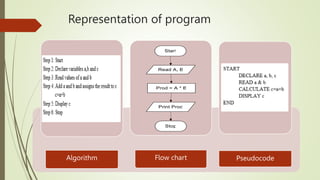
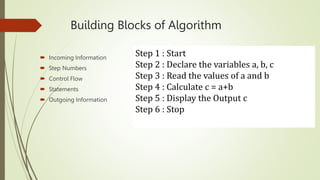
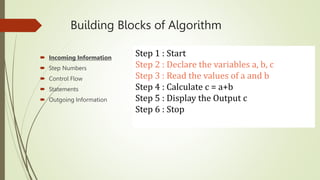
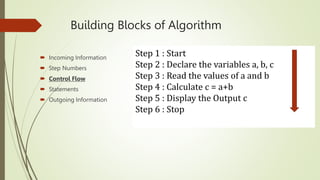
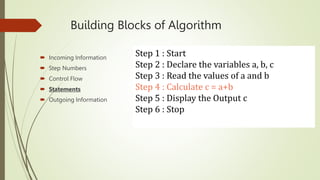
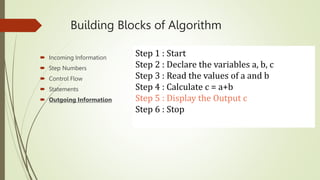
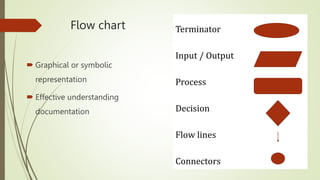
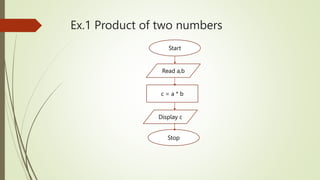
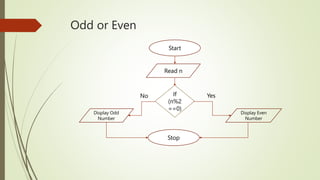
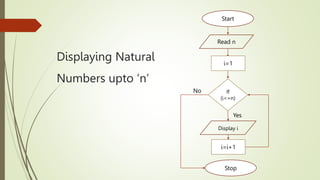
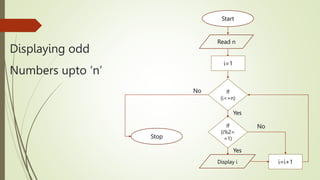
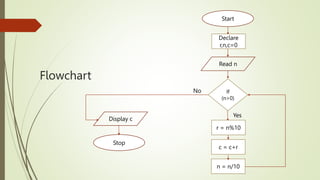
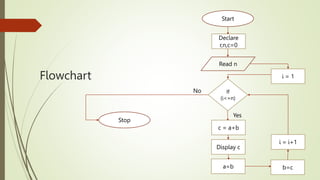
The document introduces computational thinking and algorithms. It discusses fundamentals of computing including algorithms, their building blocks, and notation. It provides examples of algorithms to find the minimum in a list, insert a card in a sorted list, guess a number in a range, and solve the Towers of Hanoi problem. It also discusses representing algorithms using flow charts and pseudocode, and the basic building blocks of algorithms including inputs, steps, control flow, statements, and outputs.