s and 1s and send them to the Data Link layer, which will put the frame back together. Slides Prepared by Aneeb.A Assiatant Professor HM College of Science and Technology Manjeri
- 65. The functions of the physical layer are : 1. Bit rate control: The Physical layer also defines the transmission rate i.e. the number of bits sent per second. 2. Physical topologies: Physical layer specifies the way in which the different, devices/nodes are arranged in a network i.e. bus, star or mesh topolgy. 3. Transmission mode: Physical layer also defines the way in which the data flows between the two connected devices. The various transmission modes possible are: Simplex-One direction only communication Eg:Radio half-duplex -At a time one direction only-Eg:Walkie Talkie and full-duplex.-Two way communication Eg:Telephone * Hub, Repeater, Modem, Cables are Physical Layer devices. ** Network Layer, Data Link Layer and Physical Layer are also known as Lower Layers or Hardware Layers.
- 67. Data Link Layer Data Link Layer provides or acts as an intermediate, ensuring delivery of data message to its respective destination in the network by using the physical address of the device known as MAC (Media Access Control) Address. This layer translates the data received in the form of bits from physical layer into respective format and forwards it to network layer. The data link layer is responsible for the node to node delivery of the message. The main function of this layer is to make sure data transfer is error-free from one node to another, over the physical layer. Data Link Layer is divided into two sub layers : o Logical Link Control (LLC) o Media Access Control (MAC) The packet received from Network layer is further divided into frames depending on the frame size of NIC(Network Interface Card). DLL also encapsulates Sender and Receiver’s MAC address in the header
- 68. The functions of the data Link layer are : Framing: Framing is a function of the data link layer. It provides a way for a sender to transmit a set of bits(frame) that are meaningful to the receiver. This can be accomplished by attaching special bit patterns to the beginning and end of the frame. Physical addressing: After creating frames, Data link layer adds physical addresses (MAC address) of sender and/or receiver in the header of each frame. Error control: Data link layer provides the mechanism of error control in which it detects and retransmits damaged or lost frames. Flow Control: The data rate must be constant on both sides else the data may get corrupted thus , flow control coordinates that amount of data that can be sent before receiving acknowledgement. Access control: When a single communication channel is shared by multiple devices, MAC sub-layer of data link layer helps to determine which device has control over the channel at a given time. * Packet in Data Link layer is referred as Frame. ** Data Link layer is handled by the NIC (Network Interface Card) and device drivers of host machines. *** Switch & Bridge are Data Link Layer devices
- 70. Network Layer The network layer is responsible for facilitating data transfer between two different networks. If the two devices communicating are on the same network, then the network layer is unnecessary. Ie Network layer works for the transmission of data from one host to the other located in different networks Ie it enable source to destination transfer of packets The network layer breaks up segments from the transport layer into smaller units, called packets, on the sender ’s device, and reassembling these packets on the receiving device. The network layer also finds the best physical path for the data to reach its destination; this is known as routing.
- 71. Functions Logical addressing. The physical addressing implemented by the data link layer handles the addressing problem locally. If a packet passes the network boundary, we need another addressing system to help distinguish the source and destination systems Called IP Address. The network layer adds a header to the packet coming from the upper layer that, among other things, includes the logical addresses of the sender and receiver. Routing. When independent networks or links are connected to create intemetworks (network of networks) or a large network, the connecting devices (called routers or switches) route or switch the packets to their final destination. Segment in Network layer is referred as Packet. Network layer is implemented by networking devices such as routers.
- 72. Transport Layer The transport layer is responsible for process-to-process delivery of the entire message. A process is an application program running on a host.. Layer 4 is responsible for end-to-end communication between the two devices. This includes taking data from the session layer and breaking it up into chunks called segments before sending it to layer 3. The transport layer on the receiving device is responsible for reassembling the segments into data the session layer can consume. The transport layer also provides the acknowledgement of the successful data transmission and re-transmits the data if an error is found Functions of Transport Layers 1. Segmentation and Reassembly: This layer accepts the message from the (session) layer , breaks the message into smaller units(Segments) . Each of the segment produced has a header associated with it. The transport layer at the destination station reassembles the message. 2. Service Point Addressing: In order to deliver the message to correct process, transport layer header includes a type of address called service point address or port address. Thus by specifying this address, transport layer makes sure that the message is delivered to the correct process.
- 73. The services provided by the transport layer : Connection Oriented Service: It is a three-phase process which include – Connection Establishment – Data Transfer – Termination / disconnection In this type of transmission, the receiving device sends an acknowledgement, back to the source after a packet or group of packet is received. This type of transmission is reliable and secure. Connection less service: It is a one-phase process and includes Data Transfer. In this type of transmission, the receiver does not acknowledge receipt of a packet. This approach allows for much faster communication between devices. Connection- oriented service is more reliable than connectionless Service. * Data in the Transport Layer is called as Segments. ** Transport layer is operated by the Operating System. It is a part of the OS and communicates with the Application Layer by making system calls. Transport Layer is called as Heart of OSI model.
- 74. Session Layer The session layer (layer 5) is responsible for establishing, managing, synchronizing and terminating sessions between end-user application processes. The main functions of the session layer are as follows − It works as a dialog controller. It allows the systems to communicate in either half-duplex or full-duplex mode of communication. It is responsible for token management. Through this, it prevents the two users to simultaneously attempt the same critical operation. It synchronizes communication. It adds synchronization points or checkpoints in data streams for long communications. This ensures that data streams up to the checkpoints are successfully received and acknowledged. In case of any failures, only the streams after the checkpoints have to be re-transmitted.
- 75. Presentation Layer (Layer 6) : Presentation layer is also called the Translation layer.The data from the application layer is extracted here and manipulated as per the required format to transmit over the network. The functions of the presentation layer are : 1.Translation : For example, ASCII to EBCDIC. 2.Encryption/ Decryption : Data encryption translates the data into another form or code. The encrypted data is known as the cipher text and the decrypted data is known as plain text. A key value is used for encrypting as well as decrypting data. 3.Compression: Reduces the number of bits that need to be transmitted on the network.
- 76. Application Layer The application layer enables the user, whether human or software, to access the network. It provides user interfaces and support for services such as electronic mail, remote file access and transfer, shared database management, and other types of distributed information services. It is the user interface layer. Ex: Application – Browsers, Skype Messenger etc.
- 77. TCP/IP PROTOCOL MODEL The OSI Model we just looked at is just a reference/logical model. It was designed to describe the functions of the communication system by dividing the communication procedure into smaller and simpler components. But when we talk about the TCP/IP model, it was designed and developed by Department of Defense (DoD) in 1960s and is based on standard protocols. It stands for Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol. The TCP/IP model is a concise version of the OSI model. It contains four layers, unlike seven layers in the OSI model. Network Access Layer/Link layer internet Layer host-to-host or Transport Layer, and application Layer
- 79. 1. Network Access Layer – This layer corresponds to the combination of Data Link Layer and Physical Layer of the OSI model. It looks out for hardware addressing and the protocols present in this layer allows for the physical transmission of data. 2. Internet Layer – This layer parallels the functions of OSI’s Network layer. It defines the protocols which are responsible for logical transmission of data over the entire network. The main protocols residing at this layer are : 1. IP – stands for Internet Protocol and it is responsible for delivering packets from the source host to the destination host by looking at the IP addresses in the packet headers. IP has 2 versions: IPv4 and IPv6. IPv4 is the one that most of the websites are using currently. But IPv6 is growing as the number of IPv4 addresses are limited in number when compared to the number of users. 2. ICMP – stands for Internet Control Message Protocol. It is encapsulated within IP datagrams and is responsible for providing hosts with information about network problems. 3. ARP – stands for Address Resolution Protocol. Its job is to find the hardware address of a host(MAC Addres) from a known IP address. On a typical physical network, such as a LAN, each device on a link is identified by a physical or station address called MAC Address, usually imprinted on the network interface card (NIC). ARP is used to find the physical address of the node when its Internet address is known. ARP has several types: Reverse ARP, Proxy ARP, Gratuitous ARP and Inverse ARP
- 80. 3. Host-to-Host Layer – This layer is analogous to the transport layer of the OSI model. It is responsible for end-to- end communication and error-free delivery of data. It shields the upper-layer applications from the complexities of data. The two main protocols present in this layer are : 1. Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) – It is known to provide reliable and error-free communication between end systems. It performs sequencing and segmentation of data. It also has acknowledgment feature and controls the flow of the data through flow control mechanism. It is a very effective protocol but has a lot of overhead due to such features. Increased overhead leads to increased cost. User Datagram Protocol (UDP) – Is also provide unrealiable communication between end systems.On the other hand does not provide any such features error free,flow control.. Unlike TCP, which is connection-oriented protocol, UDP is connectionless
- 81. Application Layer – This layer performs the functions of top three layers of the OSI model: Application, Presentation and Session Layer. It is responsible for node-to-node communication and controls user-interface specifications. Some of the protocols present in this layer are: HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, TFTP, Telnet, SSH, SMTP, SNMP, NTP, DNS, DHCP, NFS, X Window, LPD. Have a look at Protocols in Application Layer for some information about these protocols. Protocols other than those present in the linked article are : 1.HTTP and HTTPS – HTTP stands for Hypertext transfer protocol. It is used by the World Wide Web to manage communications between web browsers and servers. HTTPS stands for HTTP-Secure. It is a combination of HTTP with SSL(Secure Socket Layer). It is efficient in cases where the browser need to fill out forms, sign in, authenticate and carry out bank transactions. 2.Telnet-Enable remote logging
- 82. PHYSICAL LAYER Physical layer in the OSI model plays the role of interacting with actual hardware and signaling mechanism. Physical layer is the only layer of OSI network model which actually deals with the physical connectivity of two different stations. This layer defines the hardware equipment, cabling, wiring, frequencies, pulses used to represent binary signals etc. Physical layer provides its services to Data-link layer. Data-link layer hands over frames to physical layer. Physical layer converts them to electrical pulses, which represent binary data.The binary data is then sent over the wired or wireless media. DATA TERMINAL EQUIPMENT (DTE) Data Terminal Equipment is equipment which acts as source or destinations in digital communication and which is capable of converting information to signals and also reconverting received signals.The data terminal equipment may be a single piece of equipment or an interconnected subsystem of multiple pieces of equipment that perform all the required functions necessary to permit users to communicate. A user interacts with the DTE (e.g. through a human-machine interface), or the DTE may be the user. Usually, the DTE device is the terminal (or a computer emulating a terminal), and the DCE is a modem
- 83. DATA CIRCUIT-TERMINATING EQUIPMENT (DCE) Data Communications Equipment, or DCE, is any device that supports data transmission over a serial telecommunications link. Typically, data communications equipment (DCE) refers to modems, Channel Service Unit/Data Service Units (CSU/DSUs), multiplexers, and similar devices. The purpose of a DCE is to provide termination for the telecommunications link and an interface for connecting data terminal equipment (DTE) to the link. A data circuit-terminating equipment (DCE) is a device that sits between the data terminal equipment (DTE) and a data transmission circuit. It is also called data communication(s) equipment and data carrier equipment. Usually, the DTE device is the terminal (or computer), and the DCE is a modem
- 84. Slides Prepared by Aneeb.A Assiatant Professor HM College of Science and Technology Manjeri