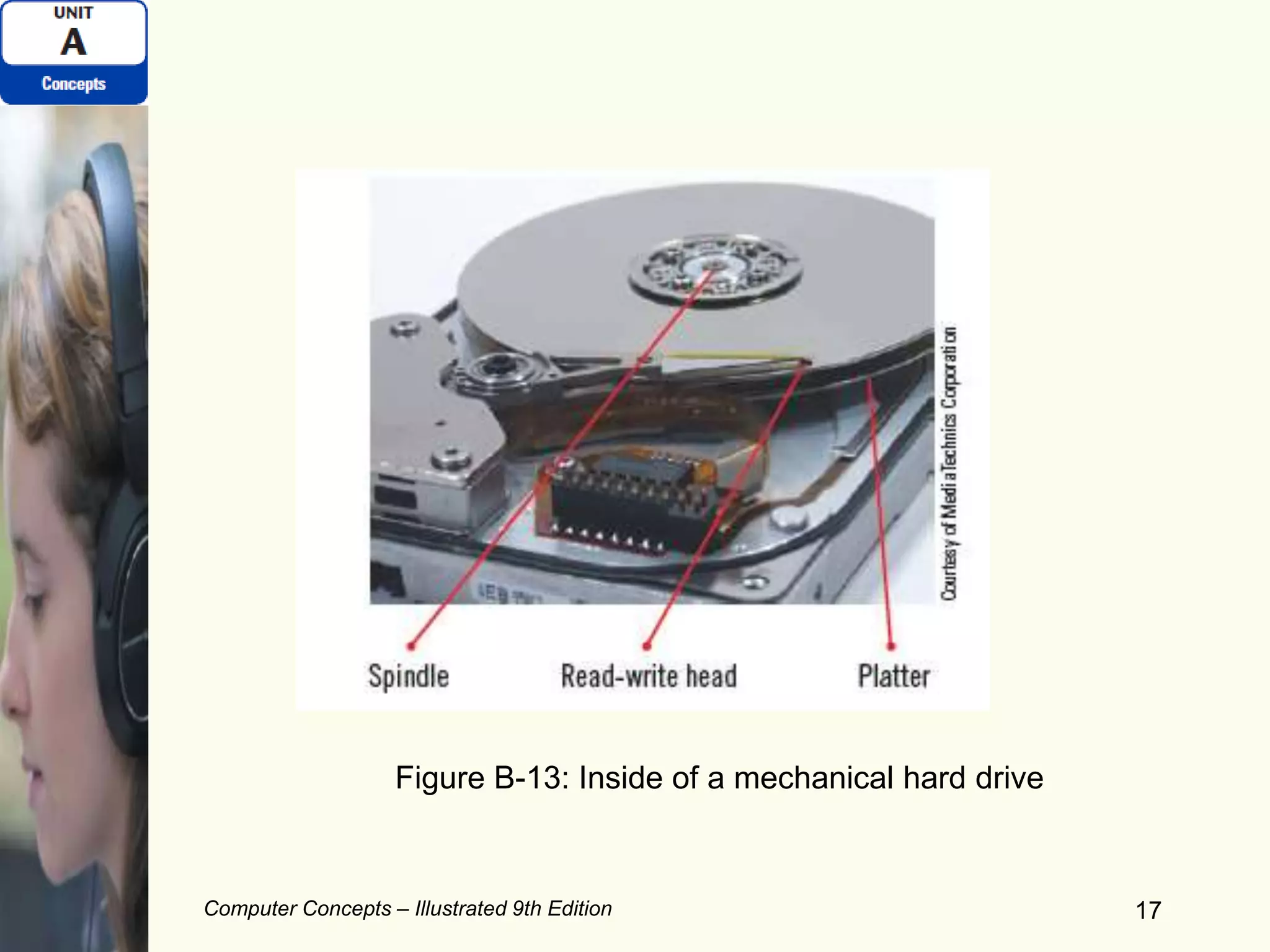
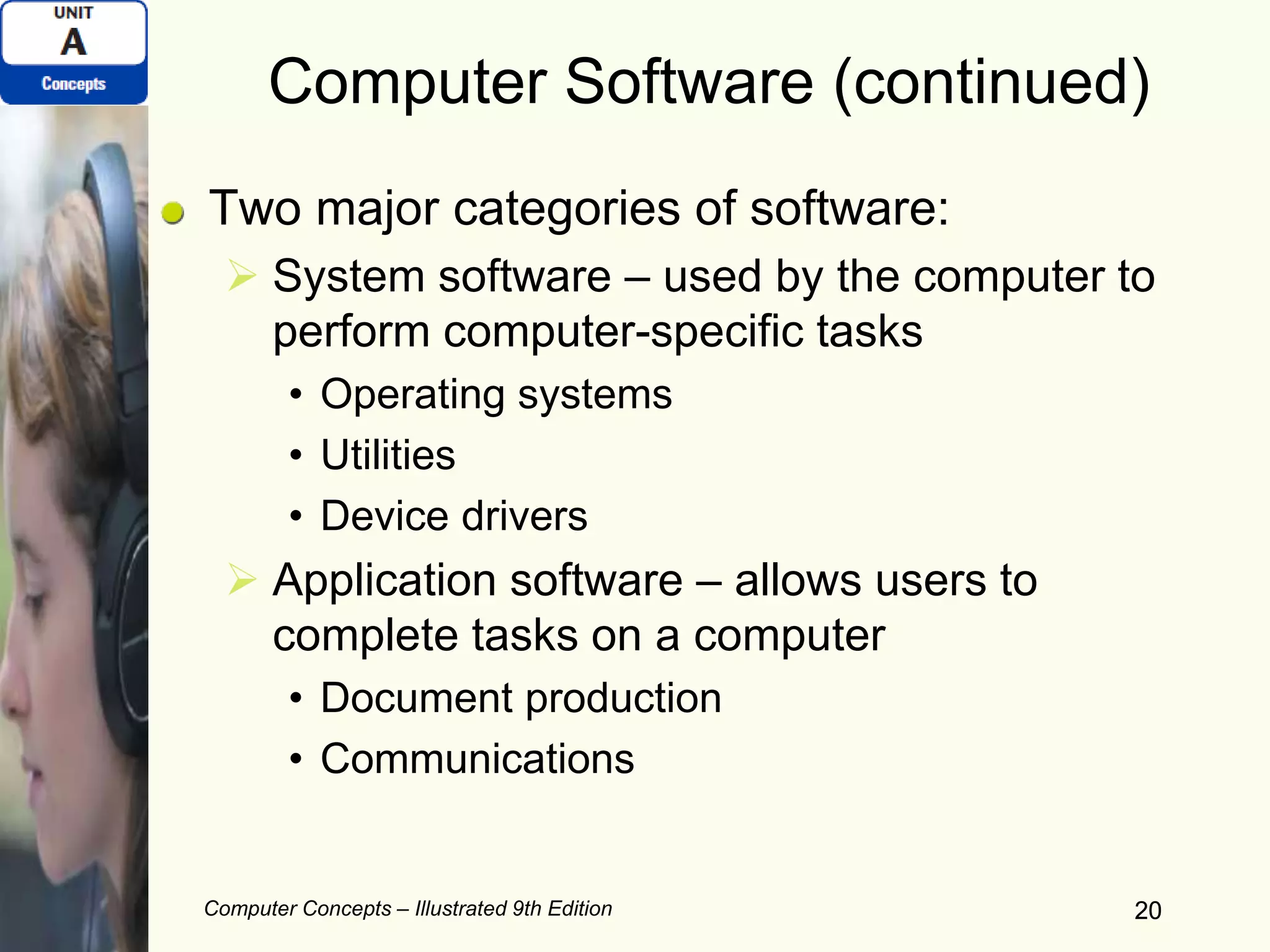
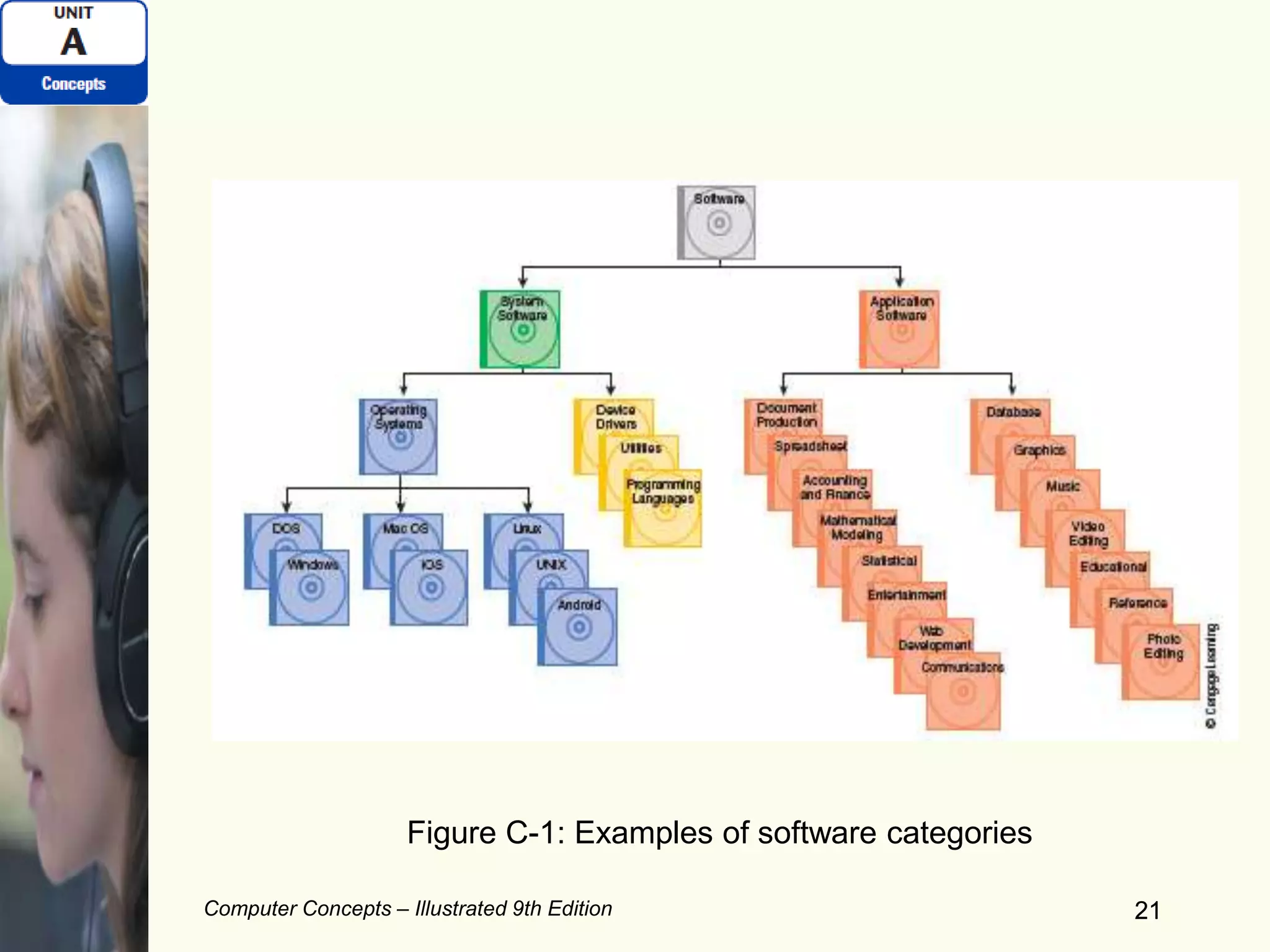
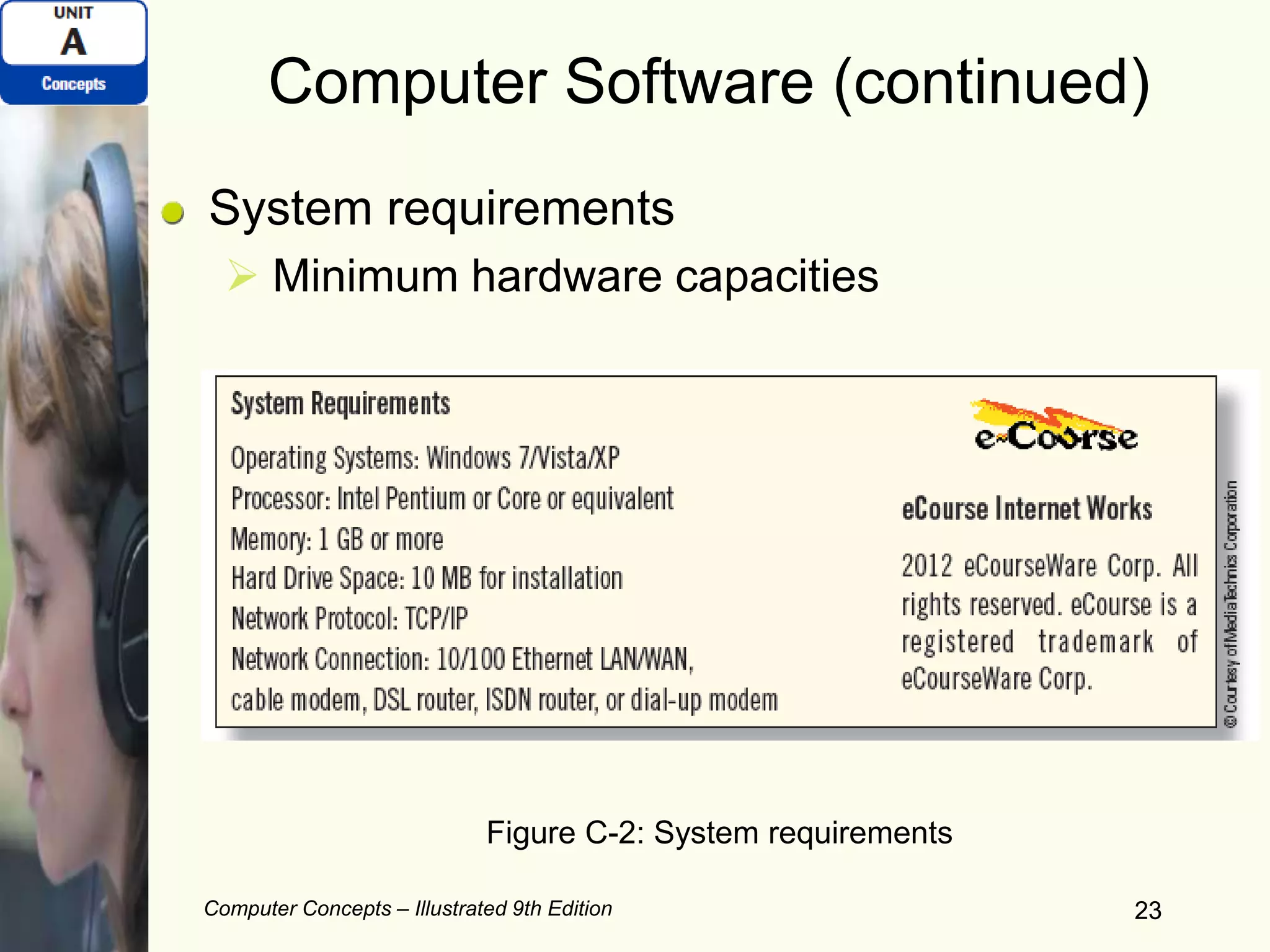
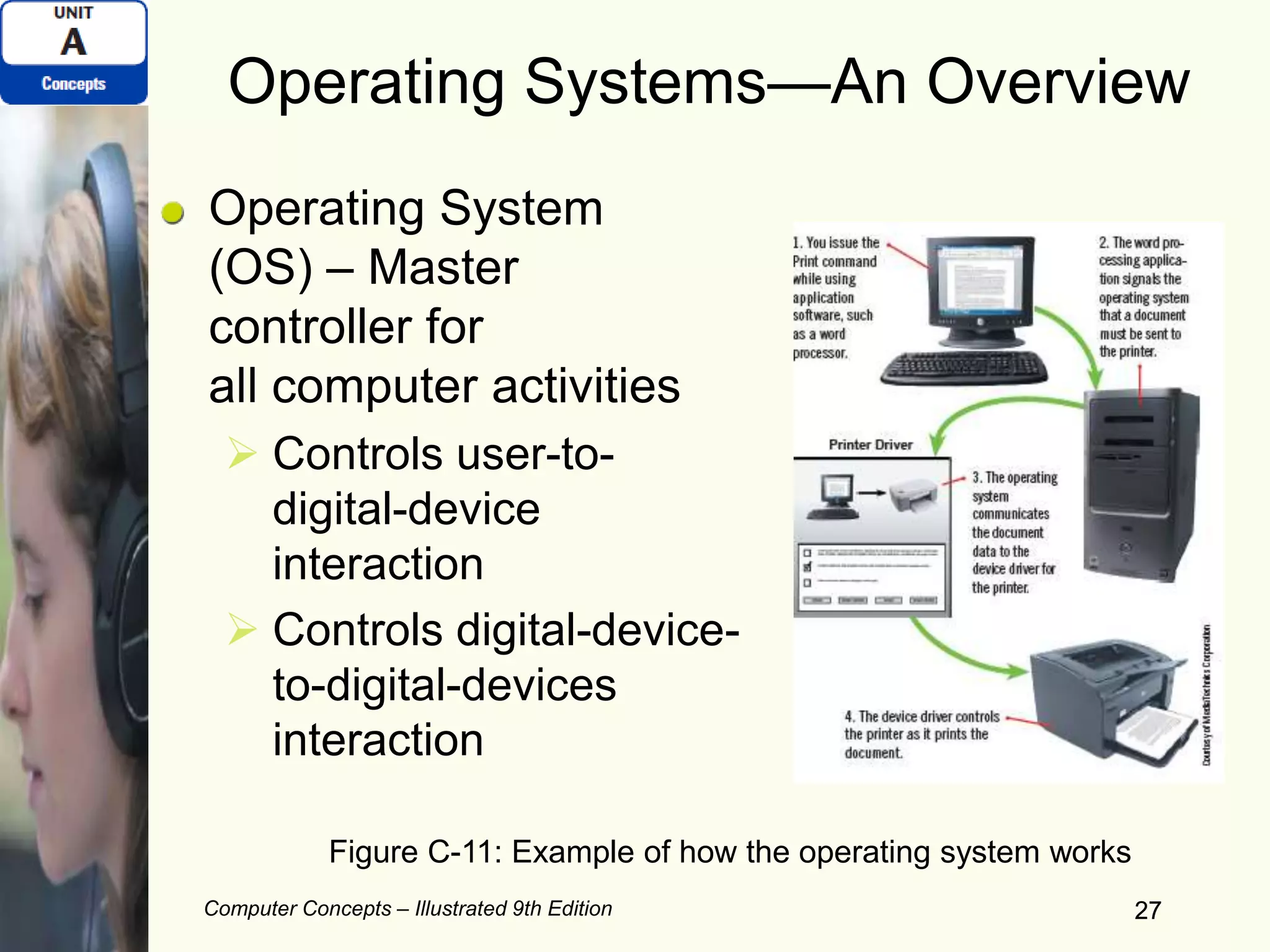
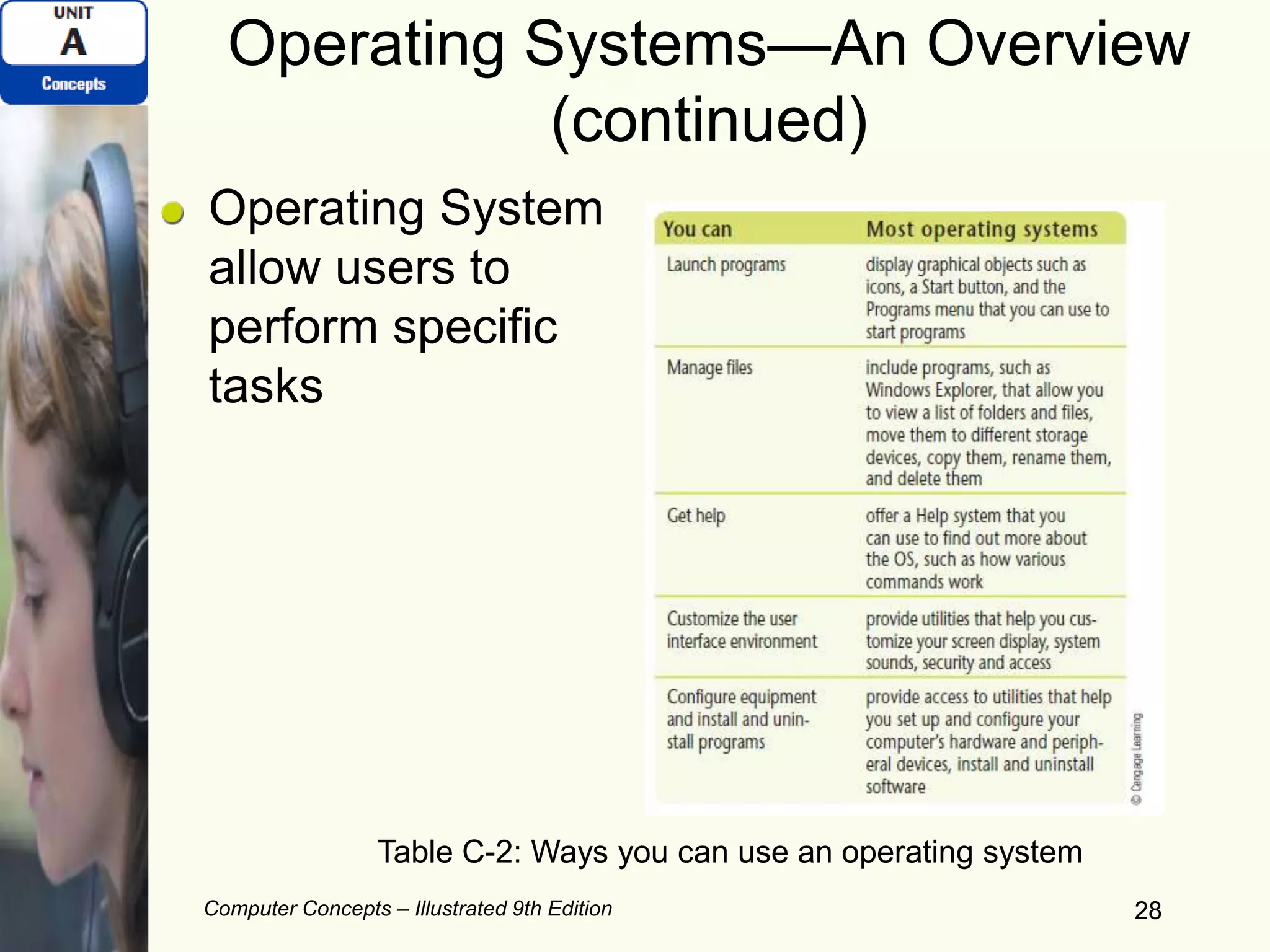
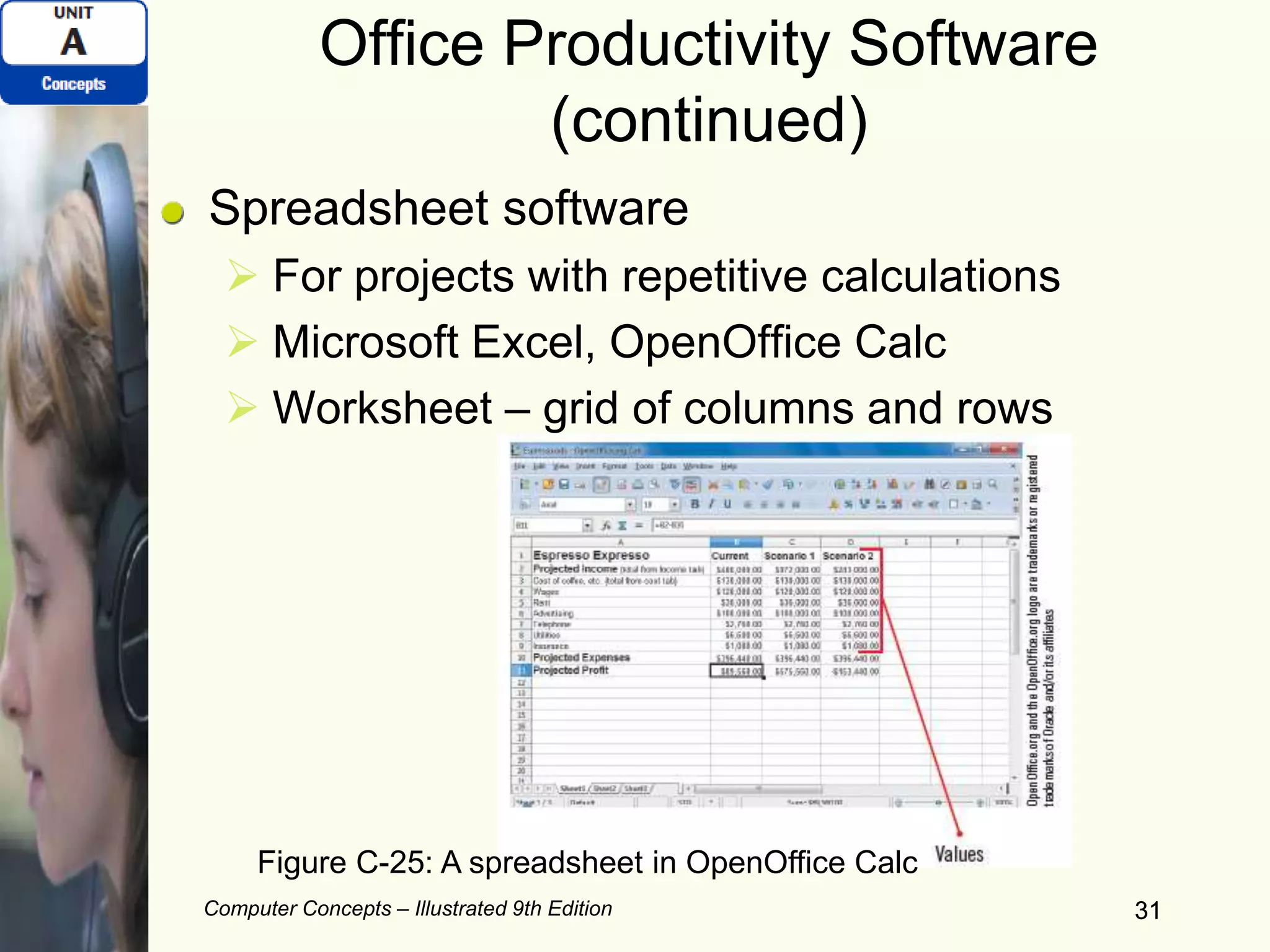
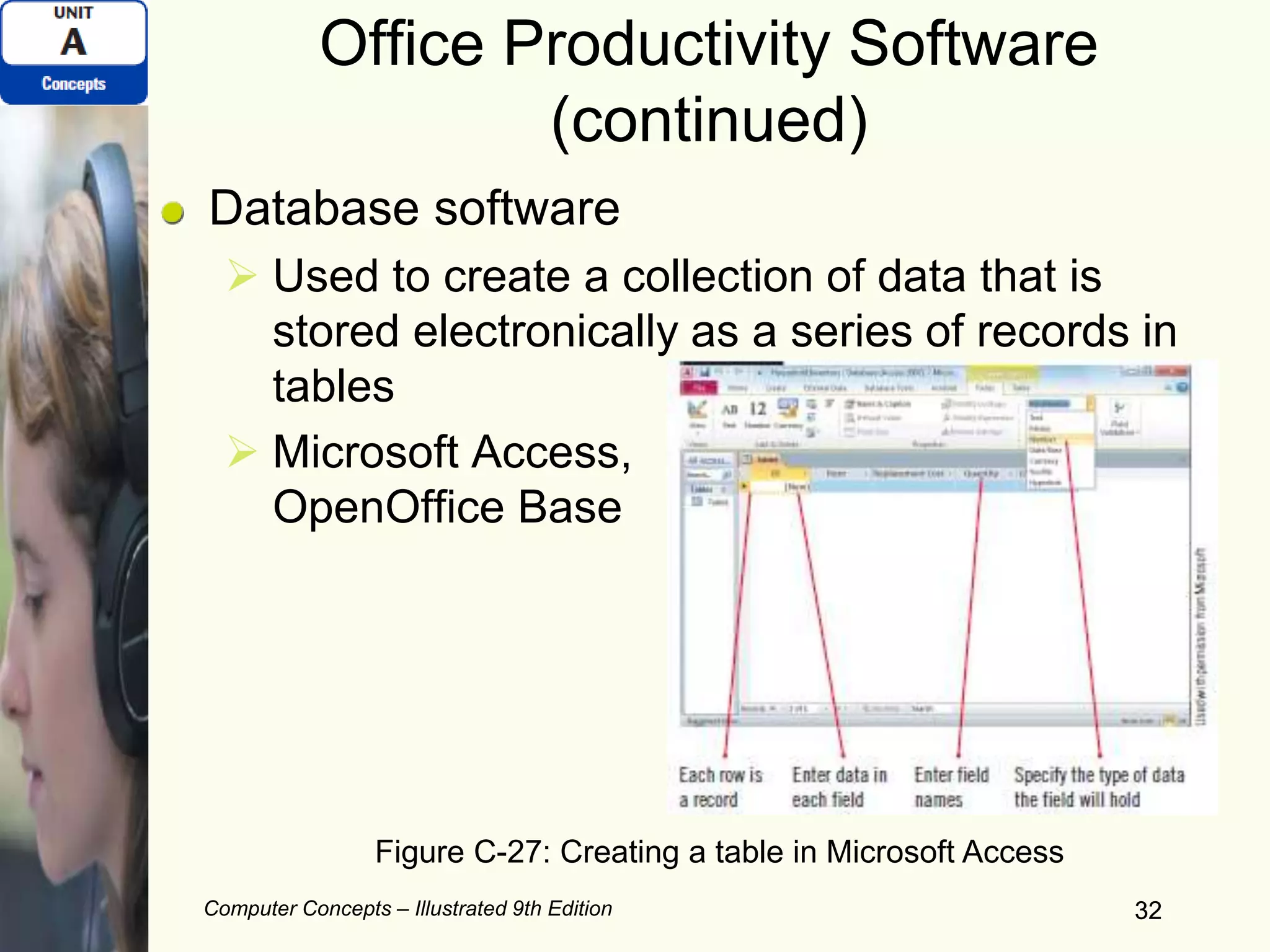
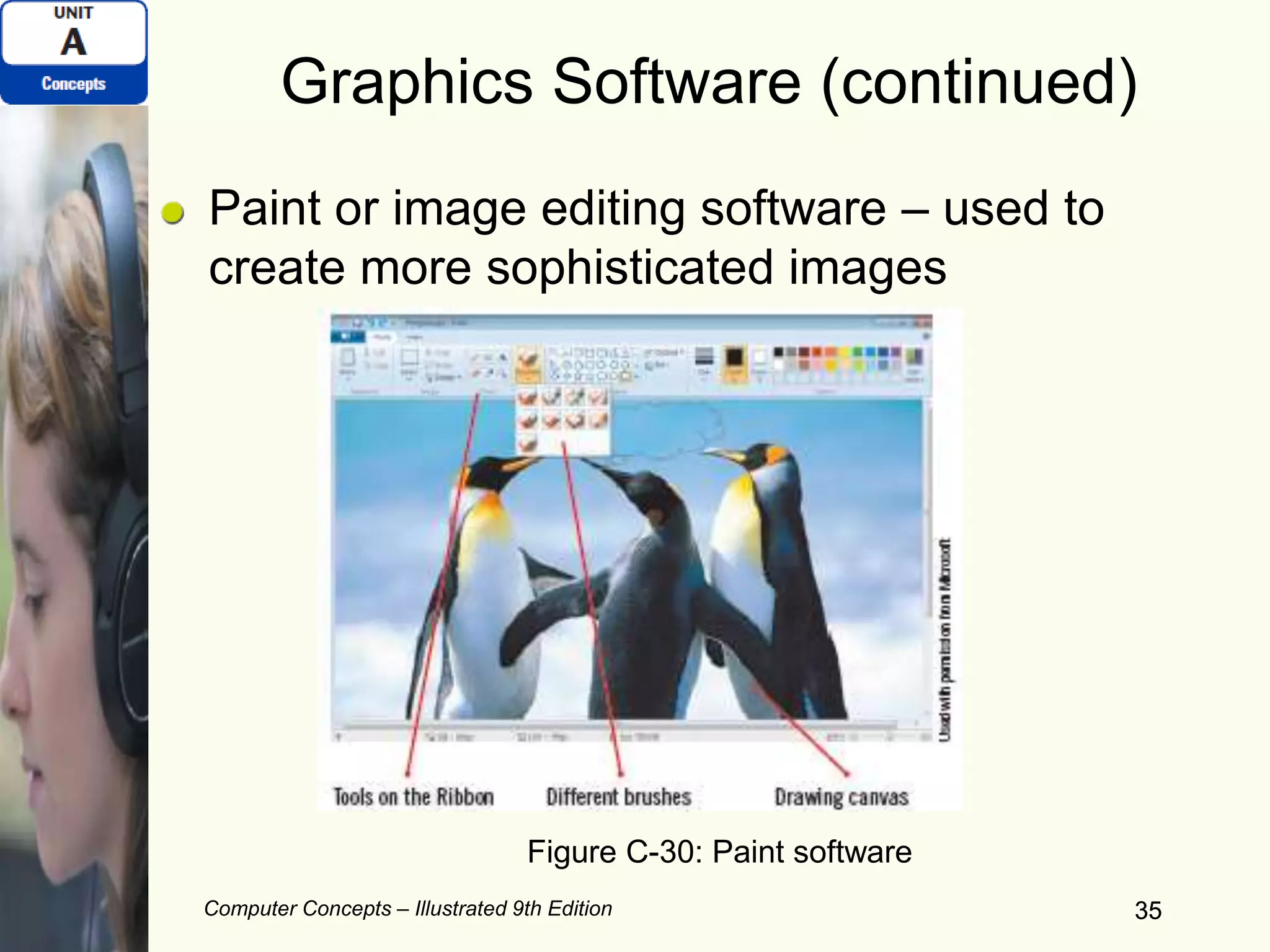
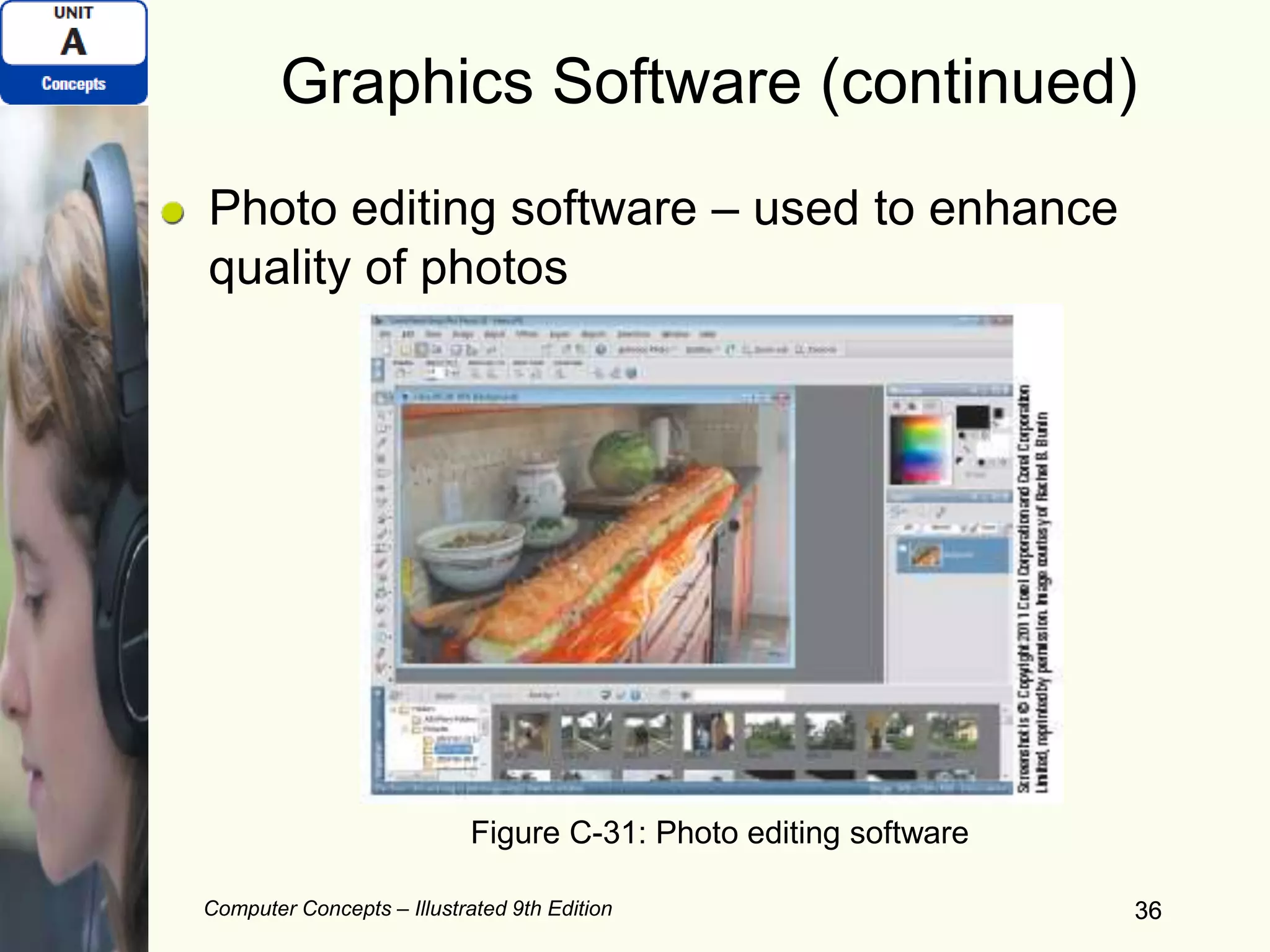
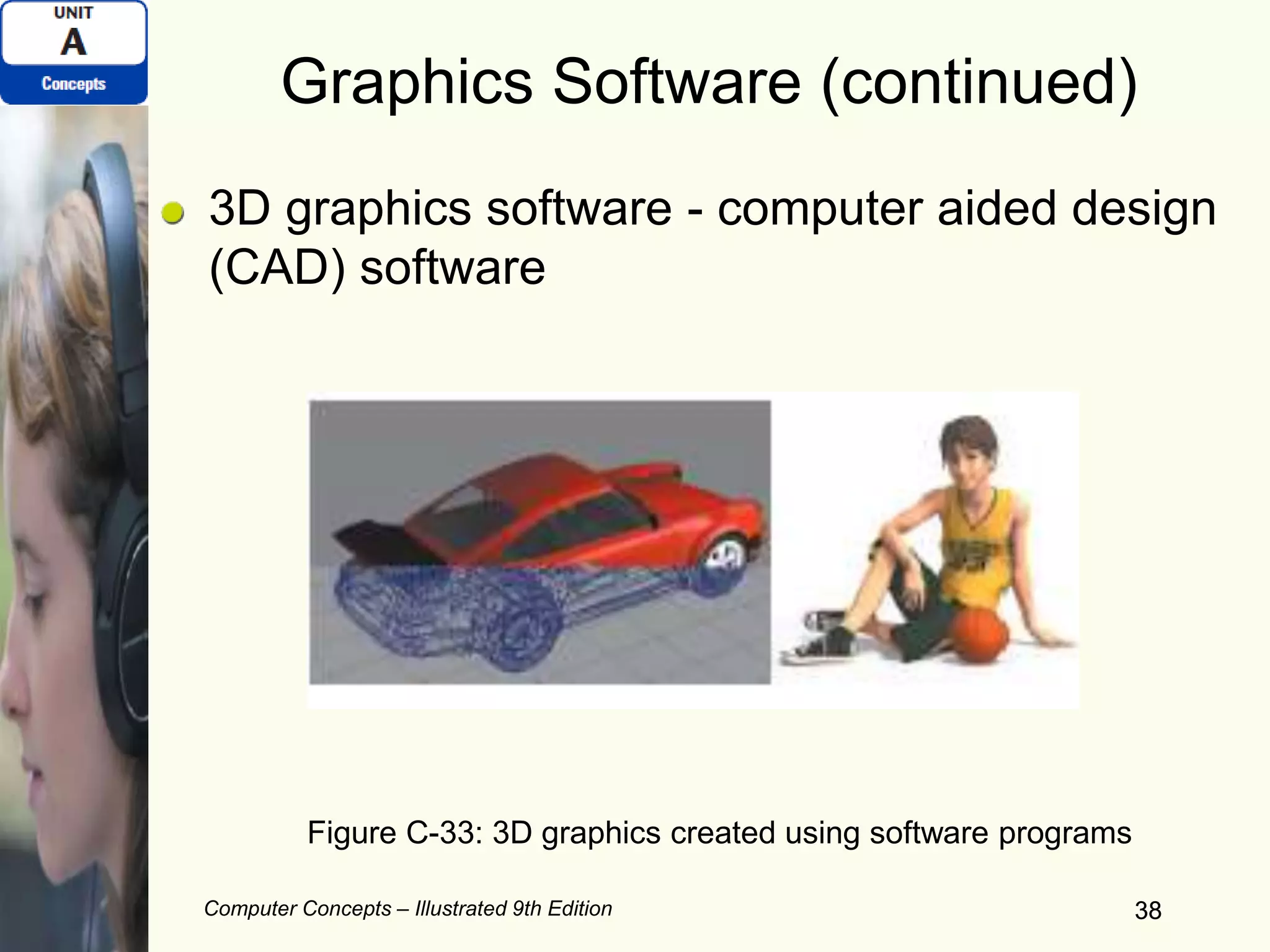
This document provides an overview of computers and their components. It discusses how computers accept input, process and store data, and produce output. It describes common computer hardware components like the system unit, peripheral devices, and input/output devices. It also covers computer software, including system software, application software, and common productivity applications. The document provides examples and illustrations of these core computer concepts.